Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 2 Micro Eco
Uploaded by
Rezoan Farhan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views8 pagesOriginal Title
2. Chapter 2 micro eco
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views8 pagesChapter 2 Micro Eco
Uploaded by
Rezoan FarhanCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
Chapter 2
Markets and Government in a
Modern Economy
What is a Market
• A mechanism through which buyers and
sellers interact to set prices and exchange
goods and services
Market Equilibrium
• Represents a balance among all the different
buyers and sellers
How Market Solve Three Economic
Problems
• What goods and services will be produced
• How things are produced
• For whom things are produced
Factor Markets
Three Distinguishing Features of Modern
Economy
• Trade: Contains specialization and division of
labor
• Money: The lubricants of exchange
• Capital: factors of production, a durable input
which is itself an output of the economy.
(Land and labor are the primary factors of
production and the rest are secondary factors
of production)
The Economic Role of Government
• Efficiency (Imperfect
competition,
externalities, public
goods)
• Equity like tax
imposition
• Macroeconomic
stability like inflation
Govt. Can Remedy of Short-coming of Markets
Failure of Market Economy Government Intervention Current Examples of Government
Inefficiency Policy
Monopoly Encourage competition Antitrust laws, deregulation
Externalities Intervene in markets Antipollution laws, antismoking
Public goods Encourage beneficial activities ordinances
Build lighthouses, provide public
education
Inequality: Redistribute income Progressive taxation of income and
Unacceptable inequalities of wealth
income and wealth Income-support or transfer programs
(e.g., food stamps)
Macroeconomic problems: Stabilize through macroeconomic Monetary policies (e.g., changes in
Business cycles (high inflation policies money supply and interest rates)
and unemployment) Stimulate growth Fiscal policies (e.g., taxes and spending
Slow economic growth programs)
Invest in education
Raise national savings rate by reducing
budget deficit or increasing budget
surplus
You might also like
- Supply-Side PoliciesDocument35 pagesSupply-Side Policiesmihirjoshi5727No ratings yet
- 2-Financial Management - Chapter 2Document38 pages2-Financial Management - Chapter 2Amal MubarakovNo ratings yet
- Econs - Group1 - Tutorial 1Document8 pagesEcons - Group1 - Tutorial 1Darshilla Rive ChandramNo ratings yet
- Política EconómicaDocument26 pagesPolítica Económicajorge lNo ratings yet
- Gcse Economics (Ocr) Revision Guide: Unit 2: Name: FormDocument21 pagesGcse Economics (Ocr) Revision Guide: Unit 2: Name: FormEstherNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Demand and Supply-Side PoliciesDocument13 pages5.1 Demand and Supply-Side PoliciesMarisa VetterNo ratings yet
- IGCSE MacroEcon HandoutDocument57 pagesIGCSE MacroEcon Handoutdenny_sitorusNo ratings yet
- Supply-Side Policy 2021Document21 pagesSupply-Side Policy 2021ardagursel85No ratings yet
- #2022166 Magalhaes Ivan SupplySide Policies - BrazilDocument20 pages#2022166 Magalhaes Ivan SupplySide Policies - BrazilIvanNo ratings yet
- Checklist Policies For Paper 3 Ib EconomicsDocument2 pagesChecklist Policies For Paper 3 Ib Economicstesde lujoNo ratings yet
- Notes Public EconomicsDocument132 pagesNotes Public EconomicsTWIZERIMANA EVARISTENo ratings yet
- MacroeceonomicsDocument70 pagesMacroeceonomicsHundeNo ratings yet
- Introduction VT2024Document39 pagesIntroduction VT2024aleema anjumNo ratings yet
- Supply Side PoliciesDocument29 pagesSupply Side PoliciesAnaNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Updated Apr2021Document44 pagesMacroeconomics Updated Apr2021Aashish sahuNo ratings yet
- Ch. 2 - Microeconmics StabilizationDocument48 pagesCh. 2 - Microeconmics Stabilizationborifanmaru2016No ratings yet
- Economic Survey Chapter 1: WWW - Anujjindal.In Successrbi@Anujjindal - inDocument11 pagesEconomic Survey Chapter 1: WWW - Anujjindal.In Successrbi@Anujjindal - inRoshan SinghNo ratings yet
- Economic Influences On Business ActivityDocument22 pagesEconomic Influences On Business Activitywaniahnoor15No ratings yet
- Topic 2Document30 pagesTopic 2Hoàng OanhNo ratings yet
- GovernmentDocument36 pagesGovernmentMa. Rudeline Tito SollanoNo ratings yet
- 6c34fb42-1 2 24 Government+Intervention+Document19 pages6c34fb42-1 2 24 Government+Intervention+Edward ShawNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Macroeconomics: Daniel AdjeiDocument46 pagesIntroduction To Macroeconomics: Daniel AdjeiDaniel AdjeiNo ratings yet
- Angel Conworld Mod.7Document8 pagesAngel Conworld Mod.7angelNo ratings yet
- Health Economics Lecture OneDocument28 pagesHealth Economics Lecture OnesmartisaacNo ratings yet
- JK Institute of Technology and Management: Managerial Economics AssignmentDocument12 pagesJK Institute of Technology and Management: Managerial Economics AssignmentVineet GanviNo ratings yet
- MAEcono Pol 1Document29 pagesMAEcono Pol 1Edimarf SatumboNo ratings yet
- Economics Notes - Introduction To EconomicsDocument16 pagesEconomics Notes - Introduction To Economicskkesarwani727No ratings yet
- Public FinanceDocument38 pagesPublic FinanceAl MahmudNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - Fiscal Policymaking FinalDocument53 pagesGroup 2 - Fiscal Policymaking FinalIVY CAPITONo ratings yet
- Macro Economics 10 YearsDocument97 pagesMacro Economics 10 YearsManish Jha 2086No ratings yet
- Chap 3Document26 pagesChap 3Jawad ArkoNo ratings yet
- Development Problem 1 (ch3)Document49 pagesDevelopment Problem 1 (ch3)AbelNo ratings yet
- MACROECONOMICSDocument35 pagesMACROECONOMICSSumedha ZopeNo ratings yet
- Macro - Consumption & InvestmentDocument77 pagesMacro - Consumption & InvestmentannsaralondeNo ratings yet
- Economic Challenges Facing Contemoprary BusinessesDocument24 pagesEconomic Challenges Facing Contemoprary BusinessesMHPNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 ACCA F1Document13 pagesChapter 19 ACCA F1sikshaNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Government InterventionDocument19 pages1.3 Government InterventionSilver ChenNo ratings yet
- BE 3 Unit RecentDocument49 pagesBE 3 Unit RecentHasrat AliNo ratings yet
- Section 4Document9 pagesSection 4samNo ratings yet
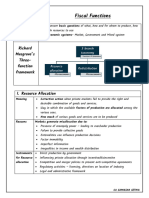
- Fiscal FunctionsDocument2 pagesFiscal FunctionsfarahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 - Overview of Macroeconomics: Macroeconomics Is The Study of The Behavior of The Economy As A WholeDocument30 pagesChapter 20 - Overview of Macroeconomics: Macroeconomics Is The Study of The Behavior of The Economy As A WholeAngelo RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 2 CSHYle 9 CXP Qen DWDocument17 pages2 CSHYle 9 CXP Qen DWFarhan AlamNo ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument129 pagesNational IncomeBabli PattanaikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 ECONDocument9 pagesChapter 1 ECONMelody ViernesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Macroenomics: WWW - Debrina.lecture - Ub.ac - IdDocument23 pagesIntroduction To Macroenomics: WWW - Debrina.lecture - Ub.ac - IdNicko Nur RakhmaddianNo ratings yet
- Economics Exam RevisionDocument50 pagesEconomics Exam Revisiondfsgvfffgbfdgwsgewt43t64hNo ratings yet
- ECONOMICS Assesment Outcome 3Document10 pagesECONOMICS Assesment Outcome 3ManjaleeNo ratings yet
- Performance of The Australian EconomyDocument25 pagesPerformance of The Australian EconomyAnisha ImamNo ratings yet
- MODULE 3 - Chapter 6 (Trade Protectionism) PDFDocument7 pagesMODULE 3 - Chapter 6 (Trade Protectionism) PDFAangela Del Rosario CorpuzNo ratings yet
- 5.1-Government Economic PolicyDocument4 pages5.1-Government Economic PolicyMahnoor ArshadNo ratings yet
- Applied EconomicDocument77 pagesApplied EconomicLykaNo ratings yet
- Public Finance (MA in Economics)Document139 pagesPublic Finance (MA in Economics)Karim Virani91% (11)
- 02 Ch2 Public Finance - Practice SheetDocument17 pages02 Ch2 Public Finance - Practice SheetDhruvi VachhaniNo ratings yet
- Understanding Wealth Distribution, Public Deficits, The Spanish Job Market, and Total Factor ProductionDocument7 pagesUnderstanding Wealth Distribution, Public Deficits, The Spanish Job Market, and Total Factor ProductionJuan GallegoNo ratings yet
- F1-04 The Macro-Economic EnvironmentDocument26 pagesF1-04 The Macro-Economic EnvironmentAsghar AliNo ratings yet
- Global Wealth Inequality ANSWERSDocument28 pagesGlobal Wealth Inequality ANSWERSNivi MiNo ratings yet
- Government Intervention in MarketsDocument48 pagesGovernment Intervention in MarketsSoha MalikNo ratings yet
- Be Unit 2 Part IDocument9 pagesBe Unit 2 Part Isai prabashNo ratings yet
- Monetary and Fiscal ReportDocument14 pagesMonetary and Fiscal ReportShoaib AbbasNo ratings yet
- Kamor Ul Islam Jakoan Kobir Riad Omar Faruk Iqramul Hasan MD Abdur Rahman MD Kamrul Hasan FahimDocument16 pagesKamor Ul Islam Jakoan Kobir Riad Omar Faruk Iqramul Hasan MD Abdur Rahman MD Kamrul Hasan FahimRezoan FarhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1-Eco-101Document16 pagesChapter-1-Eco-101Rezoan FarhanNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting (Theory of Constraint)Document5 pagesCost Accounting (Theory of Constraint)Rezoan FarhanNo ratings yet
- Internship Report On Constructing Optimal Portfolio and Efficient Frontier PDFDocument55 pagesInternship Report On Constructing Optimal Portfolio and Efficient Frontier PDFRezoan Farhan0% (1)
- Housing, Real Estate Sector in Bangladesh Present Status and Policies ImplicationsDocument16 pagesHousing, Real Estate Sector in Bangladesh Present Status and Policies ImplicationsRezoan FarhanNo ratings yet
- Brief For The Grand Finale: Business Case Competition 2017Document2 pagesBrief For The Grand Finale: Business Case Competition 2017Rezoan FarhanNo ratings yet
- Comparative Methods Act and Fallacy of Dhaka Stock Exchange: Valuation: FDocument11 pagesComparative Methods Act and Fallacy of Dhaka Stock Exchange: Valuation: FRezoan FarhanNo ratings yet
- Answer To The Question NO: 01Document2 pagesAnswer To The Question NO: 01Rezoan FarhanNo ratings yet
- Jakoan Kobir Riad: ObjectiveDocument3 pagesJakoan Kobir Riad: ObjectiveRezoan FarhanNo ratings yet
- FashionwareDocument1 pageFashionwareRezoan FarhanNo ratings yet
- Gropup List of Money and Banking PresentationDocument3 pagesGropup List of Money and Banking PresentationRezoan FarhanNo ratings yet
- Jakoan Kobir Riad: ObjectiveDocument3 pagesJakoan Kobir Riad: ObjectiveRezoan FarhanNo ratings yet
- "An Assignment For The MID TERM Exam ": Bangladesh StudiesDocument8 pages"An Assignment For The MID TERM Exam ": Bangladesh StudiesRezoan FarhanNo ratings yet
- Question 1 Marketing Management Is The Demand Management - A Logical DiscussionDocument7 pagesQuestion 1 Marketing Management Is The Demand Management - A Logical DiscussionRezoan FarhanNo ratings yet
- The World of Ecommerce Has Come A Long Way The Past Couple of YearsDocument3 pagesThe World of Ecommerce Has Come A Long Way The Past Couple of YearsRezoan FarhanNo ratings yet
- Question 3: The Battle of Pallashy Has Unlimited Importance in The Politics of Bengal Even in The Whole Subcontinent - Justify The StatementDocument2 pagesQuestion 3: The Battle of Pallashy Has Unlimited Importance in The Politics of Bengal Even in The Whole Subcontinent - Justify The StatementRezoan FarhanNo ratings yet
- Delta Brac Housing Profitability AnalysisDocument22 pagesDelta Brac Housing Profitability AnalysisRezoan FarhanNo ratings yet
- "An Assignment For The MID TERM Exam": Introduction To SociologyDocument10 pages"An Assignment For The MID TERM Exam": Introduction To SociologyRezoan FarhanNo ratings yet
- Constructing Portfolio and Efficient FrontierDocument40 pagesConstructing Portfolio and Efficient FrontierRezoan FarhanNo ratings yet
- Positioning StrategyDocument1 pagePositioning StrategyRezoan FarhanNo ratings yet
- Test 1 DERIVATIVES & INTEREST RATE RISK MANAGEMENTDocument6 pagesTest 1 DERIVATIVES & INTEREST RATE RISK MANAGEMENTprakhar rawatNo ratings yet
- Notes Margin of Safety 2008, 2013, 2014Document7 pagesNotes Margin of Safety 2008, 2013, 2014Aaron ForbesNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 13 The Strategy of International BusinessDocument6 pagesCHAPTER 13 The Strategy of International Businessmasfiq HossainNo ratings yet
- GROWTH FACTOR MCQ'sDocument12 pagesGROWTH FACTOR MCQ'sKumari SnehNo ratings yet
- Lec 1-Agricultural Marketing-Definition ScopeDocument17 pagesLec 1-Agricultural Marketing-Definition ScopeLav VickyNo ratings yet
- Goods and ServicesDocument4 pagesGoods and ServicesValentin StancuNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1Document7 pagesQuiz 1MaiXuanPhamNo ratings yet
- News Vendor Model SummaryDocument7 pagesNews Vendor Model Summaryivar120No ratings yet
- BR PPT 2Document11 pagesBR PPT 2Vipul RawatNo ratings yet
- Tanishq Case StudyDocument2 pagesTanishq Case StudyHutanshuNo ratings yet
- Ch4 - Consumer Behaviour and Individual DemandDocument6 pagesCh4 - Consumer Behaviour and Individual DemandNabh GargNo ratings yet
- Module Wise Important Questions and AnswersDocument31 pagesModule Wise Important Questions and AnswersViraja GuruNo ratings yet
- B2B MarketingDocument33 pagesB2B MarketingJawad ArshedNo ratings yet
- 2017-JAIBB PBE NovDocument2 pages2017-JAIBB PBE Novfarhadcse30No ratings yet
- Marketing JAIIBDocument23 pagesMarketing JAIIBamar dihingia100% (1)
- Cambridge O Level: Economics 2281/12Document12 pagesCambridge O Level: Economics 2281/12Zoya RashdiNo ratings yet
- Free-Business English - English Marketing and Sales VocabularyDocument3 pagesFree-Business English - English Marketing and Sales VocabularyMF NNo ratings yet
- MGT603 Final Term Paper 2009 Solved by Vuzs Team With Ref 7Document15 pagesMGT603 Final Term Paper 2009 Solved by Vuzs Team With Ref 7Fan CageNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Science Lesson Note For JSS3 (Basic 9) Second TermDocument8 pagesAgricultural Science Lesson Note For JSS3 (Basic 9) Second TermNurain KhalilullahNo ratings yet
- Ecoe312 - Uodl - Toets 4. Vakinhoud. 27 April 2024Document11 pagesEcoe312 - Uodl - Toets 4. Vakinhoud. 27 April 2024thandimnguni72No ratings yet
- Med Net CaseDocument3 pagesMed Net CaseVineet Bajaj100% (1)
- Retail Planning - Burger Shack: Situation AnalysisDocument2 pagesRetail Planning - Burger Shack: Situation Analysisaq GreaterNo ratings yet
- Sqqm1023 Managerial Mathematics Assignment 1 SESSION 2013/2014 SEMESTER 1Document4 pagesSqqm1023 Managerial Mathematics Assignment 1 SESSION 2013/2014 SEMESTER 1Michelle Xin YanNo ratings yet
- Materi 5: Tipe-Tipe Strategi: SIFO03203 - Manajemen StrategisDocument24 pagesMateri 5: Tipe-Tipe Strategi: SIFO03203 - Manajemen StrategisTimothy DouglasNo ratings yet
- PHME311 - Week 2 - Day 2 - Module 5 Product Mix, Decision and StrategiesDocument61 pagesPHME311 - Week 2 - Day 2 - Module 5 Product Mix, Decision and StrategiesJanella GarciaNo ratings yet
- EC345 2022 - 23 Week 10 Welfare and PolicyDocument60 pagesEC345 2022 - 23 Week 10 Welfare and Policyfilipa barbosaNo ratings yet
- Product Line and Product Mix DecisionsDocument3 pagesProduct Line and Product Mix DecisionsM.n.SaiNadhNo ratings yet
- BS Project Synopsis For SaltDocument4 pagesBS Project Synopsis For SaltManav NagpalNo ratings yet
- Basics of Retail MerchandisingDocument38 pagesBasics of Retail MerchandisingRishabh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Batara Markets and WelfareDocument7 pagesBatara Markets and WelfareBriel BataraNo ratings yet