Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Forces and Motion
Uploaded by
Erwin Ello0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views11 pagesOriginal Title
FORCES AND MOTION.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views11 pagesForces and Motion
Uploaded by
Erwin ElloCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
Changing direction requires a force
Force changing motion
The unit use for measuring the forces is the
Newton (N)
Forces appear when two object interact with
each other
Force produce acceleration
The mass of an object measure in kilogram,
tells you how much matter it is composed of
Weight = the name given to the force of
gravity acting on an object with mass
Weight = Mass x Gravity
Object fall to the ground because they have
weight. And their weight cause by
gravitational field
Terminal velocity
F =mxa
The greater the mass of an object, the
smaller the acceleration it is given by a
particular force
Momentum can be related with the force
effect
The effect of a force F depends on two
things:
1. how big the force is
2. the time t it acts for
F.t = m.v – m.u
Where: F.t = Impulse
m.v = momentum
So, chenge of momentum = m.v – m.u
Before the collition: the racket is moving to the
right; it has momentum. The ball is stationary, it has
no momentum.
After the collition: the racket is moving to the right,
but more slowly than before. It has lost momentum.
The ball is moving rapidly to the right. It has gained
momentum.
The total momentum before = the total momentum
after
Force is a vector quantity because it has a
direction as well as a magnitude
Adding/Resultan forces rules:
Draw arrows end-to-end, so the end of one is the
start of the next
Join the start of the first arrow to the end of the
last arrow to find the resultant
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5807)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- National Olympiad Practice 6Document2 pagesNational Olympiad Practice 6Erwin ElloNo ratings yet
- National Olympiad Practice 7Document2 pagesNational Olympiad Practice 7Erwin ElloNo ratings yet
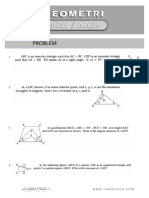
- GEOMETRI Angle ChasingDocument3 pagesGEOMETRI Angle ChasingErwin ElloNo ratings yet
- Angles, Area, Surface, and Volume: Problem SolutionDocument8 pagesAngles, Area, Surface, and Volume: Problem SolutionErwin ElloNo ratings yet
- Geometri: Garis Dan Sudut, Bangun Datar Dan Bangun Ruang, Dan Transformasi GeometriDocument6 pagesGeometri: Garis Dan Sudut, Bangun Datar Dan Bangun Ruang, Dan Transformasi GeometriErwin ElloNo ratings yet
- Test Wmi 3Document2 pagesTest Wmi 3Erwin ElloNo ratings yet
- DivisionDocument25 pagesDivisionErwin ElloNo ratings yet
- Practice WMIDocument6 pagesPractice WMIErwin Ello100% (1)
- Geometry (Volume of Composite Figure/Surfece Area)Document10 pagesGeometry (Volume of Composite Figure/Surfece Area)Erwin ElloNo ratings yet
- Geometry (Volume of Composite Figure/Surfece Area)Document10 pagesGeometry (Volume of Composite Figure/Surfece Area)Erwin ElloNo ratings yet
- Forces and MotionDocument7 pagesForces and MotionErwin ElloNo ratings yet
- Physics Question PaperDocument45 pagesPhysics Question PaperErwin ElloNo ratings yet