0% found this document useful (0 votes)
104 views28 pagesOverview of Bio-Sensors and Applications
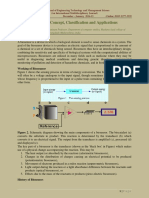
A biosensor is a device that uses biological components like enzymes or antibodies to detect analytes. It consists of a biological recognition element and a transducer. The biological element interacts with the target analyte and the transducer converts this interaction into a measurable electrical signal. Common examples are glucose biosensors and pregnancy tests. Electrochemical, optical, thermal and resonant techniques are used for detection. Biosensors have applications in medical diagnosis, food analysis, environmental monitoring and more.
Uploaded by
Dream BoyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
104 views28 pagesOverview of Bio-Sensors and Applications
A biosensor is a device that uses biological components like enzymes or antibodies to detect analytes. It consists of a biological recognition element and a transducer. The biological element interacts with the target analyte and the transducer converts this interaction into a measurable electrical signal. Common examples are glucose biosensors and pregnancy tests. Electrochemical, optical, thermal and resonant techniques are used for detection. Biosensors have applications in medical diagnosis, food analysis, environmental monitoring and more.
Uploaded by
Dream BoyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd