Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 6 Receivables - Additional Concepts
Chapter 6 Receivables - Additional Concepts
Uploaded by
Ana Leah DelfinCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 6 Receivables - Additional Concepts
Chapter 6 Receivables - Additional Concepts
Uploaded by
Ana Leah DelfinCopyright:
Available Formats
(Intermediate Accounting 1A)
LECTURE AID
2019
ZEUS VERNON B. MILLAN
Chapter 6 RECEIVABLES –
ADDITIONAL CONCEPTS
Learning Objectives
• Explain the accounting for origination
costs and fees.
• Account for the impairment of
receivables.
• Identify the instances where
derecognition of receivable is
appropriate.
INTERMEDIATE ACCTG 1A (by:
MILLAN)
Loans receivable
• Receivables are initially recognized at fair value plus
transaction costs.
Direct origination costs are added to the carrying
amount of a loan receivable. Indirect origination costs
are expensed when incurred.
Origination fees are deducted from the carrying
amount of a loan receivable.
INTERMEDIATE ACCTG 1A (by:
MILLAN)
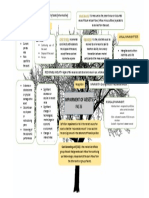
Impairment
• The expected credit loss model (ECL)
INTERMEDIATE ACCTG 1A (by:
MILLAN)
General approach
INTERMEDIATE ACCTG 1A (by:
MILLAN)
Definition of terms
• Loss allowance – is the allowance for expected credit losses on financial assets
that are within the scope of the impairment requirements of PFRS 9.
• Expected credit losses – is the weighted average of credit losses with the
respective risks of a default occurring as the weights.
• Credit loss – is the difference between all contractual cash flows that are due to
an entity in accordance with the contract and all the cash flows that the entity
expects to receive (i.e., all cash shortfalls), discounted at the original effective
interest rate (or credit-adjusted effective interest rate for purchased or originated
credit-impaired financial assets).
INTERMEDIATE ACCTG 1A (by:
MILLAN)
Definition of terms
• 12-month expected credit losses – The portion of lifetime expected
credit losses that represent the expected credit losses that result from
default events on a financial instrument that are possible within the 12
months after the reporting date.
• Credit risk – The risk that one party to a financial instrument will cause
a financial loss for the other party by failing to discharge an obligation.
• Lifetime expected credit losses – The expected credit losses that
result from all possible default events over the expected life of a financial
instrument.
INTERMEDIATE ACCTG 1A (by:
MILLAN)
Simplified approach
• An entity shall always measure the loss allowance at amount
equal to lifetime expected credit losses for its trade receivables or
contract assets that do not contain a significant financing
component.
• Examples: Provision matrix and Single loss rate
INTERMEDIATE ACCTG 1A (by:
MILLAN)
Derecognition of receivables
• Financial assets are derecognized when:
a) the contractual rights to the cash flows from the financial asset
expire; or
b) the financial assets are transferred and the transfer qualifies for
derecognition.
• Derecognition (of a financial instrument) means the removal of a
previously recognized financial asset or financial liability from an
entity’s statement of financial position.
INTERMEDIATE ACCTG 1A (by:
MILLAN)
Evaluation of transfers of receivables
• If control over the receivable is:
a) Substantially transferred, the receivable is derecognized.
b) Substantially retained, the receivable is not derecognized but continued
to be recognized. Any cash received from the transfer is recognized as
liability.
c) Partially transferred and partially retained, the portion transferred is
derecognized while the portion retained is continued to be recognized.
INTERMEDIATE ACCTG 1A (by:
MILLAN)
Offsetting of financial assets and financial
liabilities
• A financial asset and a financial liability shall be offset and the net
amount presented in the statement of financial position only when
both of the following conditions are met:
a. The entity currently has a legally enforceable right to set off the
recognized amounts; and
b. The entity intends either to settle on a net basis, or to realize the
asset and settle the liability simultaneously.
INTERMEDIATE ACCTG 1A (by:
MILLAN)
Receivable financing
1. Pledge (hypothecation)
2. Assignment
a. Notification basis
b. Non-notification basis
3. Factoring
4. Discounting of notes receivable
NP = MV – D
MV = P + i
D = MV x Dr x Dp
Dr = Discount rate
Dp = Discount period (the unexpired term of the note)
Interest income = interest accrued on the expired term of the note
INTERMEDIATE ACCTG 1A (by:
MILLAN)
APPLICATION OF CONCEPTS
PROBLEM 2: FOR CLASSROOM DISCUSSION
INTERMEDIATE ACCTG 1A (by: MILLAN)
OPEN FORUM
QUESTIONS????
REACTIONS!!!!!
INTERMEDIATE ACCTG 1A (by: MILLAN)
END
INTERMEDIATE ACCTG 1A (by: MILLAN)
You might also like
- Stephen Elias, Bethany K. Laurence - Bankruptcy For Small Business Owners - How To File For Chapter 7-Nolo (2010)Document612 pagesStephen Elias, Bethany K. Laurence - Bankruptcy For Small Business Owners - How To File For Chapter 7-Nolo (2010)anassNo ratings yet
- VALIX - IA 1 (2020 Ver.) Government GrantDocument9 pagesVALIX - IA 1 (2020 Ver.) Government GrantAriean Joy DequiñaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 Borrowing CostsDocument22 pagesChapter 19 Borrowing Costsmariel evangelistaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 Intangible AssetsDocument27 pagesChapter 21 Intangible Assetsshelou_domantayNo ratings yet
- PFRS 5Document28 pagesPFRS 5Erica AbegoniaNo ratings yet
- Securities Analysis and Portfolio Management PDFDocument64 pagesSecurities Analysis and Portfolio Management PDFShreya s shetty100% (1)
- Accounts ReceivableDocument34 pagesAccounts ReceivableRose Aubrey A Cordova100% (1)
- Bosses Build Business Credit 2022 Edition 2Document13 pagesBosses Build Business Credit 2022 Edition 2Philip JenyoNo ratings yet
- La Salle University College of Business and Accountancy Integrated Enhancement Course For Accountancy Multiple ChoiceDocument3 pagesLa Salle University College of Business and Accountancy Integrated Enhancement Course For Accountancy Multiple ChoiceChristal Jam LaureNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Current LiabilitiesDocument17 pagesChapter 1 - Current LiabilitiesCaladhiel100% (1)
- IA 1 Valix 2020 Ver. Accounts ReceivableDocument8 pagesIA 1 Valix 2020 Ver. Accounts ReceivableAriean Joy DequiñaNo ratings yet
- Pas 36 - Impairment of AssetsDocument20 pagesPas 36 - Impairment of AssetsCyril Grace Alburo BoocNo ratings yet
- Long Quiz in Intermediate Accounting 1 PART 1aDocument4 pagesLong Quiz in Intermediate Accounting 1 PART 1aGillian mae Garcia0% (2)
- Financial Asset at Amortized CostDocument14 pagesFinancial Asset at Amortized CostLorenzo Diaz DipadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 - Financial Asset at Amortized Cost PDFDocument21 pagesChapter 19 - Financial Asset at Amortized Cost PDFTurksNo ratings yet
- Investments in Debt and Equity SecuritiesDocument41 pagesInvestments in Debt and Equity SecuritiesMonica Monica0% (1)
- Chapter 9 InvestmentsDocument21 pagesChapter 9 InvestmentsAna Leah Delfin100% (1)
- 2019 Wiley FRM Part II Study Guide SampleDocument40 pages2019 Wiley FRM Part II Study Guide SampleWalter ArceNo ratings yet
- (Intermediate Accounting 1A) : Lecture AidDocument25 pages(Intermediate Accounting 1A) : Lecture AidShe RC100% (2)
- Chapter 21 - Reclassification of Financial Asset PDFDocument9 pagesChapter 21 - Reclassification of Financial Asset PDFTurksNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Current LiabilitiesDocument15 pagesChapter 1-Current LiabilitiesMonique AlarcaNo ratings yet
- Notes Payable: Intermediate Accounting 2Document13 pagesNotes Payable: Intermediate Accounting 2Rolando Verano TanNo ratings yet
- PA1 M 1404 InventoriesDocument30 pagesPA1 M 1404 InventoriesShaina Santiago Alejo100% (1)
- Chapter 19 Borrowing CostsDocument17 pagesChapter 19 Borrowing CostsjuennaguecoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Shareholders' Equity Part 2Document20 pagesChapter 11 - Shareholders' Equity Part 2Camille GarciaNo ratings yet
- Government Grants: Use The Following Information For The Next Three QuestionsDocument2 pagesGovernment Grants: Use The Following Information For The Next Three QuestionsJEFFERSON CUTENo ratings yet
- QUIZ - CHAPTER 16 - PPE PART 2 - 2020edDocument5 pagesQUIZ - CHAPTER 16 - PPE PART 2 - 2020edjanna napiliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Investments - Additional ConceptsDocument15 pagesChapter 11 Investments - Additional ConceptsAna Leah Delfin100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Accounts ReceivableDocument13 pagesChapter 4 Accounts ReceivableAna Leah DelfinNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Framework and Acctg Standards 1.9: SolutionDocument4 pagesConceptual Framework and Acctg Standards 1.9: SolutionKrissa Mae LongosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Inventory EstimationDocument13 pagesChapter 8 Inventory EstimationAna Leah DelfinNo ratings yet
- Loans and Receivables Sample ProblemsDocument2 pagesLoans and Receivables Sample ProblemsNimrod Sobremisana Adaptar100% (1)
- Far 09 Government GrantsDocument9 pagesFar 09 Government GrantsJoshua UmaliNo ratings yet
- Activity 03 Depletion Exploration and Evaluation Asset Ramirezlawrenz 1 - CompressDocument5 pagesActivity 03 Depletion Exploration and Evaluation Asset Ramirezlawrenz 1 - CompressDanna VargasNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Loans and ReceivablesDocument55 pagesModule 4 Loans and Receivableschuchu tvNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 - Retail Inventory Method PDFDocument9 pagesChapter 14 - Retail Inventory Method PDFTurksNo ratings yet
- BBA Final Year 6th Sem Project Report.Document53 pagesBBA Final Year 6th Sem Project Report.Mamidishetty Manasa67% (3)
- QUIZ - PPE PART 1 Answer KeyDocument4 pagesQUIZ - PPE PART 1 Answer KeyRena Rose MalunesNo ratings yet
- Notes ReceiDocument2 pagesNotes ReceiDIANE EDRANo ratings yet
- Pfrs 5 NotesDocument18 pagesPfrs 5 NotesMartha Nicole MaristelaNo ratings yet
- Aud Application 2 - Handout 8 Intangible (UST)Document4 pagesAud Application 2 - Handout 8 Intangible (UST)RNo ratings yet
- Sol. Man. - Chapter 11 - Investments - Additional ConceptsDocument10 pagesSol. Man. - Chapter 11 - Investments - Additional ConceptsChristian James RiveraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 InventoriesDocument25 pagesChapter 7 InventoriesAna Leah DelfinNo ratings yet
- Intacc 1a Reviewer Conceptual Framework and Accounting StandardsDocument32 pagesIntacc 1a Reviewer Conceptual Framework and Accounting StandardsKatherine Cabading InocandoNo ratings yet
- Notes ReceivableDocument16 pagesNotes Receivabledenice.dimantagaNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Accounting 1 Solution Manual: Chapter 15 - Property, Plant and Equipment To Chapter 17 - Depletion of Mineral ResourcesDocument20 pagesIntermediate Accounting 1 Solution Manual: Chapter 15 - Property, Plant and Equipment To Chapter 17 - Depletion of Mineral ResourcesMckenzieNo ratings yet
- Financial Asset at Amortized CostDocument18 pagesFinancial Asset at Amortized CostJay-L Tan100% (1)
- Ia Chapter 4 Valix 2019Document5 pagesIa Chapter 4 Valix 2019M100% (1)
- PAS 36 Concept MapDocument1 pagePAS 36 Concept MapMicah RamaykaNo ratings yet
- 1 LiabilitiesDocument39 pages1 LiabilitiesDiana Faith TaycoNo ratings yet
- Activity - Chapter 6 - Statement of Cash FlowsDocument4 pagesActivity - Chapter 6 - Statement of Cash FlowsKaren RiraoNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was Shared Via: Solution 23-2 Answer DDocument5 pagesThis Study Resource Was Shared Via: Solution 23-2 Answer DDummy GoogleNo ratings yet
- Module 3. Part 1 - Accounts Receivable For StudentsDocument36 pagesModule 3. Part 1 - Accounts Receivable For Studentslord kwantoniumNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - Other Long-Term InvestmentsDocument3 pagesChapter 12 - Other Long-Term InvestmentsJEFFERSON CUTENo ratings yet
- Depletion PDFDocument3 pagesDepletion PDFAlexly Gift UntalanNo ratings yet
- Pas 2 Inventories W RecordingDocument13 pagesPas 2 Inventories W Recordingwendy alcoseba100% (1)
- Conceptual With Correct AnswersDocument5 pagesConceptual With Correct AnswersElle Vernez0% (2)
- Sol. Man. - Chapter 17 - Depletion of Mineral Resources - Ia Part 1BDocument3 pagesSol. Man. - Chapter 17 - Depletion of Mineral Resources - Ia Part 1BMahasia MANDIGANNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument4 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsJohn Michael SorianoNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Accounting Second Sem ReviewerDocument7 pagesIntermediate Accounting Second Sem ReviewerchxrlttxNo ratings yet
- C8 Statement of Financial PositionDocument14 pagesC8 Statement of Financial PositionAllaine ElfaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Receivables Additional ConceptsDocument14 pagesChapter 6 Receivables Additional ConceptsElaiza RegaladoNo ratings yet
- Module 2c Additional Concepts - ReceivablesDocument15 pagesModule 2c Additional Concepts - ReceivablesMelanie RuizNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document17 pagesChapter 1Mydel AvelinoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Investments in Debt Securities and Other Long Term InvestmentDocument30 pagesChapter 4 Investments in Debt Securities and Other Long Term InvestmentAngelica Joy ManaoisNo ratings yet
- Credit DerivativesDocument22 pagesCredit Derivativesdiwa77777No ratings yet
- Altman (2020)Document28 pagesAltman (2020)Juan PerezNo ratings yet
- Cicc - Pi - 1.2 - M02L05-2 - 2017 - en - V02 PDFDocument2 pagesCicc - Pi - 1.2 - M02L05-2 - 2017 - en - V02 PDFPrashant ShindeNo ratings yet
- 90 Day Planning Workbook-1Document18 pages90 Day Planning Workbook-1bruno martinsNo ratings yet
- Short-Term Financial Management Decisions: Working Capital ManagementDocument12 pagesShort-Term Financial Management Decisions: Working Capital ManagementNhel AlvaroNo ratings yet
- NNN Financial Class Application 2023Document3 pagesNNN Financial Class Application 2023WNDUNo ratings yet
- Banking Question Bank (NME)Document11 pagesBanking Question Bank (NME)aswinsai615No ratings yet
- EMI Prepayment CalculatorDocument13 pagesEMI Prepayment CalculatornadeemNo ratings yet
- WCM Toyota STDocument18 pagesWCM Toyota STferoz khanNo ratings yet
- Loan Portfolio ManagementDocument4 pagesLoan Portfolio ManagementPapal NuncioNo ratings yet
- 98 - G.R. No. L-41320 Vda. de Squia V JacintoDocument6 pages98 - G.R. No. L-41320 Vda. de Squia V JacintoJoffrey UrianNo ratings yet
- Dosri AccountsDocument4 pagesDosri AccountsRon VirayNo ratings yet
- Resreach Final 3DRA10Document41 pagesResreach Final 3DRA10Ermias Assaminew AlmazNo ratings yet
- Exam Code 1 ObDocument4 pagesExam Code 1 ObHuỳnh Lê Yến VyNo ratings yet
- CDO: Collateralized Debt ObligationDocument15 pagesCDO: Collateralized Debt ObligationAbhijeet PatilNo ratings yet
- Sunita Co-Op. Housing Society LTD.: Piot No. 6 & 8, Opp. Nakhva High School, Tilak Road, THANE (East) - 400 603Document1 pageSunita Co-Op. Housing Society LTD.: Piot No. 6 & 8, Opp. Nakhva High School, Tilak Road, THANE (East) - 400 603vinayak tiwariNo ratings yet
- Oliver v. Philippine Savings Bank and CastroDocument15 pagesOliver v. Philippine Savings Bank and CastroTESDA MIMAROPANo ratings yet
- DIONISIO MOJICA vs. CA, and RURAL BANK OF YAWIT, INC.Document2 pagesDIONISIO MOJICA vs. CA, and RURAL BANK OF YAWIT, INC.Jan Mar Gigi GallegoNo ratings yet
- Obli Con SemifinalsDocument32 pagesObli Con SemifinalsMingNo ratings yet
- Synergy Webinar 6.0 Project Finance Structuring A DealDocument36 pagesSynergy Webinar 6.0 Project Finance Structuring A DealMoulik DhawanNo ratings yet
- Ft2020czech RepublicDocument11 pagesFt2020czech RepublicvisegaNo ratings yet
- Loan Risk Prediction Using User Transaction InformationDocument3 pagesLoan Risk Prediction Using User Transaction InformationAbhi ShikthNo ratings yet
- HLS Lending Case StudyDocument17 pagesHLS Lending Case StudyjatinNo ratings yet
- Cet Band4 Test 202009-1Document8 pagesCet Band4 Test 202009-1AngieNo ratings yet
- Prudential Norms IracDocument26 pagesPrudential Norms IracsgjatharNo ratings yet