0% found this document useful (0 votes)
790 views2 pagesThe Sandmeyer Reaction: Replacement of The Diazonium Group by CL, BR, or CN
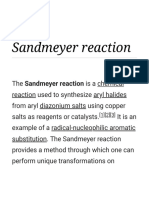
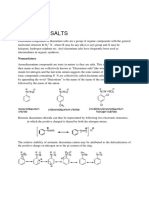
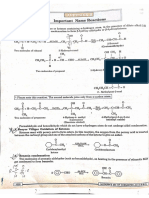
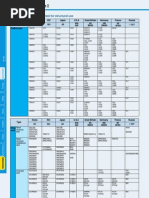
The Sandmeyer Reaction involves replacing the diazonium group of arenediazonium salts with halides (Cl, Br, CN) or other groups. Specific examples show o-toluidine reacted with copper chloride to form o-chlorotoluene. m-Chloroaniline reacted with copper bromide to form m-bromochlorobenzene. o-Nitroaniline reacted with copper cyanide to form o-nitrobenzonitrile. p-Nitroaniline reacted with potassium iodide to form p-iodonitrobenzene. m-Toluidine reacted with fluoroboric acid and heat to form m-fluorotoluene
Uploaded by
Usman GhaniCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
790 views2 pagesThe Sandmeyer Reaction: Replacement of The Diazonium Group by CL, BR, or CN
The Sandmeyer Reaction involves replacing the diazonium group of arenediazonium salts with halides (Cl, Br, CN) or other groups. Specific examples show o-toluidine reacted with copper chloride to form o-chlorotoluene. m-Chloroaniline reacted with copper bromide to form m-bromochlorobenzene. o-Nitroaniline reacted with copper cyanide to form o-nitrobenzonitrile. p-Nitroaniline reacted with potassium iodide to form p-iodonitrobenzene. m-Toluidine reacted with fluoroboric acid and heat to form m-fluorotoluene
Uploaded by
Usman GhaniCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd