Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cork: A Traditional Material As Source For New Natural Based
Cork: A Traditional Material As Source For New Natural Based
Uploaded by
Semana de Engenharia '2010Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cork: A Traditional Material As Source For New Natural Based
Cork: A Traditional Material As Source For New Natural Based
Uploaded by
Semana de Engenharia '2010Copyright:
Available Formats
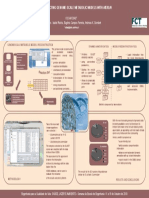
CORK: A TRADITIONAL MATERIAL AS SOURCE FOR NEW NATURAL BASED
Author* IVO M. AROSO
University of Minho Supervisors: Rui L. Reis, João F. Mano
School of Engineering
Centre of Biological Engineering
* ivo.aroso@dep.uminho.pt
Introduction
dichloromethane presents a residual value and it can be considered
Cork material was submitted to chemical treatments in order to break
that phenolic molecules are absent. The DPPH EC50 value and trend
its structure and to obtain its components[1,2]. The fractions obtained
comprise individual fractions obtained with dichloromethane, ethanol are consistent with the total phenols trend. As lower the EC 50 value,
and water. The extractive fractions total phenol content was the more effective the extract is in quenching the radicals, therefore,
determined (Folin-Ciocalteau assay) and correlated with the less quantity is required for the same effect. The ethanol extract
antioxidant capacity (DPPH assay). It was found that the higher the presents the higher scavenging activity followed by the water extract.
phenolic content the higher the antioxidant capacity is. These The dichloromethane extract doesn´t seem to have radical
procedures envision the valorization of cork as a potential natural scavenging activity.
source for new chemicals. Conclusions
Considering the results obtained so far, ethanol and water extracts are
Materials and Methods the most promising as a potential source for natural antioxidants.
Cork material used was in the form of powder with particle dimensions Moreover, the present results were obtained using crude extracts, as
of less than 1mm and obtained from boiled natural cork of the best obtained. A subsequent work in identification and isolation of the
quality. active molecules or fractioning could substantially increase the extract
Cork extractives were obtained through soxhlet extractions. Each activity.
extraction procedure is carried for 6h after which the solvent is
removed by evaporation under reduced pressure, suspended in water
Bibliography
and lyophilized.
[1] Conde, E., E. Cadahia, et al. (1998). "Chemical characterization of
Total phenols content (Folin-Ciocalteau) was determined follows: Fig. 2: Extractions flow chart with the differente solvents used: DCM- reproduction cork from Spanish Quercus suber." Journal of Wood
2.5mL of diluted (1:10) Folin-Ciocalteu reagent and 2mL of 20% dichloromethane; EtOH-ethanol; Water. Chemistry and Technology 18(4): 447-469.
sodium carbonate are added to 0.5mL of accurately weighed extract.
[2] Silva, S. P., M. A. Sabino, et al. (2005). "Cork: properties,
Suitable gallic acid solutions are used for standards, and total phenols
capabilities and applications." International Materials Reviews 50(6):
content is calculated from the Absorbance value at 760nm and Results and Discussion 345-365.
expressed as gallic acid equivalents[3].
[3] Santos, S. A. O., P. C. R. O. Pinto, et al. "Chemical composition
DPPH radical scavenging activity was determined as follows: 0.25mL
In Table 1 are presented the values for total phenols and DPPH EC50 and antioxidant activity of phenolic extracts of cork from Quercus
of DPPH 0.8mM in MeOH was added to accurately weighed aliquots
suber L." Industrial Crops and Products 31(3): 521-526.
of the extracts. The absorbance of the mixture was measured after radical scavenging activity.
30min at 517nm. EC50 is calculated from the plot of scavenging
activity against extract concentration and represent the amount of Table 1: Total Phenols and DPPH EC50 values Acknowledgements
extract necessary to decrease the initial DPPH concentration by 50% The authors would like to thank FCT for the awarding of a Ph.D grant
[3]. (SFRH/BD/42273/2007) to Ivo M. Aroso. Amorim group is gratefuly
Total Phenols acknowledged for supplying cork powder.
Extract DPPH EC50 (gextract/gDPPH)
(mgGAeq/gextract)
DCM 2.7 1.33 IVO AROSO obtained a degree in chemistry by the Sciences College,
University of Oporto in 2003. In 2007 has concluded pos-grad studies
H2O 471 0,24 in processing and characterization of materials in University of Minho.
Since 2008 is conducting research related to cork chemicals in order
to obtain its PhD.
EtOH 587 0,13
The extracts obtained with water and ethanol presents the higher
values for the total phenols content, with special relevance for the
Fig. 1: Cork oak tree after bark stripping and cork powder used for latest which presents the highest value. The extract obtained with
the extractions procedures.
