0% found this document useful (0 votes)
964 views12 pagesCell Biology: Verma and Agrawal Kotpal Rastogi
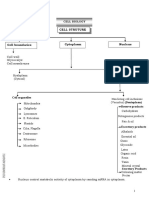
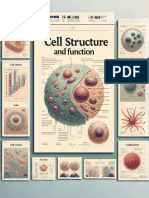
The document describes the basic structures and components of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells like bacteria have a cell wall and membrane, cytoplasm, ribosomes, and a nucleoid region containing DNA. Eukaryotic cells contain a nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplasts, Golgi bodies, endoplasmic reticulum, and other membrane-bound organelles that perform specialized functions. The document provides an overview of the key structural differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Uploaded by
Sabina MaharjanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
964 views12 pagesCell Biology: Verma and Agrawal Kotpal Rastogi
The document describes the basic structures and components of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells like bacteria have a cell wall and membrane, cytoplasm, ribosomes, and a nucleoid region containing DNA. Eukaryotic cells contain a nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplasts, Golgi bodies, endoplasmic reticulum, and other membrane-bound organelles that perform specialized functions. The document provides an overview of the key structural differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Uploaded by
Sabina MaharjanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd