0% found this document useful (0 votes)
68 views28 pagesJava Programming Basics: Data Types & Ops
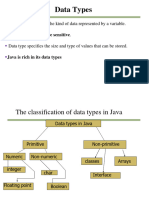
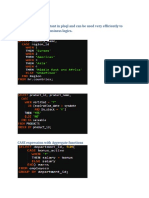
The document provides an overview of primitive data types in Java including integer, floating point, boolean, and character types. It discusses variable declaration and literals. Arithmetic operators for basic math operations are also covered. Examples are provided for each data type and operators to demonstrate their usage.
Uploaded by
Judith NelsonCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
68 views28 pagesJava Programming Basics: Data Types & Ops
The document provides an overview of primitive data types in Java including integer, floating point, boolean, and character types. It discusses variable declaration and literals. Arithmetic operators for basic math operations are also covered. Examples are provided for each data type and operators to demonstrate their usage.
Uploaded by
Judith NelsonCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd