Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drive Mechanism in Reservoir
Drive Mechanism in Reservoir
Uploaded by
PRATIK MARANDI0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views10 pagesMechanism that is involved in a reservoir that act as a source of driving force to support primary production. Primary recovery mechanism that are involved are 1) Rock and liquid expansion drive
2) Depletion drive
3) Gas cap drive
4) Water drive
5) Combination drive
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMechanism that is involved in a reservoir that act as a source of driving force to support primary production. Primary recovery mechanism that are involved are 1) Rock and liquid expansion drive
2) Depletion drive
3) Gas cap drive
4) Water drive
5) Combination drive
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views10 pagesDrive Mechanism in Reservoir
Drive Mechanism in Reservoir
Uploaded by
PRATIK MARANDIMechanism that is involved in a reservoir that act as a source of driving force to support primary production. Primary recovery mechanism that are involved are 1) Rock and liquid expansion drive
2) Depletion drive
3) Gas cap drive
4) Water drive
5) Combination drive
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
Drive Mechanism In Reservoir
NATURAL PRODUCING MECHANISM
The reservoir engineers is primarily concerned with two points:
1. the amount of oil and gas which will ultimately recovered
2. the rate at which this oil and gas will be recovered
DRIVING FORCE FOR PRODUCTION
The expansion of the reservoir fluid, which is a function of their volume and
compressibility, act as a source of drive energy to support primary
production
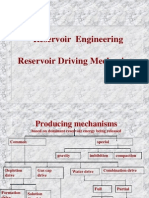
PRIMARY RECOVERY MECHANISMS
Five driving mechanisms
1. Rock and liquid expansion drive
2. Depletion drive
3. Gas cap drive
4. Water drive
5. Combination drive
Rock and Liquid Expansion
Undersaturated oil reservoir.
The reservoir rock compressibility is the result of two factors:
• Expansion of the individual rock grains
• Formation compaction
Reduction of the porosity.
least efficient driving force
recovery of only a small percentage of the
total oil in place.
The Depletion Drive Mechanism / Solution gas
drive / Dissolved gas drive / Internal gas drive
No initial gas cap & No underlying active aquifer
Source of energy is a result of gas liberation from the crude oil
Expansion of the solution gas
Gas Cap Drive:
Initial gas cap
Little or no underlying water drive
two sources:
Expansion of the gas-cap gas
• Expansion of the solution gas as it is liberated
The Water-Drive Mechanism
Production from the oil column creates a pressure drop – water moves into
the oil column to replace the voidage
The Combination-Drive Mechanism
The driving mechanism most commonly encountered is one
in which both water and free gas are available in some
degree to displace the oil toward the producing wells
You might also like
- Reservoir Material BalanceDocument37 pagesReservoir Material BalancejacobNo ratings yet
- Reservoir Drive MechanismsDocument28 pagesReservoir Drive Mechanismsnovia100% (1)
- Reservoir Drive MechanismsDocument36 pagesReservoir Drive MechanismsUsman HasanNo ratings yet
- Drive MechanismsDocument12 pagesDrive Mechanismsl3gsdNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Polymeric Materials For ChemEORDocument45 pagesEvaluation of Polymeric Materials For ChemEORIhsan ArifNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Factors Impacting Water FloodingDocument42 pagesChapter 2 - Factors Impacting Water FloodingMohamed ModerNo ratings yet
- Drive MechanismDocument48 pagesDrive MechanismtalhahafeezmNo ratings yet
- Reservoir Engineering-: Primary Recovery MechanismsDocument16 pagesReservoir Engineering-: Primary Recovery Mechanismsعلي حسين جميل100% (1)
- Drive MechanismsDocument36 pagesDrive MechanismsLemony SnickitNo ratings yet
- Water FloodingDocument48 pagesWater FloodingMohammed Mizbauddin50% (2)
- Drive MechanismDocument21 pagesDrive Mechanismcrown212100% (1)
- Construction Crane at Sunset PowerPoint Templates StandardDocument19 pagesConstruction Crane at Sunset PowerPoint Templates StandardAnwar SaedNo ratings yet
- Chap 3 - Drive Mechanism & MBEDocument29 pagesChap 3 - Drive Mechanism & MBEMohammed BahramNo ratings yet
- 8a. Reservoir Drive Mechanics and Recovery Factors PDFDocument16 pages8a. Reservoir Drive Mechanics and Recovery Factors PDFShadan JavedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document28 pagesChapter 3peter.pucciNo ratings yet
- Material Balance Equation-Driving MechanismsDocument43 pagesMaterial Balance Equation-Driving Mechanismsserept100% (1)
- Primary RecoveryDocument20 pagesPrimary RecoveryMohammed OmranNo ratings yet
- Drive MechanismsDocument26 pagesDrive MechanismsSualihu MoroNo ratings yet
- Reservoir Drive MechanismsDocument7 pagesReservoir Drive MechanismsgorkemerkanliNo ratings yet
- Chapter4 Reservior EngineeringDocument50 pagesChapter4 Reservior Engineeringlovely petsNo ratings yet
- SC RE Chap11-Drive MechanismsDocument45 pagesSC RE Chap11-Drive Mechanismsweldsv100% (1)
- Various Methods of Oil Recovery: By:-Geikaran Patel ROLL NO:-U10CH025Document26 pagesVarious Methods of Oil Recovery: By:-Geikaran Patel ROLL NO:-U10CH025duyvkNo ratings yet
- Pro Tech 1 CH 2Document29 pagesPro Tech 1 CH 2weldsvNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Intro To Petroleum Production (Reservoir Drive Mechanism)Document25 pagesChapter 2 - Intro To Petroleum Production (Reservoir Drive Mechanism)PrincessFaraBPNo ratings yet
- EMOR PresentationDocument51 pagesEMOR Presentationben7251No ratings yet
- Primary Recovery of Crude OilDocument2 pagesPrimary Recovery of Crude OilOjomopeterNo ratings yet
- Natural Gas Production: FormationDocument11 pagesNatural Gas Production: FormationmohamedNo ratings yet
- Reservoir Drive MechanismsDocument7 pagesReservoir Drive MechanismsMuhammad shahbazNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Oil RecoveryDocument8 pagesEnhanced Oil RecoveryRohan JindalNo ratings yet
- اسس هندسة نفطDocument6 pagesاسس هندسة نفطليث علي احمد حريفشNo ratings yet
- Reservoir Engineering Reservoir Driving MechanismsDocument23 pagesReservoir Engineering Reservoir Driving MechanismsAnoo SebastianNo ratings yet
- MSC (PET) 02reservoir Production Concept-6 SlidesDocument11 pagesMSC (PET) 02reservoir Production Concept-6 SlidesUsman HasanNo ratings yet
- Gemsa Company Exam From AONG WebsiteDocument12 pagesGemsa Company Exam From AONG WebsiteezioNo ratings yet
- 5 Drive MechsDocument31 pages5 Drive MechsHafiz AsyrafNo ratings yet
- Reservoir Drive MechanismsDocument22 pagesReservoir Drive MechanismsSafwan NasirNo ratings yet
- Reservoir Drive MechanismsDocument22 pagesReservoir Drive MechanismsHasnain TariqNo ratings yet
- Cbe 555Document22 pagesCbe 555sereptNo ratings yet
- Cbe 555: Chemical Engineeringconnections: Impact of Chemical Engineering On The Outside WorldDocument22 pagesCbe 555: Chemical Engineeringconnections: Impact of Chemical Engineering On The Outside WorldsereptNo ratings yet
- Drive Mechanisms For Reservoir EngineeringDocument9 pagesDrive Mechanisms For Reservoir Engineeringrichardkasana54No ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Exploration and General Methods For Oil Recovery NotesDocument18 pagesChapter 5: Exploration and General Methods For Oil Recovery NotesAnonymous rKosw5xbJtNo ratings yet
- Teaching Plan Course Outline: Pre-UpstreamDocument43 pagesTeaching Plan Course Outline: Pre-UpstreamAmit VermaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Reservoir DrivesDocument14 pagesChapter 3: Reservoir Drivesardie rayNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Eor Processes Introduction To Eor Processes: Dr. Shivanjali SharmaDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Eor Processes Introduction To Eor Processes: Dr. Shivanjali SharmaRavi ShankarNo ratings yet
- Seminar Paper FinalDocument10 pagesSeminar Paper Finalyimam aliNo ratings yet
- .The Term Refers To The Production of Hydrocarbons From A Reservoir Without The Use of Any Process (Such As Fluid Injection) To Supplement The Natural Energy of The ReservoirDocument32 pages.The Term Refers To The Production of Hydrocarbons From A Reservoir Without The Use of Any Process (Such As Fluid Injection) To Supplement The Natural Energy of The ReservoirHomam MohammadNo ratings yet
- Reservoir Drive MechanismsDocument34 pagesReservoir Drive MechanismsUPES AAPG STUDENT CHAPTERNo ratings yet
- Natural Drive MechanismsDocument4 pagesNatural Drive MechanismsWaleed Ejaz0% (1)
- Cbe 555: Chemical Engineeringconnections: Impact of Chemical Engineering On The Outside WorldDocument22 pagesCbe 555: Chemical Engineeringconnections: Impact of Chemical Engineering On The Outside WorldsereptNo ratings yet
- Cbe 555: Chemical Engineeringconnections: Impact of Chemical Engineering On The Outside WorldDocument22 pagesCbe 555: Chemical Engineeringconnections: Impact of Chemical Engineering On The Outside WorldArpan BiswasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Rock and Fluid PropertiesDocument32 pagesChapter 3 Rock and Fluid PropertiesDeniz AkoumNo ratings yet
- Artificial Lift MechanismDocument22 pagesArtificial Lift MechanismKaran MathurNo ratings yet
- Mekanisme Aliran FluidaDocument24 pagesMekanisme Aliran FluidaFaisal FadilahNo ratings yet
- Production Operation Unit 1Document104 pagesProduction Operation Unit 1aspirantNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Oil Recovery TechniquesDocument18 pagesEnhanced Oil Recovery Techniquesavula43No ratings yet
- EOR-Prof KharratDocument140 pagesEOR-Prof Kharratchentika bungaNo ratings yet
- Cbe 555: Chemical Engineeringconnections: Impact of Chemical Engineering On The Outside WorldDocument22 pagesCbe 555: Chemical Engineeringconnections: Impact of Chemical Engineering On The Outside WorldVlassis SarantinosNo ratings yet
- Heavy Oil Production Pumping SystemDocument26 pagesHeavy Oil Production Pumping SystemrahulNo ratings yet
- Exploration of Crude PetroleumDocument13 pagesExploration of Crude PetroleumUsman IsrarNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Oil Recovery Techniques: Jntu Iv Year B.Tech Petroleum EngineeringDocument54 pagesEnhanced Oil Recovery Techniques: Jntu Iv Year B.Tech Petroleum EngineeringNadeemSKNo ratings yet