0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views18 pagesGrievance Procedures in Collective Bargaining
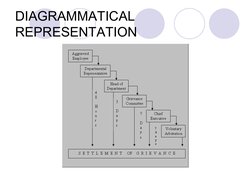
This document discusses grievance procedures and collective bargaining. It defines grievances as feelings of dissatisfaction among workers regarding their work. It outlines a step-ladder grievance policy where workers address issues with supervisors and higher levels of management if not resolved. Collective bargaining is defined as determining employment conditions through representatives of workers and employers. Key aspects of collective bargaining include identifying issues, negotiating, and reaching settlement agreements. The document also discusses importance and challenges of grievance procedures and collective bargaining.
Uploaded by
Shalu PalCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views18 pagesGrievance Procedures in Collective Bargaining
This document discusses grievance procedures and collective bargaining. It defines grievances as feelings of dissatisfaction among workers regarding their work. It outlines a step-ladder grievance policy where workers address issues with supervisors and higher levels of management if not resolved. Collective bargaining is defined as determining employment conditions through representatives of workers and employers. Key aspects of collective bargaining include identifying issues, negotiating, and reaching settlement agreements. The document also discusses importance and challenges of grievance procedures and collective bargaining.
Uploaded by
Shalu PalCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd