100% found this document useful (1 vote)
498 views28 pagesBenefits of Shear Walls in Seismic Areas
Buildings with shear walls are preferred in seismic regions for the following reasons:
1) Shear walls are vertical reinforced concrete walls designed to resist lateral forces like wind and earthquakes.
2) Shear walls provide large strength, high stiffness, and ductility to smoothly transfer seismic forces through the building.
3) In past earthquakes, buildings with shear walls performed much better than reinforced concrete frame buildings, experiencing less damage.
Uploaded by
Harold Jackson MtyanaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
498 views28 pagesBenefits of Shear Walls in Seismic Areas
Buildings with shear walls are preferred in seismic regions for the following reasons:
1) Shear walls are vertical reinforced concrete walls designed to resist lateral forces like wind and earthquakes.
2) Shear walls provide large strength, high stiffness, and ductility to smoothly transfer seismic forces through the building.
3) In past earthquakes, buildings with shear walls performed much better than reinforced concrete frame buildings, experiencing less damage.
Uploaded by
Harold Jackson MtyanaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Introduction to Shear Walls: Introduces the concept of shear walls in seismic regions and their importance.
- Definition of Shear Wall: Defines what a shear wall is and its role in resisting forces during earthquakes.
- RC Building Systems: Describes common lateral load resisting systems in reinforced concrete buildings.
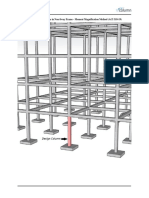
- Shear Wall in RC Buildings: Explains the integration and role of shear walls within RC buildings, emphasizing their vertical nature.
- Examples of Shear Walls: Provides visual examples of buildings with shear walls, specifically Prince Arthur Avenue.
- Principal Attributes: Outlines the main characteristics of shear walls such as strength, stiffness, and ductility.
- Role of Shear Walls: Discusses how shear walls distribute seismic forces throughout the structure.
- Advantages of Shear Walls: Highlights the benefits of using shear walls, including enhanced performance and cost-effectiveness.
- Architectural Aspects: Examines the architectural considerations when integrating shear walls in buildings, emphasizing their placement and continuity.
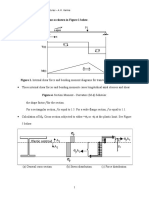
- Seismic Behavior: Explores both undesirable and desirable modes of failure in shear walls under seismic conditions.
- Seismic Design of RC Walls: Covers design strategies for reinforcing walls against seismic forces, including ductile detailing and geometric considerations.
- Conclusion: Concludes the presentation and thanks the audience.