100% found this document useful (1 vote)
423 views24 pagesFall Prevention Strategies for Seniors
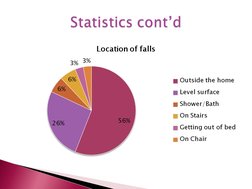
This document discusses falls in older adults and prevention strategies. It notes that falls are a major issue, especially for those over 65, and are a leading cause of injury. Risk factors include age-related changes and home hazards. Prevention strategies include exercises to improve balance and strength, home modifications, and safe transfer training. Occupational and physical therapists can assess fall risks, recommend modifications and exercises, and provide education and devices to prevent falls.
Uploaded by
littleshortgurlCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
423 views24 pagesFall Prevention Strategies for Seniors
This document discusses falls in older adults and prevention strategies. It notes that falls are a major issue, especially for those over 65, and are a leading cause of injury. Risk factors include age-related changes and home hazards. Prevention strategies include exercises to improve balance and strength, home modifications, and safe transfer training. Occupational and physical therapists can assess fall risks, recommend modifications and exercises, and provide education and devices to prevent falls.
Uploaded by
littleshortgurlCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd