0% found this document useful (0 votes)
135 views29 pagesNew Product Development Strategies
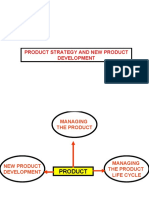
The document discusses new product development, including defining new products and classifying them. It also covers understanding a product's life cycle, which involves distinct stages from idea generation through commercialization. New product development processes at leading companies like Toshiba, Sony, Applied Materials, and Intel are then reviewed. These processes typically involve concurrent research, development, design, testing, and production stages with feedback loops.
Uploaded by
duff_808Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
135 views29 pagesNew Product Development Strategies
The document discusses new product development, including defining new products and classifying them. It also covers understanding a product's life cycle, which involves distinct stages from idea generation through commercialization. New product development processes at leading companies like Toshiba, Sony, Applied Materials, and Intel are then reviewed. These processes typically involve concurrent research, development, design, testing, and production stages with feedback loops.
Uploaded by
duff_808Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd