Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 10 Aes
Uploaded by
Gowtham Ganesan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views14 pagesAuger Electron Spectroscopy Class
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAuger Electron Spectroscopy Class
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views14 pagesChapter 10 Aes
Uploaded by
Gowtham GanesanAuger Electron Spectroscopy Class
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
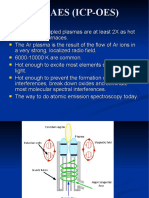
ICP-AES (ICP-OES)
Inductively coupled plasmas are at least 2X as hot
as flames or furnaces.
The Ar plasma is the result of the flow of Ar ions in a
very strong, localized radio field.
6000-10000 K are common.
Hot enough to excite most elements so they emit
light.
Hot enough to prevent the formation of most
interferences, break down oxides and eliminate
most molecular spectral interferences.
The way to do atomic emission spectroscopy today.
How does ICP work?
Radio frequency electrical current and associated magnetic field
Ionization of Ar gas (sparked by a Tesla coil)
Acceleration of ions and electrons by magnetic field
Energy in transferred from the electrons to the gas by collision so the
gas is heats up.
Production of high concentartion of both EXCITED ATOMS and ions
Plasmas gas or
Three gases Support gas or
auxiliary gas
How to measure temperature?
The plasma is thermodynamic equilibrium
Cannot characterize a single temperature
Four temperatures can be used
Excitation Temp (Texc): measure of population density of the
energy levels (Boltzman equilibrium)
Ionization Temp (Tion): measure of population density of
different ionization states (Saha equilibrium)
Electron Temp (Te): a measure of the kinetic energy of the
electrons (related to the velocity of free electrons)
Gas Temp (Tg or T kinetic): a measure of the kinetic energy of
the atoms.
Tg < Texc < Tion < Te
N1/N0 = g1/go exp(∆E/kT)
Hydride generation
3BH4- +3H+ +4H3AsO3 3H3BO3 + 4AsH3 + 3H20
Performance characteristics
Elements determined
~ 60 elements
Line selection
Most elements have several lines that can be selected
Linear range
Better than AAS
Interferences
Chemical interferences (lowered)
Spectral interferences (still a problem)
Detection limits
Comparable or better than other atomic spectral
techniques
You might also like
- 10000005441ea Courier 6iSL Product Data SheetDocument6 pages10000005441ea Courier 6iSL Product Data SheetWalter Ivan100% (1)
- Atomic Spectroscopy Techniques Sample Introduction SourcesDocument35 pagesAtomic Spectroscopy Techniques Sample Introduction SourcesAndrés PacompíaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Emission Spectroscopy - University NotesDocument22 pagesAtomic Emission Spectroscopy - University NotesLilac44100% (1)
- AAS vs ICP-OES Elemental Analysis TechniquesDocument8 pagesAAS vs ICP-OES Elemental Analysis TechniquesKim HiềnNo ratings yet
- Minerals in WaterDocument7 pagesMinerals in WaterK JNo ratings yet
- Atomic Spectroscopy: A Guide To Selecting The Appropriate Technique and SystemDocument17 pagesAtomic Spectroscopy: A Guide To Selecting The Appropriate Technique and SystemAnonymous gpNrjv0No ratings yet
- Zeenit: Quality Is The DifferenceDocument16 pagesZeenit: Quality Is The DifferenceImad Aghila50% (2)
- An 44392 Analysis of Infant Formulae and Milk Powders Using The Thermo Scientific Icap 7400 Icp Oes DuoDocument6 pagesAn 44392 Analysis of Infant Formulae and Milk Powders Using The Thermo Scientific Icap 7400 Icp Oes DuoDewi WulandhariNo ratings yet
- ICAP-7000 Detection LimitsDocument2 pagesICAP-7000 Detection LimitsKhalidNo ratings yet
- FAS 서비스 매뉴얼 3Document36 pagesFAS 서비스 매뉴얼 3ak_thimiriNo ratings yet
- Thermo Scientific Icap Q Icp-Ms: Gain More Performance, Experience More SimplicityDocument8 pagesThermo Scientific Icap Q Icp-Ms: Gain More Performance, Experience More SimplicityAnonymous UGpigqNo ratings yet
- History of JetDocument50 pagesHistory of JetMarko IstenicNo ratings yet
- TN43183 - E 11-13C-St2-HighDocument3 pagesTN43183 - E 11-13C-St2-HighYan RiveraNo ratings yet
- En ASFA AU Koplik Atomic SpectrometryDocument15 pagesEn ASFA AU Koplik Atomic SpectrometryRizka MaharanaNo ratings yet
- Inductively Coupled Plasma SpectrosDocument1 pageInductively Coupled Plasma SpectrosBoonGen GeamNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Optical Emission Spectroscopy (OES) in <40 charsDocument30 pagesIntroduction to Optical Emission Spectroscopy (OES) in <40 charsKleverton JunioNo ratings yet
- 5991 3719enDocument8 pages5991 3719enTrịnh Ngọc ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Glass Expansion Catalogue - Issue 9 2014 PDFDocument59 pagesGlass Expansion Catalogue - Issue 9 2014 PDFPalika MedinaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Spectroscopy - A Guide To Selecting The Appropriate Technique and System PDFDocument16 pagesAtomic Spectroscopy - A Guide To Selecting The Appropriate Technique and System PDFAdamu OnakpaNo ratings yet
- AA Troubleshooting and Maintenance GuideDocument12 pagesAA Troubleshooting and Maintenance Guiderichard008100% (1)
- New Product AAS IntroductionDocument63 pagesNew Product AAS IntroductionNguyễnHoàngDanhNo ratings yet
- AX309 Xilinx Spartan-6 Development Board Users ManualDocument38 pagesAX309 Xilinx Spartan-6 Development Board Users ManualjekNo ratings yet
- ICP-OES 700 Sparepart CatalogueDocument4 pagesICP-OES 700 Sparepart CatalogueNirza FardhanaNo ratings yet
- ICP-MS - ICP-MS Instrumentation, ICP-MS Analysis, Strengths and LimitationDocument9 pagesICP-MS - ICP-MS Instrumentation, ICP-MS Analysis, Strengths and LimitationHd NsNo ratings yet
- Boron by ICP AESDocument10 pagesBoron by ICP AESNam Phạm Văn100% (1)
- XilinxDocument20 pagesXilinxAvila Cruz JaimeNo ratings yet
- Agilent 700 Series ICP-OESDocument52 pagesAgilent 700 Series ICP-OESRoger ManzanarezNo ratings yet
- Atomic Spectroscopy 3Document36 pagesAtomic Spectroscopy 3Anonymous KzCCQoNo ratings yet
- PerkinElmer Avio ICP-OES Product Line History and FeaturesDocument41 pagesPerkinElmer Avio ICP-OES Product Line History and FeaturesNguyễnHoàngDanhNo ratings yet
- Icp-Ms Icap RQ CatalogDocument12 pagesIcp-Ms Icap RQ CatalogriskaNo ratings yet
- KK-CHP 3 (Aas)Document125 pagesKK-CHP 3 (Aas)ShafiqahFazyaziqahNo ratings yet
- Avio 200-500 ICP-OES ConsumablesDocument27 pagesAvio 200-500 ICP-OES ConsumablesNguyễnHoàngDanhNo ratings yet
- De-62 Manual Software Equipo de AA ThermoDocument105 pagesDe-62 Manual Software Equipo de AA ThermoMelisa L CastrillonNo ratings yet
- Seafast For Nexion IcpmsDocument2 pagesSeafast For Nexion Icpmsta quang khanhNo ratings yet
- Quantx SpecificationsDocument8 pagesQuantx SpecificationsHasan Zaity100% (1)
- Atomic Absorption SpectrosDocument2 pagesAtomic Absorption SpectrosSoumitra NathNo ratings yet
- An 70048 Environmental Water Applications Notebook AN70048 EDocument134 pagesAn 70048 Environmental Water Applications Notebook AN70048 EKALLIOPINo ratings yet
- Skoog 10Document33 pagesSkoog 10Tnieey HashimNo ratings yet
- Atomic Emission SpectrosDocument18 pagesAtomic Emission Spectrosmatin5No ratings yet
- Determination of Phosphorus in Fertilizers by IcpDocument7 pagesDetermination of Phosphorus in Fertilizers by IcpharoldNo ratings yet
- Evo Sem SopDocument13 pagesEvo Sem SopAswr100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Biological MS and Proteomics Carr 5 15 PDFDocument43 pagesFundamentals of Biological MS and Proteomics Carr 5 15 PDFCarlos Julio Nova LopezNo ratings yet
- Varioskan BrochureDocument4 pagesVarioskan BrochureSaurabh SaxenaNo ratings yet
- PreviewpdfDocument68 pagesPreviewpdfJoel Ccallo HuaquistoNo ratings yet
- Mass SpectrometryDocument30 pagesMass SpectrometryfatemaNo ratings yet
- Paper: Understanding Cation Effects in Electrochemical CO ReductionDocument14 pagesPaper: Understanding Cation Effects in Electrochemical CO ReductionMaría esquivia100% (1)
- Innovate T5Document14 pagesInnovate T5oambesi100% (1)
- 03 GenX RaysDocument14 pages03 GenX RaysEdward PittsNo ratings yet
- Icp-Aes S1Document57 pagesIcp-Aes S1fitriana dewi kurniawatiNo ratings yet
- HPLC Vs ECDocument20 pagesHPLC Vs ECFrancisco Erik González JiménezNo ratings yet
- Belec Vario Lab: High-Performance Spectrometer For Metal AnalysisDocument4 pagesBelec Vario Lab: High-Performance Spectrometer For Metal AnalysisGoran DjuricNo ratings yet
- Atomic Spectroscopy and Atomic Absorption SpectrosDocument80 pagesAtomic Spectroscopy and Atomic Absorption SpectrosMuhammad Mustafa IjazNo ratings yet
- ICP-MS Primer PDFDocument84 pagesICP-MS Primer PDFJohanna Rios GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Intro and Theory of XRF-Product Overview (Compatibility Mode)Document30 pagesIntro and Theory of XRF-Product Overview (Compatibility Mode)Yuli Yanti SundeNo ratings yet
- AA700Usr PDFDocument194 pagesAA700Usr PDFvitoco1500No ratings yet
- Mks - TksDocument12 pagesMks - TksNguyen Duong HieuNo ratings yet
- Description of ICP Optical Emission SpectrometryDocument5 pagesDescription of ICP Optical Emission SpectrometrySalman MuhamadNo ratings yet
- Datasheet Spartan 6Document22 pagesDatasheet Spartan 6Luis Pabon100% (1)
- Slab Planar: Charged Species Migration Rate Electric FieldDocument15 pagesSlab Planar: Charged Species Migration Rate Electric FieldEng Leng LeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 AESDocument14 pagesChapter 10 AESjenyup123No ratings yet
- Lego Exercise Part II Lean State: Grow & InnovateDocument20 pagesLego Exercise Part II Lean State: Grow & InnovateGowtham GanesanNo ratings yet
- 1 PB PDFDocument6 pages1 PB PDFMAHESH CHANDNo ratings yet
- ASNT L3 Exam ExperienceDocument5 pagesASNT L3 Exam ExperienceShahazad Shaik100% (1)
- DSC Beginners GuideDocument9 pagesDSC Beginners GuideŞükrü_talaşNo ratings yet
- Steel ProductionDocument18 pagesSteel ProductionSenathipathi KalimuthuNo ratings yet
- TransformYourHabits EditedDocument60 pagesTransformYourHabits EditedGowtham GanesanNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 PlasticityDocument34 pagesChapter2 PlasticityGowtham GanesanNo ratings yet
- Buehler's Guide To Sample PreparationDocument74 pagesBuehler's Guide To Sample PreparationGowtham GanesanNo ratings yet
- 02 Intro To MinitabDocument36 pages02 Intro To MinitabGowtham GanesanNo ratings yet
- 03 Project SelectionDocument66 pages03 Project SelectionGowtham GanesanNo ratings yet
- Unit 01 Engineering EthicsDocument71 pagesUnit 01 Engineering EthicsGowtham GanesanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Screening Tools: Grow & InnovateDocument71 pagesIntroduction To Screening Tools: Grow & InnovateGowtham GanesanNo ratings yet
- Green Belt "Jump Start": Grow & InnovateDocument22 pagesGreen Belt "Jump Start": Grow & InnovateGowtham GanesanNo ratings yet
- Corp Finance 2 SHVDocument49 pagesCorp Finance 2 SHVGowtham GanesanNo ratings yet
- 01 03 FindinganswersDocument6 pages01 03 FindinganswersNico TuscaniNo ratings yet