0% found this document useful (0 votes)
136 views25 pages3D Truss Analysis and Deformation Calculation
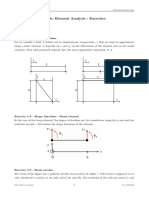
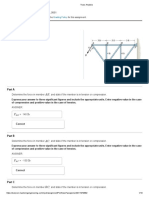
The document provides instructions for using finite element analysis software to analyze a 3D truss. It describes creating the model by defining the material properties, adding nodes at the specified coordinates, connecting the nodes to create elements, applying boundary conditions by restraining nodes, applying a load to one node, solving the model, and reviewing the stress and displacement results. The deformation of point A is 1.736 x10-5 m in the x-direction and 6.944 x10-5 m downward, element 3 experiences the highest tensile stress of 2.22 x 106 N/m2, and elements 1 and 2 experience compressive stresses of 1.11 x 106 N/m2.
Uploaded by
Nik JaffCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
136 views25 pages3D Truss Analysis and Deformation Calculation
The document provides instructions for using finite element analysis software to analyze a 3D truss. It describes creating the model by defining the material properties, adding nodes at the specified coordinates, connecting the nodes to create elements, applying boundary conditions by restraining nodes, applying a load to one node, solving the model, and reviewing the stress and displacement results. The deformation of point A is 1.736 x10-5 m in the x-direction and 6.944 x10-5 m downward, element 3 experiences the highest tensile stress of 2.22 x 106 N/m2, and elements 1 and 2 experience compressive stresses of 1.11 x 106 N/m2.
Uploaded by
Nik JaffCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd