Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Development of Dentition
Uploaded by
Swati Pawar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views5 pagesOriginal Title
development of dentition
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views5 pagesDevelopment of Dentition
Uploaded by
Swati PawarCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
Development of dentition
and
occlusion
Dr. Swati Pawar
P.G. Ist year
CONTENT
FORMATION OF TOOTH
The embryonic oral cavity is lined by startified
squamous epithelium known as the oral
ectoderm.
Around the 6th week of intra-uterine life , the inferio-lateral
border of maxillary arch and the supero-lateral border of
mandibular arch show localized proliferation of oral ectoderm
resulting in the formation of horse-shoe shaped band of tissue
called the dental lamina.
This dental lamina plays an important role in the development
of the dentition .
The decidious teeth are formed in direct proliferation of dental
lamina.
The permanent molars develop as a result of its distal
proliferation while the permanent teeth teeth that replace
deciduous teeth develop from a lingual extension of dental
lamina.
Thua all teeth originate from the dental lamina.
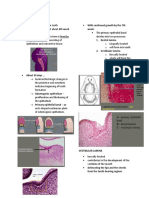
The ectoderm in certain areas of the dental lamina proliferates
and forms knob – like structures that grow into the underlying
mesenchyma.
Each of
You might also like
- Tooth Development BasicDocument58 pagesTooth Development BasicSasidhar VajralaNo ratings yet
- Development of Dentition - FinalDocument60 pagesDevelopment of Dentition - FinalDrkamesh M100% (1)
- Developmentofteeth StagesDocument45 pagesDevelopmentofteeth Stagesimi4100% (1)
- Development of PeriodontiumDocument24 pagesDevelopment of Periodontiumpalak sharma100% (1)
- Tooth DevelopmentDocument15 pagesTooth DevelopmentSascha WuNo ratings yet
- Development of ToothDocument57 pagesDevelopment of ToothDr.Rakshith BkNo ratings yet
- Development of ToothDocument68 pagesDevelopment of Toothpvspartan0933% (3)
- Dental Lamina and Its Fate: Prepared By: Nur Amira Illani Binti Roslan I BDS 2016/17Document28 pagesDental Lamina and Its Fate: Prepared By: Nur Amira Illani Binti Roslan I BDS 2016/17NUR AMIRA ILLANI ROSLANNo ratings yet
- Odonto Gens IsDocument8 pagesOdonto Gens Ismary frisanNo ratings yet
- 1.tooth Development Edited1Document6 pages1.tooth Development Edited1drpnnreddy100% (4)
- Lecture 2 - 1Document9 pagesLecture 2 - 1ahmedfawakh0No ratings yet
- ZohrabianDocument10 pagesZohrabianJorge Peña100% (1)
- Colorful Creative Social Media Brainstorm PresentationDocument24 pagesColorful Creative Social Media Brainstorm PresentationSatria MandalaNo ratings yet
- Development of Teeth: by - Dr. Priyanka Singh. M.D.S I YearDocument61 pagesDevelopment of Teeth: by - Dr. Priyanka Singh. M.D.S I YearJerry TurtleNo ratings yet
- Tooth Development: Bell StageDocument6 pagesTooth Development: Bell StageAbdulrahman UdayNo ratings yet
- Oral Histology Lec.2Document18 pagesOral Histology Lec.2imi40% (1)
- Odontogenesis NotesDocument14 pagesOdontogenesis NotesClarisse Mendoza100% (1)
- Development of TeethDocument23 pagesDevelopment of TeethSAGAR SINGHNo ratings yet
- Teeth Development IIDocument65 pagesTeeth Development IIggNo ratings yet
- Tooth Origin and Formation - by Bugnariu Paul, Buterchi Codrut, Chit-Stinean AdonisDocument73 pagesTooth Origin and Formation - by Bugnariu Paul, Buterchi Codrut, Chit-Stinean AdonisVlad FlaviusNo ratings yet
- Development of TeethDocument25 pagesDevelopment of TeethDrShweta Saini100% (1)
- DENT215 Embryological Development of The Dental Pulp Prof. Dr. Işıl KüçükayDocument29 pagesDENT215 Embryological Development of The Dental Pulp Prof. Dr. Işıl Küçükayezoafaneh0No ratings yet
- Teeth DevelopmentDocument12 pagesTeeth DevelopmentMostafa El GendyNo ratings yet
- Development of DentitionDocument79 pagesDevelopment of Dentitionswathi datrika100% (1)
- Tutorial Skenario 2Document25 pagesTutorial Skenario 2Amalia Sholihah MukhtarNo ratings yet
- Development of TeethDocument30 pagesDevelopment of TeethsiyaNo ratings yet
- Development of Dentition: - G.Shekar Subramanian Iyr MdsDocument96 pagesDevelopment of Dentition: - G.Shekar Subramanian Iyr MdsShekar SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Origin and development of oral tissuesDocument30 pagesOrigin and development of oral tissuesAnh Do Thi VanNo ratings yet
- Tooth Development 1Document14 pagesTooth Development 1ahmedfawakh0No ratings yet
- DCH Notebook Development of ToothDocument8 pagesDCH Notebook Development of ToothmanujNo ratings yet
- Radiological and Histological Correlation of Cysts of The Jaws Part - IDocument56 pagesRadiological and Histological Correlation of Cysts of The Jaws Part - IAARYANo ratings yet
- Development of Teeth and TongueDocument79 pagesDevelopment of Teeth and TongueOmanakuttan Kr100% (1)
- Early Tooth Development, Root Development (Including Cementogenesis) and Tooth EruptionDocument6 pagesEarly Tooth Development, Root Development (Including Cementogenesis) and Tooth Eruptionnoelah salcedoNo ratings yet
- Congenital Anomalies - 2016 - Kawashima - Odontoblasts Specialized Hard Tissue Forming Cells in The Dentin Pulp ComplexDocument10 pagesCongenital Anomalies - 2016 - Kawashima - Odontoblasts Specialized Hard Tissue Forming Cells in The Dentin Pulp ComplexDevin KwanNo ratings yet
- 2-Dev. To GeometriesDocument12 pages2-Dev. To GeometriesFLORENCE GERENTENo ratings yet
- Enamel HandoutDocument93 pagesEnamel HandoutIqra EjazNo ratings yet
- Odonto GenesisDocument3 pagesOdonto GenesisyashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- Sequence and Timing of Dental Growth: Department of Forensic Odontology Faculty of Dental Medicine Airlangga UniversityDocument36 pagesSequence and Timing of Dental Growth: Department of Forensic Odontology Faculty of Dental Medicine Airlangga UniversityJanice HamdaniNo ratings yet
- Tooth Development Stages and Types of TeethDocument17 pagesTooth Development Stages and Types of TeethsusanthNo ratings yet
- Tooth Development StagesDocument16 pagesTooth Development StagesAdam AliraqiNo ratings yet
- 1 IntroductionDocument38 pages1 IntroductionMimo HemadNo ratings yet
- Tooth Development and Supporting TissuesDocument68 pagesTooth Development and Supporting TissuesSaud IqbalNo ratings yet
- ToothDocument34 pagesToothfathimanesrin537No ratings yet
- Tooth DevelopmentDocument20 pagesTooth DevelopmentArslan Jokhio0% (1)
- The Development of The TeethDocument17 pagesThe Development of The TeethYasmin A. AhmedNo ratings yet
- Seminar 3Document96 pagesSeminar 3Dilip Kumar ChevuriNo ratings yet
- Zahn Entwicklung EnglDocument10 pagesZahn Entwicklung EnglinfoNo ratings yet
- 5 OdontogenesisDocument3 pages5 OdontogenesisDr-Osama ShaalanNo ratings yet
- Tooth Formation: Chapter 1Document5 pagesTooth Formation: Chapter 1_RedX_No ratings yet
- Development of TeethDocument74 pagesDevelopment of TeethdeepaelizaNo ratings yet
- Tooth Dcevelopment 07Document71 pagesTooth Dcevelopment 07Daniel Vega AdauyNo ratings yet
- Development of ToothDocument68 pagesDevelopment of ToothMamatha M KarthikNo ratings yet
- Pulp-Dentin Complex: SR No Content Page NoDocument16 pagesPulp-Dentin Complex: SR No Content Page NoNaren RamachandranNo ratings yet
- tooth developmentDocument2 pagestooth developmentxv2yccj585No ratings yet
- Development of Tooth Lecture-1Document63 pagesDevelopment of Tooth Lecture-1Dimple KashyapNo ratings yet
- Development of Dentition and Occlusion - Dr. Nabil Al-ZubairDocument124 pagesDevelopment of Dentition and Occlusion - Dr. Nabil Al-ZubairNabil Al-Zubair75% (4)
- Oral Medicine & Pathology from A-ZFrom EverandOral Medicine & Pathology from A-ZRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (9)
- Functional Examination: Preceptor:-Dr - Payalsharma (H.O.D) DR - ShalajbhatnagarDocument119 pagesFunctional Examination: Preceptor:-Dr - Payalsharma (H.O.D) DR - ShalajbhatnagarSwati PawarNo ratings yet
- Functional Occlusion 2Document30 pagesFunctional Occlusion 2Swati PawarNo ratings yet
- Myofunctional AppliancesDocument179 pagesMyofunctional AppliancesSwati PawarNo ratings yet
- Myofunctional Gen Concepts and Construction BiteDocument105 pagesMyofunctional Gen Concepts and Construction BiteSwati PawarNo ratings yet
- Functional OcclusionDocument21 pagesFunctional OcclusionSwati Pawar100% (1)
- Balanced SmileDocument38 pagesBalanced SmileSwati PawarNo ratings yet
- Growth and Development of Cranial and Facial RegionDocument81 pagesGrowth and Development of Cranial and Facial RegionSwati PawarNo ratings yet
- Gypsum ProductsDocument79 pagesGypsum ProductsSwati Pawar100% (1)
- Soldering and WeldingDocument101 pagesSoldering and WeldingSwati PawarNo ratings yet
- Balanced SmileDocument38 pagesBalanced SmileSwati PawarNo ratings yet
- Gypsum ProductsDocument79 pagesGypsum ProductsSwati Pawar100% (1)
- Sterilization in OrthodonticsDocument121 pagesSterilization in OrthodonticsSwati PawarNo ratings yet
- Soldering and WeldingDocument102 pagesSoldering and WeldingSwati PawarNo ratings yet