0% found this document useful (0 votes)
597 views22 pagesSingle Photon Emission Tomography Overview
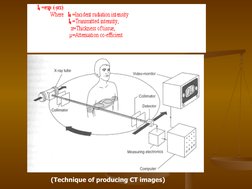
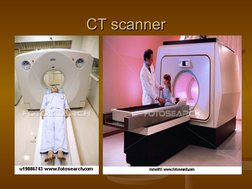
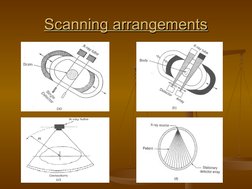
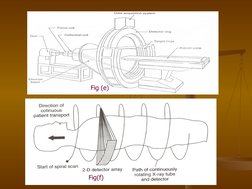
Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) uses gamma rays and a computer to create 3D images of functional processes in the body. It involves injecting a small amount of radioactive tracer into the body and using gamma camera detectors to take images from different angles to be processed by a computer to generate cross-sectional images. SPECT provides molecular level information about physiological processes like tissue perfusion, metabolism and receptor binding. It has advantages over other imaging techniques as it can image bone and soft tissues simultaneously while being less sensitive to movement, and has various medical applications.
Uploaded by
Manju KiranCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
597 views22 pagesSingle Photon Emission Tomography Overview
Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) uses gamma rays and a computer to create 3D images of functional processes in the body. It involves injecting a small amount of radioactive tracer into the body and using gamma camera detectors to take images from different angles to be processed by a computer to generate cross-sectional images. SPECT provides molecular level information about physiological processes like tissue perfusion, metabolism and receptor binding. It has advantages over other imaging techniques as it can image bone and soft tissues simultaneously while being less sensitive to movement, and has various medical applications.
Uploaded by
Manju KiranCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography
- Contents
- Introduction
- Basic Principle
- System Components
- Advantages
- Disadvantages
- Typical Scan Doses
- Conclusion
- References