Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Worm Gears
Uploaded by
tanya0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
47 views5 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
47 views5 pagesWorm Gears
Uploaded by
tanyaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
Worm Gears
•A worm gear is an inclined plane wrapped
around a central axle. It is a gear with one or
more teeth in the form of screwed threads.
Worm gears are made of two parts: the pinion
and the worm gear. The pinion has small
number of teeth and they wrap around the
pitch cylinder. The worm gear has concave
faces to fit the curvature of the worm in order
to provide line of contact instead of point of
contact. They are cut helically for better
mating. Worm gears can provide a high
angular velocity between non-intersecting
shafts at right angles. They are capable of
transmitting high tooth loads, the only
disadvantage is the high sliding velocities
across the teeth. They provide ultimate power
ratio.
Advantages
• The efficiency of worm gear depends on the lead angle, sliding
speed, and lubricant, surface quality and installation conditions.
They offer smoothest, quietest form of gearing. They provide high-
ratio speed reduction in minimal spaces. Worm gears are used
when large gear reductions are required. Worm gear has a unique
property of easily turning the gear. The gear cannot turn the worm
because the angle on the worm is shallow and when the gear tries
to spin the worm, the friction between the two holds the worm in
place.
Worm gears work under difficult conditions, presenting unique
lubrication demands. The types of oils most commonly used to
lubricate worm gears are compounded mineral oils, EP mineral gear
oils and synthetics.
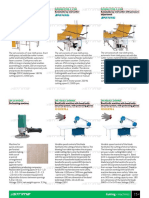
Mechanism
• Worm gear is always used as the input gear. For
the operation of worm gear, torque is applied to
the input end of the worm shaft by a driven
sprocket or electric motor. The worm and the
worm shaft are supported by anti-friction roller
bearings. Because of high friction worm gears
are very inefficient. There is lot of friction
between a worm gear and the gear being driven
by the worm gear. When used in high torque
applications, the friction causes the wear on the
gear teeth and erosion of restraining surface.
Types
• There are three types of worm gears:
• Non throated- a helical gear with a straight worm. Tooth
contact is a single moving point on the worm drive.
• Single throated- has concave helical teeth wrap around
the worm. This leads to line contact.
• Double throated- called a cone or hourglass. It has
concave teeth both on the worm and helical gear.
Applications
• Worm gears are widely used in packaging
machinery, material handling, machine
tools, indexing and food processing. They
are used widely in conveyor systems.
They are also used in torsen differential,
used on some high-performance cars and
trucks. They serve as speed reducers in
many different industries.
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- You Exec - Brand Positioning Strategy CompleteDocument18 pagesYou Exec - Brand Positioning Strategy CompleteDianne DimoriNo ratings yet
- Color Palettes v1.1.0 PDFDocument152 pagesColor Palettes v1.1.0 PDFSteve Jobs50% (2)
- Sample Request Letter For Police Clearance Certificate in QatarDocument15 pagesSample Request Letter For Police Clearance Certificate in QatarJayson Benedick Colobong0% (2)
- Value-Based Pricing: The Driver To Increased Short-Term ProfitsDocument4 pagesValue-Based Pricing: The Driver To Increased Short-Term ProfitsRiz DeenNo ratings yet
- Zorki - 4k ManualDocument22 pagesZorki - 4k ManualOtto HandNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan On DVTDocument18 pagesLesson Plan On DVTAlma Susan100% (1)
- Cars4u Project: Proprietary Content. © Great Learning. All Rights Reserved. Unauthorized Use or Distribution ProhibitedDocument30 pagesCars4u Project: Proprietary Content. © Great Learning. All Rights Reserved. Unauthorized Use or Distribution ProhibitedAbhay Poddar100% (2)
- Session 5Document3 pagesSession 5Sistine Rose Labajo100% (1)
- Introduction To SAP UI5Document11 pagesIntroduction To SAP UI5EugeneNo ratings yet
- RopesDocument13 pagesRopestanyaNo ratings yet
- ClutchesDocument5 pagesClutchestanyaNo ratings yet
- Dayang Dydb-3 2,5M Dayang Dydb-2 2,5M Dayang Dydb-1 2,6M: Cutting - MachinesDocument1 pageDayang Dydb-3 2,5M Dayang Dydb-2 2,5M Dayang Dydb-1 2,6M: Cutting - MachinestanyaNo ratings yet
- Ergonomics Evaluation of Body Posture of PDFDocument5 pagesErgonomics Evaluation of Body Posture of PDFtanyaNo ratings yet
- Cooper Form 6 Control ManualDocument3 pagesCooper Form 6 Control ManualReinhad HutabaratNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Marmol Artificial - Kingkonree International China Surface Industrial Co., LTDDocument67 pagesCatalogo Marmol Artificial - Kingkonree International China Surface Industrial Co., LTDTDNRamonNo ratings yet
- Telephone Directory 2018Document6 pagesTelephone Directory 2018CLO GENSANNo ratings yet
- Sample Reciprocity LetterDocument1 pageSample Reciprocity LetterRrichard Prieto MmallariNo ratings yet
- Prosiding Faperta 2018 Fix PDFDocument676 pagesProsiding Faperta 2018 Fix PDFAgus Kaspun100% (1)
- HES-005-Session-9-SASDocument9 pagesHES-005-Session-9-SASDave Ortiz Robert MaglasangNo ratings yet
- 48900-Article Text-64551-1-10-20091210Document6 pages48900-Article Text-64551-1-10-20091210Muguo Mouafo BriceNo ratings yet
- Annex 4 - Testing Centers - Amtec Cemtre & LatlDocument17 pagesAnnex 4 - Testing Centers - Amtec Cemtre & LatlHarvy LucinadaNo ratings yet
- 200 SongsDocument5 pages200 SongsJocelyn Atangan Alaba50% (2)
- DinosaursDocument4 pagesDinosaursGayani Dulmala ImbulanaNo ratings yet
- Arkansas Department of Human Services: Application For An Independently Licensed PractitonerDocument2 pagesArkansas Department of Human Services: Application For An Independently Licensed PractitonerHarold LowryNo ratings yet
- What Is National Security ActDocument3 pagesWhat Is National Security ActlolNo ratings yet
- Cae Letter of RecommendationDocument4 pagesCae Letter of RecommendationsimonaNo ratings yet
- Object TrackingDocument23 pagesObject TrackingRahul PaulNo ratings yet
- Stormbrixx - Fisa TehnicaDocument108 pagesStormbrixx - Fisa Tehnicamureseanu_deliaNo ratings yet
- 9700 BIOLOGY: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2012 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersDocument14 pages9700 BIOLOGY: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2012 Question Paper For The Guidance of Teacherslianghoo94No ratings yet
- The Boat Safety Scheme Essential GuideDocument16 pagesThe Boat Safety Scheme Essential GuideCostin RotaruNo ratings yet
- Managing The Finance FunctionDocument12 pagesManaging The Finance FunctionDumplings DumborNo ratings yet
- عتبات النص في التراث العربيDocument12 pagesعتبات النص في التراث العربيREZKALLAH OMARNo ratings yet
- Dim 1001Document7 pagesDim 1001Kokxing KkxNo ratings yet
- A Proposed Medium-Term Development Plan For Data Center College of The Philippines Laoag City CampusDocument3 pagesA Proposed Medium-Term Development Plan For Data Center College of The Philippines Laoag City Campussheng cruzNo ratings yet