0% found this document useful (0 votes)
880 views27 pagesChapter 5 Electrical Machine
An electrical machine can convert either mechanical energy to electrical energy (generator) or electrical energy to mechanical energy (motor). Almost all practical motors and generators use magnetic fields to convert energy. There are several types of electrical machines including DC machines, synchronous machines, AC motors, and induction motors. DC machines can operate on direct current and are used where variable speed or good speed regulation is required. Synchronous machines operate on alternating current and are used for power generation and applications requiring constant synchronous speed.
Uploaded by
Birhex FeyeCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
880 views27 pagesChapter 5 Electrical Machine
An electrical machine can convert either mechanical energy to electrical energy (generator) or electrical energy to mechanical energy (motor). Almost all practical motors and generators use magnetic fields to convert energy. There are several types of electrical machines including DC machines, synchronous machines, AC motors, and induction motors. DC machines can operate on direct current and are used where variable speed or good speed regulation is required. Synchronous machines operate on alternating current and are used for power generation and applications requiring constant synchronous speed.
Uploaded by
Birhex FeyeCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Introduction to Electrical Machines: Provides an overview of what electrical machines do, covering energy conversions between mechanical and electrical forms.
- Magnetic Field Principles: Describes how magnetic fields function in electrical machines, with insights into Ampere's law and magnetic permeability.
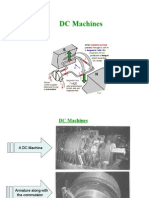
- DC Machines Overview: Explains the types and operations of DC machines, detailing both the generator and motor functions.
- Classification of DC Machines: Covers different types of DC motors and their uses, as well as the applications of DC generators.
- Understanding Synchronous Machines: Explains the function and advantages of synchronous machines over DC systems.
- AC Machines Functionality: Delves into the workings of AC motors, covering types such as synchronous and induction motors.
- Introduction to AC Generators: Covers fundamental concepts of AC generators, including their components and operational advantages.