Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Expression of The Homeobox Gene Shox2 in The Cranial Neural Crest Derived Mesenchymal Cells of The Maxilla-Mandibular Junction
The Expression of The Homeobox Gene Shox2 in The Cranial Neural Crest Derived Mesenchymal Cells of The Maxilla-Mandibular Junction
Uploaded by
MUSHAHID HASAN0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views5 pagesThe document discusses the expression of the homeobox gene Shox2 in cranial neural crest-derived mesenchymal cells in the maxilla-mandibular junction of mouse embryos. It shows that Shox2 is expressed in this tissue at various embryonic stages. To study the role of Shox2 in TMJ development, they used a conditional knockout approach to inactivate Shox2 in craniofacial neural crest cells. The knockout mice showed abnormal fusions of the TMJ disc and condyle with surrounding tissues.
Original Description:
Congenital disorders affecting TMJ development
Original Title
1. Sachin Sir
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the expression of the homeobox gene Shox2 in cranial neural crest-derived mesenchymal cells in the maxilla-mandibular junction of mouse embryos. It shows that Shox2 is expressed in this tissue at various embryonic stages. To study the role of Shox2 in TMJ development, they used a conditional knockout approach to inactivate Shox2 in craniofacial neural crest cells. The knockout mice showed abnormal fusions of the TMJ disc and condyle with surrounding tissues.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views5 pagesThe Expression of The Homeobox Gene Shox2 in The Cranial Neural Crest Derived Mesenchymal Cells of The Maxilla-Mandibular Junction
The Expression of The Homeobox Gene Shox2 in The Cranial Neural Crest Derived Mesenchymal Cells of The Maxilla-Mandibular Junction
Uploaded by
MUSHAHID HASANThe document discusses the expression of the homeobox gene Shox2 in cranial neural crest-derived mesenchymal cells in the maxilla-mandibular junction of mouse embryos. It shows that Shox2 is expressed in this tissue at various embryonic stages. To study the role of Shox2 in TMJ development, they used a conditional knockout approach to inactivate Shox2 in craniofacial neural crest cells. The knockout mice showed abnormal fusions of the TMJ disc and condyle with surrounding tissues.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
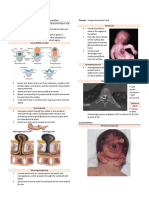
The expression of the homeobox gene Shox2 in the cranial
neural crest derived mesenchymal cells of the maxilla-
mandibular junction.
E10.5 mouse embryo A coronal section of an
A coronal section of an
shows the presence of E11.5 mouse head
E13.5 mouse head
Shox2 transcripts in the shows strong Shox2
shows a restricted
brain, limb buds, and the expression in the
Shox2 expression in
maxillamandibular mesenchymal tissue of
the condylar
junction the maxilla-mandibular
condensation.
junction.
To study the role of Shox2 in the TMJ development :-
• They took a conditional knockout approach to inactivate Shox2 in the
craniofacial neural crest-derived cells by using a Wnt1-Cre transgenic line
and a floxed Shox2 allele.
The LacZ staining of the Wnt1-Cre;R26R TMJ unambiguously.
Cell proliferation Reduced
in the condylar level of cell
condensation of
proliferation
an E13.5 wild
type embryo.
shows a distinct synovial
disc and the clearly
separated upper
synovial cavity and lower
synovial cavity
This fibrous adhesion of the joint components,
clinically defined as TMJ ankylosis, could restrain
the jaw movement
shows abnormal fusions
of the disc with condyle
(black arrows) and the
glenoid fossa (open
arrows
TMJ the osteogenic consequence in the absence of Shox2. By using the Azon
red/Anilin blue staining method, which stains bone matrix in red
FC, flattered chondrocyte zone;
F/P. fibrous/polymorphic layers
HC, hypertrophic chondrocyte zone
Appear much thinner, as compared to
the wild type control
Reduced expression of Osteocalcin in
the TMJ
You might also like
- A Mouse Model For Human Deafness DFNB22 Reveals That Hearing Impairment Is Due To A Loss of Inner Hair Cell StimulationDocument6 pagesA Mouse Model For Human Deafness DFNB22 Reveals That Hearing Impairment Is Due To A Loss of Inner Hair Cell StimulationRana Sabouni TabariNo ratings yet
- NeurulationDocument7 pagesNeurulationFranTeodosioNo ratings yet
- Scleraxis Is Required For Maturation: of Tissue Domains For Proper Integration of The Musculoskeletal SystemDocument16 pagesScleraxis Is Required For Maturation: of Tissue Domains For Proper Integration of The Musculoskeletal Systemsindika anastasyaNo ratings yet
- Review Exam 1 PDFDocument3 pagesReview Exam 1 PDFZehra Naqvi (xxzehramahonexx)No ratings yet
- A Morphological Classification of Sincipital EncephalomeningocelesDocument11 pagesA Morphological Classification of Sincipital EncephalomeningocelesRizqan Fahlevvi AkbarNo ratings yet
- JDB 08 00018Document27 pagesJDB 08 00018Carol Gissel FloresNo ratings yet
- Sox2 Acts As A Rheostat of Epithelial To Mesenchymal Transition During Neural Crest DevelopmentDocument12 pagesSox2 Acts As A Rheostat of Epithelial To Mesenchymal Transition During Neural Crest DevelopmentAngelicaNo ratings yet
- Development of The Juxta-Oral Organ in Rat EmbryoDocument7 pagesDevelopment of The Juxta-Oral Organ in Rat EmbryoMackarenna NarvaezNo ratings yet
- Osificación Endocondral 1Document20 pagesOsificación Endocondral 1Fabian BarretoNo ratings yet
- Neural CrestDocument33 pagesNeural CrestCarlo ManguilNo ratings yet
- 10.1007@s12105 020 01189 1Document7 pages10.1007@s12105 020 01189 1Diana PerezNo ratings yet
- Articulo 1Document11 pagesArticulo 1Karla DavilaNo ratings yet
- CT and MR Findings of Michel Anomaly: Inner Ear Aplasia: Case ReportDocument4 pagesCT and MR Findings of Michel Anomaly: Inner Ear Aplasia: Case ReportEBE THTNo ratings yet
- Tsukushi Functions As An Organizer Inducer by Inhibition of - 2004 - DevelopmenDocument12 pagesTsukushi Functions As An Organizer Inducer by Inhibition of - 2004 - Developmenhalil sahanNo ratings yet
- SMJ 55 E85Document2 pagesSMJ 55 E85romyNo ratings yet
- Iulianella Et Al-2019-Developmental DynamicsDocument8 pagesIulianella Et Al-2019-Developmental DynamicsAbsjeyNo ratings yet
- Adc 8810Document5 pagesAdc 8810dna1979No ratings yet
- 1 - Newman1973Document16 pages1 - Newman1973Eduardo HernandezNo ratings yet
- Nakajima 2015Document9 pagesNakajima 2015Carturo VduncanNo ratings yet
- Bio138 SummaryDocument1 pageBio138 SummaryYana CatherineNo ratings yet
- 2009 Inner Ear Connexins, Intercellular Signalling and DeafnessDocument6 pages2009 Inner Ear Connexins, Intercellular Signalling and DeafnessCaio LeônidasNo ratings yet
- Song 2016Document19 pagesSong 2016MarwanNo ratings yet
- 2 AC Cerebral Cortex DevelopmentDocument15 pages2 AC Cerebral Cortex Developmentcarmen benitezNo ratings yet
- Creuzet 2005Document13 pagesCreuzet 2005asdNo ratings yet
- Mielinopatía VacuolarDocument3 pagesMielinopatía VacuolarDayana DbsNo ratings yet
- Syndromes of The Orbital Fissure, Cavernous Sinus, Cerebello-Pontine Angle, and Skull BaseDocument10 pagesSyndromes of The Orbital Fissure, Cavernous Sinus, Cerebello-Pontine Angle, and Skull BaseMarlene Arbeu ReyesNo ratings yet
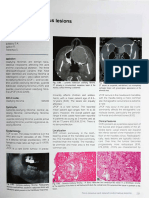
- Unique Case of Glandular Odontogenic Cyst ShowingDocument3 pagesUnique Case of Glandular Odontogenic Cyst ShowingSenussi IbtisamNo ratings yet
- Genesis Avian Cells: Classic Embryonic Induction: The of Neural Crest ADocument6 pagesGenesis Avian Cells: Classic Embryonic Induction: The of Neural Crest ARANJAN KUMARNo ratings yet
- Neuro Usmle EndpointDocument197 pagesNeuro Usmle EndpointIris BakerNo ratings yet
- Temporomandibular Joint: Aditi PGT 1 YearDocument27 pagesTemporomandibular Joint: Aditi PGT 1 Yearsachin mishraNo ratings yet
- MSX Homeobox Gene Family and Craniofacial Development PDFDocument14 pagesMSX Homeobox Gene Family and Craniofacial Development PDFElizabeth HerhuayNo ratings yet
- Fundus Autofluorescence and Optical Coherence TomoDocument4 pagesFundus Autofluorescence and Optical Coherence TomoAndi Tiara S. AdamNo ratings yet
- Pathology of Bone - DADocument95 pagesPathology of Bone - DAabdillahNo ratings yet
- Miller DiekerDocument8 pagesMiller DiekerJucsy JuxyNo ratings yet
- @1995.tamm - Innervation of Myofibroblast-Like Scleral Spur Cells in Human Monkey EyesDocument12 pages@1995.tamm - Innervation of Myofibroblast-Like Scleral Spur Cells in Human Monkey EyesReza NaghibiNo ratings yet
- Developmental Dynamics - 2008 - Hu - Effect of Bone Morphogenetic Protein Signaling On Development of The Jaw SkeletonDocument11 pagesDevelopmental Dynamics - 2008 - Hu - Effect of Bone Morphogenetic Protein Signaling On Development of The Jaw Skeletonhennysusanto18No ratings yet
- Kakigi A Et Al - Tonotopic Mapping in Auditory Cortex of The Adult Chinchilla With Amikacin Induced Cochlear Lesions - 2000 1Document10 pagesKakigi A Et Al - Tonotopic Mapping in Auditory Cortex of The Adult Chinchilla With Amikacin Induced Cochlear Lesions - 2000 1karinduarte30No ratings yet
- Salazar - 2019 IntechOpen - Anatomy of The Human Optic Nerve - Structure and FuncionDocument46 pagesSalazar - 2019 IntechOpen - Anatomy of The Human Optic Nerve - Structure and FuncionLee Vo AnNo ratings yet
- Bells PalsyDocument6 pagesBells PalsyPhub TsheringNo ratings yet
- Sci2015 601731Document7 pagesSci2015 601731angelos96papNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Fisiologi RetinaDocument28 pagesAnatomi Fisiologi RetinaAnnisak FitriyanaNo ratings yet
- Who 2017-244-253Document10 pagesWho 2017-244-253Seba OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Clinicopathologic Features of Brain Herniation in AnimalsDocument7 pagesClinicopathologic Features of Brain Herniation in AnimalsDesNo ratings yet
- Cells of The Spinal Cord. Rexed Zones. Spinal Reflexes. Receptors and EffectorsDocument34 pagesCells of The Spinal Cord. Rexed Zones. Spinal Reflexes. Receptors and Effectorsnnn nnnNo ratings yet
- Neuro AnatomyDocument4 pagesNeuro AnatomyMarianne Abnasan100% (1)
- Zeb Family Members and Boundary Cap Cells Underlie Developmental Plasticity of Sensory Nociceptive NeuronsDocument9 pagesZeb Family Members and Boundary Cap Cells Underlie Developmental Plasticity of Sensory Nociceptive NeuronsCarlos PalhaNo ratings yet
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesAmyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: PathophysiologyJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Key Points:: Questions For StudentsDocument19 pagesKey Points:: Questions For Studentssimi yNo ratings yet
- CraneocinostosisDocument18 pagesCraneocinostosisBety CamarilloNo ratings yet
- The Homeodomain Factor Lbx1 Distinguishes Two Major Programs of Neuronal Differentiation in The Dorsal Spinal CordDocument12 pagesThe Homeodomain Factor Lbx1 Distinguishes Two Major Programs of Neuronal Differentiation in The Dorsal Spinal CordaptureincNo ratings yet
- Neuro, Usmle EndpointDocument236 pagesNeuro, Usmle EndpointMorozovschi VitalieNo ratings yet
- Area-Specific Temporal Control of Corticospinal Motor Neuron Differentiation by COUP-TFIDocument6 pagesArea-Specific Temporal Control of Corticospinal Motor Neuron Differentiation by COUP-TFIFrontiersNo ratings yet
- Bercak MongolDocument3 pagesBercak MongolSintya AulinaNo ratings yet
- BOOK TRANS MegakaryopoiesisDocument3 pagesBOOK TRANS MegakaryopoiesisPaul LesterNo ratings yet
- The Anatomy of The Cerebellum: ErebellumDocument6 pagesThe Anatomy of The Cerebellum: ErebellumjoyousNo ratings yet
- Neuro-Embryology: Noel T. Boaz, PH.D., M.DDocument34 pagesNeuro-Embryology: Noel T. Boaz, PH.D., M.DsoojeanNo ratings yet
- CorticaldysplasiareviewDocument25 pagesCorticaldysplasiareviewDragonNo ratings yet
- Excitable Cells: Monographs in Modern Biology for Upper School and University CoursesFrom EverandExcitable Cells: Monographs in Modern Biology for Upper School and University CoursesNo ratings yet
- Cleft Lip and Palate Management: A Comprehensive AtlasFrom EverandCleft Lip and Palate Management: A Comprehensive AtlasRicardo D. BennunNo ratings yet
- Cell-Cell Signaling in Vertebrate DevelopmentFrom EverandCell-Cell Signaling in Vertebrate DevelopmentE.J. RobertsonRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)