Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Graduate Symposium Poster-1
Graduate Symposium Poster-1
Uploaded by
api-5299546550 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views1 pageOriginal Title
graduate symposium poster-1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views1 pageGraduate Symposium Poster-1
Graduate Symposium Poster-1
Uploaded by
api-529954655Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
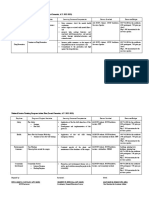
Effective Behavioral Interventions for Elementary School Aged Children
Stacy E. Rodgers
University of North Carolina at Pembroke
Introduction Check-In/Check Out
In an elementary school environment, having effective behavioral • Implemented as a Tier 2 intervention.
interventions in place is essential. Teachers often report that • Administered over an 8 week period.
disruptive behaviors take a significant amount of time away from • Cost-effective, efficient, readily available, and take minimal
instructional time. Teachers report that classroom management is time daily.
often the most challenging aspect of their job and is one in which • Student will Check-In and Check Out with a staff member each
they have the least amount of training. School counselors are day to report how their day was and to see if they met their
often asked to provide assistance and offer strategies to teachers goals for the day.
that help decrease the disruptive behaviors. Many of these • When this program is followed to fidelity there is statistically
strategies are variations of PBIS (Positive Behavioral Interventions significant reductions on office referrals for the targeted
and Support). behaviors.
(Kokkinos, Panayiotou, & Davazoglou, 2005)
What is P.B.I.S.?
Color Wheel System Social Emotional Learning
• Structured system for addressing behavior through the • Can be used as a Tier 1 intervention for a whole class or as a
prevention-oriented structuring of research-based • Social Emotional Learning (SEL) is delivered through a
Tier 2 intervention targeting an individual students behavior.
interventions and supports. curriculum by classroom teachers.
• Three sets of rules, represented by a different colors.
• Hierarchical and progressive manner for the purpose of • SEL is the process through which children understand and
• Green = Children may leave seats and move about room.
improved behavioral and academic outcomes. manage emotions, set and achieve positive goals, feel and
• Yellow = Used to reduce distractions during work time.
• PBIS is an initialism most well known to those working in Examples include raising hand and looking at teacher when
show empathy for others, establish and maintain positive
schools and similar settings and comes from the federal relationships, and make responsible decisions.
speaking.
Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA). • Reinforces behavior expectations, similar to PBIS.
• Red = Used to gain student attention so instructions can be
• In practice, this generally appears as 3 tiers of increasingly • Meta-analysis of 213 school-based SEL programs, participants
given. Examples include returning to seat, not talking when
intensive and individualized behavior interventions and demonstrated significantly improved social and emotional
teacher is talking.
supports as well as a system of data collection and analysis. skills, attitudes, and behavior, as well as an 11-percentile-point
• Teachers report, when properly trained, this intervention is
(Sadler & Sugai, 2009) gain in academic performance.
easy to apply consistently and is effective in decreasing
• Children who are socially and emotionally competent have
distracting behaviors.
more connections with positive peers, and are less likely to be
P.B.I.S Tiers rejected, isolated, or bullied.
• Tier 1 - Behavioral strategies that all students have access to. (Sadler & Sugai, 2009)
These interventions set the foundation for behavior in the
References
classroom. Without them, teachers will not be prepared to
incentivize positive behavior or respond to negative behavior. Childs, K.E., Kincaid, D., George , H.P. , & Gage, N.A. (2016). The relationship
• Tier 2 – For students who need more specific behavioral between school-wide implementation of Positive Behavior Intervention and
supports to succeed. Tier II interventions apply to a small Supports and students discipline outcomes. Journal of Positive Behavior
Interventions, 18(2), 99.
group or students. Kokkinos, C.M., Panayiotou, G., & Davazoglou, A.M. (2005). Correlates of
• Tier 3 - If a student is in need of Tier III behavioral supports this teacher appraisals of student behaviors. Psychology in the Schools, 42, 79-89.
is usually decided in a Response to Intervention or Individual Reineke, W.M., Stormont, M., Herman, K.C., Puri, R., & Goel, N. (2011).
Education Plan meeting focused on the student’s behavior. This Supporting children’s mental health in schools: Teacher perception of needs,
meeting should include the parent, teachers and relevant roles, and barriers. School Psychology Quarterly, 26, 1-13.
Sadler, C., & Sugai, G. (2009). Effective behavior and instructional support: A
service providers. Tier III behavioral supports require
district model for early identification and prevention of reading and behavior
intentionality. problems. Journal of Positive Behavior Interventions, 11, 35-46.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5813)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Basic Personality InventoryDocument8 pagesBasic Personality InventoryElisa Mae Oranza Gura100% (2)
- 2002 - The Measurement of Burnout and Engagement A Confirmatory Factor Analytic ApproachDocument24 pages2002 - The Measurement of Burnout and Engagement A Confirmatory Factor Analytic ApproachfordleeNo ratings yet
- GOC Neet Key NotesDocument40 pagesGOC Neet Key Notesiampriyatiwarii890No ratings yet
- EMI EMC Reduction TechniquesDocument24 pagesEMI EMC Reduction TechniquesEquipmentDesignNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Branches of Biology Lesson PlanDocument18 pages1.3 Branches of Biology Lesson PlanKamela100% (1)
- Financial Ratios Analysis of NestleDocument18 pagesFinancial Ratios Analysis of NestleNur WahidaNo ratings yet
- Omnova Coatings PresentationDocument12 pagesOmnova Coatings PresentationNatalia Rodriguez100% (1)
- RCW 360plusDocument1 pageRCW 360plusHaman EdilbertoNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of A Trauma Care BundleDocument7 pagesDesign and Implementation of A Trauma Care BundleNi Nyoman AstriningsihNo ratings yet
- High Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen Therapy in Long Hauler Covid-19 PatientsDocument7 pagesHigh Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen Therapy in Long Hauler Covid-19 PatientsFefiEkaWNo ratings yet
- Soudure Plastique Ultra Son PDFDocument30 pagesSoudure Plastique Ultra Son PDFamr_akram_2No ratings yet
- Investment Analysis Icmss 2013Document20 pagesInvestment Analysis Icmss 2013Panzi Aulia RahmanNo ratings yet
- Tarea 4Document6 pagesTarea 4Bladimir SánchezNo ratings yet
- Hard Gainer - Issue 61 - July 1999Document50 pagesHard Gainer - Issue 61 - July 1999api-3701884100% (7)
- Salaries & Wages - Regular Payroll PERA . Due To BIRDocument7 pagesSalaries & Wages - Regular Payroll PERA . Due To BIRAyie RomeroNo ratings yet
- Descriptions: PEG-4000 Is A Water-Soluble, Waxy Solid That Is Used Extensively in The Several Industries Such AsDocument1 pageDescriptions: PEG-4000 Is A Water-Soluble, Waxy Solid That Is Used Extensively in The Several Industries Such AsKeremNo ratings yet
- Sungai Merab PDFDocument1 pageSungai Merab PDFKiey WanNo ratings yet
- NSTP Action Plan-1Document2 pagesNSTP Action Plan-1Jee En BeeNo ratings yet
- Peterson Content Worth Having: ContentsDocument8 pagesPeterson Content Worth Having: ContentsMuhammet Fatih CantepeNo ratings yet
- FLS ValveDocument2 pagesFLS Valvegamalyehia13100% (1)
- OncologyDocument67 pagesOncologyCarlos HernándezNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Cholesteryl Ester Liquid CrystalsDocument11 pagesPreparation of Cholesteryl Ester Liquid Crystalsuttamkumar_mondol_5No ratings yet
- Flood of E-Waste: Computer Salvagers at Agbogbloshie  in Accra, GhanaDocument3 pagesFlood of E-Waste: Computer Salvagers at Agbogbloshie  in Accra, GhanaKrisNo ratings yet
- Training Oilfield Production Chemicals 20 - 23 J - 220614 - 111151Document3 pagesTraining Oilfield Production Chemicals 20 - 23 J - 220614 - 111151Lusia PratiwiNo ratings yet
- A) Extraoral Examination:: - FrontalDocument2 pagesA) Extraoral Examination:: - FrontalAnastasia .MoysoglouNo ratings yet
- Sample Size CalculationDocument2 pagesSample Size CalculationAljon AgustinNo ratings yet
- Wildlife Fact File - Mammals - Pgs. 251-260Document20 pagesWildlife Fact File - Mammals - Pgs. 251-260ClearMind84100% (3)
- Review of Related LiteratureDocument2 pagesReview of Related LiteratureDarren Ahito BernasNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometric CalculationDocument18 pagesStoichiometric CalculationSameer AhmedNo ratings yet
- Lenigrad 4 Light Meter PDFDocument9 pagesLenigrad 4 Light Meter PDFRaghul HitmanNo ratings yet