Engenharia para a Qualidade de Vida: SAÚDE, LAZER E AMBIENTE– Semana da Escola de Engenharia -11 a 16 de Outubro de 2010
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5807)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Packed Tower Design and Applications - R. F. Strigle (1994)Document354 pagesPacked Tower Design and Applications - R. F. Strigle (1994)gfrank997090% (20)
- Organic Chem Lab Report (Experiment 1)Document8 pagesOrganic Chem Lab Report (Experiment 1)Robie AngeloNo ratings yet
- ICH 2101 Mass Transfer 1 ModulesDocument79 pagesICH 2101 Mass Transfer 1 ModulesGrace Lukogho MbafumojaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) : By: 1602-031 022 024 032 046 048 Submitted to:Dr.S.B.MISHRADocument35 pagesElectrical Discharge Machining (EDM) : By: 1602-031 022 024 032 046 048 Submitted to:Dr.S.B.MISHRAmanish kumarNo ratings yet
- Chem 16 Unknown Analysis Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesChem 16 Unknown Analysis Cheat SheetJana Quismundo100% (4)
- Modelling The Cyclic Behaviour of RC StructuresDocument1 pageModelling The Cyclic Behaviour of RC StructuresSemana de Engenharia '2010No ratings yet
- A Network Flow Model For The Vehicle Routing Problem With Time Windows and Multiple RoutesDocument1 pageA Network Flow Model For The Vehicle Routing Problem With Time Windows and Multiple RoutesSemana de Engenharia '2010No ratings yet
- Modeling of Wave Propagation in Soils Using The Finite Element MethodDocument1 pageModeling of Wave Propagation in Soils Using The Finite Element MethodSemana de Engenharia '2010No ratings yet
- The Economic Impact of Higher Education Institutions On Regional Development: The Case of The Polytechnic Institute of BragançaDocument1 pageThe Economic Impact of Higher Education Institutions On Regional Development: The Case of The Polytechnic Institute of BragançaSemana de Engenharia '2010No ratings yet
- Reconstructing Genome-Scale Metabolic Models With MerlinDocument1 pageReconstructing Genome-Scale Metabolic Models With MerlinSemana de Engenharia '2010No ratings yet
- Methodologies For Safety Evaluation of Existing Timber StructuresDocument1 pageMethodologies For Safety Evaluation of Existing Timber StructuresSemana de Engenharia '2010No ratings yet
- Optimization of The Potential of Human Adult and Embryonic Stem Cells For Skin Tissue EngineeringDocument1 pageOptimization of The Potential of Human Adult and Embryonic Stem Cells For Skin Tissue EngineeringSemana de Engenharia '2010No ratings yet
- A Time-Slot Scheduling Algorithm For E-Health Wireless Sensor NetworksDocument1 pageA Time-Slot Scheduling Algorithm For E-Health Wireless Sensor NetworksSemana de Engenharia '2010No ratings yet
- Secretome Analysis of Ashbya GossypiiDocument1 pageSecretome Analysis of Ashbya GossypiiSemana de Engenharia '2010No ratings yet
- Wearable Photonic Bioelectric Monitoring DeviceDocument1 pageWearable Photonic Bioelectric Monitoring DeviceSemana de Engenharia '2010No ratings yet
- Organizational Memory: A Proposal For Diagnose and InterventionDocument1 pageOrganizational Memory: A Proposal For Diagnose and InterventionSemana de Engenharia '2010No ratings yet
- Brewing Fermentations More ProfitableDocument1 pageBrewing Fermentations More ProfitableSemana de Engenharia '2010No ratings yet
- Solved With COMSOL Multiphysics 5.1 JoulDocument10 pagesSolved With COMSOL Multiphysics 5.1 JoulKarthik RaoNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 - Air Handling SystemsDocument58 pagesTopic 3 - Air Handling SystemsAndy MakNo ratings yet
- Wave Nature of LightDocument29 pagesWave Nature of LightSumit DongardiyeNo ratings yet
- Titration Lab Report 1Document28 pagesTitration Lab Report 1api-607048551No ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium Class 10 Mcqs PDFDocument18 pagesChemical Equilibrium Class 10 Mcqs PDFadeel amjadNo ratings yet
- 4 - Kinetics of Emulsion PolymerizationDocument33 pages4 - Kinetics of Emulsion PolymerizationPaulo SilvaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry WorksheetDocument46 pagesChemistry WorksheetvsudarsanNo ratings yet
- Analizador de O2 Ametek 5100 HDDocument2 pagesAnalizador de O2 Ametek 5100 HDexploxifeNo ratings yet
- Seebeck Coefficient of Thermocouples With VariationsDocument18 pagesSeebeck Coefficient of Thermocouples With VariationsNikhil JaisinghaniNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS 2:thermal ExpansionDocument25 pagesPHYSICS 2:thermal ExpansionAndreana Amor GulayNo ratings yet
- 2017 Y5 T4 Chem Focus - Chem BondingDocument4 pages2017 Y5 T4 Chem Focus - Chem BondingxmxmxmxmxmNo ratings yet
- The Water CycleDocument4 pagesThe Water CycleSeptika RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Analytical Instrumentation Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesAnalytical Instrumentation Lesson PlanPriyanka ParasharNo ratings yet
- Rates-Of-Reaction Questions IGCSEDocument8 pagesRates-Of-Reaction Questions IGCSEToni ANo ratings yet
- F4C6 Note 2Document12 pagesF4C6 Note 2GosshanNo ratings yet
- Porous BearingDocument19 pagesPorous BearingNikita chapkeNo ratings yet
- CHEM 200 IR SpectrosDocument35 pagesCHEM 200 IR SpectrosIngrid LacsonNo ratings yet
- Le Chatelier's PrincipleDocument18 pagesLe Chatelier's PrincipleMonaliza MandacNo ratings yet
- Investigatory Project PhysicsDocument8 pagesInvestigatory Project PhysicsRonald100% (1)
- Thin Film Calculator From Dissertation - JunZhang - 080110 - Optimized PDFDocument26 pagesThin Film Calculator From Dissertation - JunZhang - 080110 - Optimized PDFAlvaroFernandezVillarNo ratings yet
- DNA Estimation Using DPA Reaction PDFDocument5 pagesDNA Estimation Using DPA Reaction PDFAnsh KumarNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure TestDocument3 pagesAtomic Structure TestHemant KumarNo ratings yet
- Competitive InhibitorsDocument5 pagesCompetitive InhibitorsLai FokNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Solids and Structures: M. Naderi, M.M. KhonsariDocument6 pagesInternational Journal of Solids and Structures: M. Naderi, M.M. KhonsariHudson MoraisNo ratings yet
- Physics LabDocument4 pagesPhysics LabHasnairah Mautin LimbotonganNo ratings yet