Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Foundry
Uploaded by
Vipin Titariya0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views4 pagesOriginal Title
foundry
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views4 pagesFoundry
Uploaded by
Vipin TitariyaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Foundry
A foundry is a factory that produces metal castings.
Metals are cast into shapes by melting them into a liquid,
pouring the metal into a mold, and removing the mold
material after the metal has solidified as it cools. The
most common metals processed are aluminium and cast
iron However, other metals, such as bronze brass, steel
and zinc are also used to produce castings in foundries.
In this process, parts of desired shapes and sizes can be
formed.
Melting
Melting is performed in a furnace Virgin material,
external scrap, internal scrap, and alloying elements
are used to charge the furnace. Virgin material refers to
commercially pure forms of the primary metal used to
form a particular alloy Alloying elements are either pure
forms of an alloying element, like electrolytic nickel or
alloys of limited composition, such as ferroalloys or
master alloys. External scrap is material from other
forming processes such as punching forging
or machining. Internal scrap consists of gates risers
defective castings, and other extraneous metal
oddments produced within the facility.
Furnace
Furnaces are refractory-lined vessels that contain the
material to be melted and provide the energy to melt it.
Modern furnace types include electric arc
furnaces (EAF), induction furnaces, cupolas, reverberatory
and crucible furnaces. Furnace choice is dependent on the
alloy system quantities produced. For ferrous materials
EAFs, cupolas, and induction furnaces are commonly
used. Reverberatory and crucible furnaces are common
for producing aluminium, bronze, and brass castings.
Foundry tools
Foundry shop is the place where the metal
casting is prepared by melting and pouring
the molten metal into moulds. Some of the
commonly used tools in foundry shop for
moulding process are showel, trowel,
riddle, rammer, draw spike, swab, vent wire
and slick tool.
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
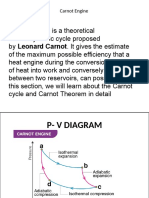
- Carnot CycleDocument9 pagesCarnot CycleVipin TitariyaNo ratings yet
- Carnot CycleDocument9 pagesCarnot CycleVipin TitariyaNo ratings yet
- PHD Thesis Christian Wolf 2013 - Simulation, Optimization and Instrumentation of Agricultural Biogas PlantsDocument225 pagesPHD Thesis Christian Wolf 2013 - Simulation, Optimization and Instrumentation of Agricultural Biogas PlantsVipin TitariyaNo ratings yet
- Wind Turbine Performance Monitoring Using Artificial Neural NetworksDocument102 pagesWind Turbine Performance Monitoring Using Artificial Neural NetworksVipin TitariyaNo ratings yet
- Thesis CDU 48865 Kelly JDocument123 pagesThesis CDU 48865 Kelly JVipin TitariyaNo ratings yet
- Wu Wentao 200322124 MASC ISE Spring2015Document158 pagesWu Wentao 200322124 MASC ISE Spring2015Vipin TitariyaNo ratings yet
- ESE 2020 Work Book Ans Key Preliminary ExamDocument2 pagesESE 2020 Work Book Ans Key Preliminary ExamVipin TitariyaNo ratings yet
- ESE 2020 Ethics Workbook Answer KeyDocument1 pageESE 2020 Ethics Workbook Answer KeyVipin TitariyaNo ratings yet
- ESE 2020 Project Management Workbook Answer Key-1Document2 pagesESE 2020 Project Management Workbook Answer Key-1Vipin TitariyaNo ratings yet
- Lathe MachineDocument8 pagesLathe MachineVipin TitariyaNo ratings yet
- FoundryDocument4 pagesFoundryVipin TitariyaNo ratings yet
- Clutch and Types of ClutchesDocument6 pagesClutch and Types of ClutchesVipin TitariyaNo ratings yet
- ForgingDocument10 pagesForgingVipin TitariyaNo ratings yet