0% found this document useful (0 votes)
42 views26 pagesCPR - Fixed
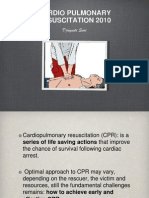
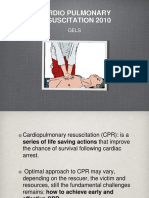
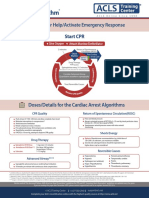
The document outlines the procedures and goals for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) and Advanced Life Support (ALS) aimed at restoring effective oxygenation, ventilation, and circulation. Key components include Basic Life Support (BLS) actions such as immediate recognition of cardiac arrest, activation of emergency response, and performing CPR and defibrillation. It also discusses the identification and correction of reversible factors affecting cardiac arrest and the complications that may arise from chest compressions.
Uploaded by
Timotius RaymondCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
42 views26 pagesCPR - Fixed
The document outlines the procedures and goals for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) and Advanced Life Support (ALS) aimed at restoring effective oxygenation, ventilation, and circulation. Key components include Basic Life Support (BLS) actions such as immediate recognition of cardiac arrest, activation of emergency response, and performing CPR and defibrillation. It also discusses the identification and correction of reversible factors affecting cardiac arrest and the complications that may arise from chest compressions.
Uploaded by
Timotius RaymondCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd