Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Family
Uploaded by
agenisus10 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views22 pagesThis document outlines a lecture on the historical development of families. It discusses how the structure and roles of families have changed over time, particularly with the advent of industrialization. Before industrialization, extended families living together was more common, production occurred within households, and community life was significant. However, industrialization led to separation of home and workplace, and emergence of the nuclear family as the predominant model with specialized gender roles. While some views suggest this was an evolutionary process, more recent research finds greater diversity in pre-industrial family forms. The lecture concludes by questioning simplistic notions of impact and highlighting the complexity of family structures over history.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document outlines a lecture on the historical development of families. It discusses how the structure and roles of families have changed over time, particularly with the advent of industrialization. Before industrialization, extended families living together was more common, production occurred within households, and community life was significant. However, industrialization led to separation of home and workplace, and emergence of the nuclear family as the predominant model with specialized gender roles. While some views suggest this was an evolutionary process, more recent research finds greater diversity in pre-industrial family forms. The lecture concludes by questioning simplistic notions of impact and highlighting the complexity of family structures over history.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views22 pagesFamily
Uploaded by
agenisus1This document outlines a lecture on the historical development of families. It discusses how the structure and roles of families have changed over time, particularly with the advent of industrialization. Before industrialization, extended families living together was more common, production occurred within households, and community life was significant. However, industrialization led to separation of home and workplace, and emergence of the nuclear family as the predominant model with specialized gender roles. While some views suggest this was an evolutionary process, more recent research finds greater diversity in pre-industrial family forms. The lecture concludes by questioning simplistic notions of impact and highlighting the complexity of family structures over history.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 22
Introduction:The family
The family is a complex social
institution
Sociologists examine social change
& how this impacts on family life
Also study the role, functions &
structure of families in society
& how this may change over time
Ann McDowell Lecture Historical 1
/ The Family
This lecture will outline some terms &
definitions of the family
& consider how the structure, functions
& roles of families have changed over
time
Pre-industrialisation
Industrialisation
Ann McDowell Lecture Historical 2
/ The Family
Sociologists point out there is no such
thing as ‘the family’ anymore
The family structure has changed
less than a quarter of households in UK
conform to model of traditional family
(Giddens 2006)
Ann McDowell Lecture Historical 3
/ The Family
Some definitions & terms
Difference between ‘families’ &
‘households’
Family - a group of people tied by
relationships of blood, marriage or
adoption
Household - a residence for one person
or a group of people (who can be family
or unrelated), sharing accommodation
Ann McDowell Lecture Historical 4
/ The Family
Nuclear family - mother, father &
children (natural or adopted)
Extended family - nuclear family + one
or more other relatives
Modified extended family - close
family members live in close proximity
to each other
Ann McDowell Lecture Historical 5
/ The Family
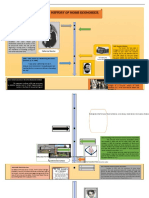
The family:
Historical developments
Before industrialisation:
Home & workplace were often in same
place
Community life was significant
(above differed from the modern
isolated nuclear family of modernity)
Ann McDowell Lecture Historical 6
/ The Family
Marriage often seen as an alliance
Production of most goods & services
was organised within the household
Family seen as the basic unit of social
production
Ann McDowell Lecture Historical 7
/ The Family
How did industrialisation impact
on family life?
Production of goods became organised
through workshops & factories
Led to separation of home & workplace
From being an integral part of family
life, work became a separate, external
activity
Thus, family mostly lost the function of
production
Ann McDowell Lecture Historical 8
/ The Family
Industrialisation led to profound changes in
family life
Wage labour - source of family income
women often excluded from social
production
Husbands seen as the principle breadwinner
However, Harris (1977) highlights a gradual
change of roles
Ann McDowell Lecture Historical 9
/ The Family
‘….industrialisation did not result
immediately in a differentiation
between domestic & industrial labour
tied to gender & the isolation of the
family. On the contrary, all members
of the family were employed in the
factories & the mines, & women &
children were only gradually excluded’
Ann McDowell Lecture Historical 10
/ The Family
Despite effects of industrialisation
on family life
Many families still produced goods
for consumption
Many women & children involved in
domestic or cottage industries
Ann McDowell Lecture Historical 11
/ The Family
Absolute dependence on purchased
goods occurred in later stages of
industrial capitalism
Ann McDowell Lecture Historical 12
/ The Family
Agricultural
economy
Extended family
Ann McDowell Lecture Historical 13
/ The Family
Industrialisation
& urbanisation
Manufacturing
economy
Nuclear family
Ann McDowell Lecture Historical 14
/ The Family
Has industrialisation altered the
structure of the family?
Traditional sociological views:
The present form of family (nuclear)
evolved from an earlier extended type
Extended family was predominant in
pre-industrial times
Modern nuclear family emerged as a
result of industrialisation &
urbanisation
Ann McDowell Lecture Historical 15
/ The Family
This refers to ‘evolutionary’ view
(supported by functionalist sociologists)
Marxists also agree with above, but
promote capitalism as the cause
(not industrialisation)
Ann McDowell Lecture Historical 16
/ The Family
Challenges to evolutionary view
Laslett (1972) researched parish
records
found evidence that extended families
were not dominant during pre-
industrialisation in Western Europe
Nuclear family more typical
Ann McDowell Lecture Historical 17
/ The Family
However, others (Anderson 1981)
studied households in Preston, a textile
area
Analysis of 1851 census data
Found evidence of extended families
Older relatives cared for children
families took in orphans & / or lodgers
Ann McDowell Lecture Historical 18
/ The Family
Later research (1950’s) Henriques &
Slaughter, “Coal is our life” found:
Similar patterns of extended family
living
Extended families could help younger
members get work
Ann McDowell Lecture Historical 19
/ The Family
Thus, for many urbanised w/c
families, industrialisation did not
result in nuclear family household
Ann McDowell Lecture Historical 20
/ The Family
Conclusion: Why is a historical
analysis of the family important?
Examined effects of industrialisation on
families & households (roles/functions)
Points to complexity of family
structures in the past
Questions simple ‘before’ & ‘after’ views
re impact of industrialisation on family
Diversity is not a modern phenomenon
Ann McDowell Lecture Historical 21
/ The Family
Next lecture
Will examine relevant sociological
theoretical debates re the family
This will include analysis of
Functionalism
Marxism
Feminism
Critical theory/New right approaches
Postmodernism
Ann McDowell Lecture Historical 22
/ The Family
You might also like
- Encyclopedia of Social History PDFDocument1,195 pagesEncyclopedia of Social History PDFAndrijaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Personal Vaues and Its DevelopmentDocument44 pagesChapter 2 Personal Vaues and Its Developmentnympha LejasNo ratings yet
- AQA A Level Sociology Families Households Flashcards SampleDocument11 pagesAQA A Level Sociology Families Households Flashcards SamplewilbertNo ratings yet
- Definitions of CommunityDocument29 pagesDefinitions of CommunityJiselle Umali100% (3)
- MINORU FUJIKI vs. MARIA PAZ GALELA MARINAYDocument2 pagesMINORU FUJIKI vs. MARIA PAZ GALELA MARINAYBo Dist100% (1)
- Popcom 50coffeebook A 02Document42 pagesPopcom 50coffeebook A 02Lora Lee Hope ArazaNo ratings yet
- Marriage and FamilyDocument6 pagesMarriage and FamilyPaul NallaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Home EconomicsDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Home EconomicsNica Garcia80% (5)
- Demographic Transition TheoryDocument411 pagesDemographic Transition TheoryJosé Vilton Costa100% (2)
- Curriculum Goals and Objectives DpdfinDocument20 pagesCurriculum Goals and Objectives Dpdfindhian1750% (4)
- Inequality in AustraliaDocument320 pagesInequality in AustraliaHansi8888No ratings yet
- Marriage and the Family in the Middle AgesFrom EverandMarriage and the Family in the Middle AgesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (53)
- Remaking Home Economics: Resourcefulness and Innovation in Changing TimesFrom EverandRemaking Home Economics: Resourcefulness and Innovation in Changing TimesNo ratings yet
- Class, State and Ideology (Wright, 1999)Document58 pagesClass, State and Ideology (Wright, 1999)agenisus1No ratings yet
- Management in Family LivingDocument571 pagesManagement in Family LivingEndugu shanti prasadNo ratings yet
- Module in Teaching Common Competencies in Home EconomicsDocument58 pagesModule in Teaching Common Competencies in Home EconomicsJhoerey D Villegas100% (14)
- The Ecovillage MovementDocument6 pagesThe Ecovillage MovementPeter BoneyNo ratings yet
- Class, State and Ideology (Wright, 2001)Document49 pagesClass, State and Ideology (Wright, 2001)agenisus1No ratings yet
- TLE 103 Home Economics - History, Concepts, Principles and PhilosophyDocument17 pagesTLE 103 Home Economics - History, Concepts, Principles and PhilosophyBENEDICT JAMES ARADANo ratings yet
- Family Life in 20th Century AmericaDocument345 pagesFamily Life in 20th Century AmericaAlenka ŠvabNo ratings yet
- Nuclear FamilyDocument7 pagesNuclear FamilyCj Lopez100% (1)
- Home Economics G1Document42 pagesHome Economics G1CARENA JAY CAMPOSNo ratings yet
- Diversity in Families 10th Edition Zinn Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesDiversity in Families 10th Edition Zinn Solutions Manualpikeaerology0fb5100% (27)
- لتحميل المحاضرة 11 لغة 1الأسرة اضغط هناDocument4 pagesلتحميل المحاضرة 11 لغة 1الأسرة اضغط هناLan HoàngNo ratings yet
- Home Economics: A History: Young Ladies at Home" This Books Helped Young Girls and Women OnDocument6 pagesHome Economics: A History: Young Ladies at Home" This Books Helped Young Girls and Women OnCharlynjoy Abañas100% (2)
- Forging The Industrial FamilyDocument13 pagesForging The Industrial FamilyAr Abhishek TripathiNo ratings yet
- Birth Order and Mortality: A Life-Long Follow-Up of 14,200 Boys and Girls Born in Early 20th Century SwedenDocument14 pagesBirth Order and Mortality: A Life-Long Follow-Up of 14,200 Boys and Girls Born in Early 20th Century Swedeneni yuliawatiNo ratings yet
- How Did Industrialization Impact On TheDocument8 pagesHow Did Industrialization Impact On TheSumnima RaiNo ratings yet
- Home-Economics G1Document41 pagesHome-Economics G1Campos , Carena JayNo ratings yet
- Broken Families: Economic Resources and Social Networks of Women Who Head FamiliesDocument11 pagesBroken Families: Economic Resources and Social Networks of Women Who Head FamiliesMarta Alija DomínguezNo ratings yet
- Households: Comparative and Historical Studies of the Domestic GroupFrom EverandHouseholds: Comparative and Historical Studies of the Domestic GroupRobert McC. NettingNo ratings yet
- FunctinalismDocument13 pagesFunctinalismGerson GeingobNo ratings yet
- Will The Purpose of Informing, Motivating, Persuading, Educating, or Entertaining The Listeners. She AlsoDocument3 pagesWill The Purpose of Informing, Motivating, Persuading, Educating, or Entertaining The Listeners. She AlsoPatricia SalomonNo ratings yet
- Coleman Marilyn, Ganong Lawrence H, Warzin Kelly (2007) Family Life in 20th Century America, GreenWood PressDocument345 pagesColeman Marilyn, Ganong Lawrence H, Warzin Kelly (2007) Family Life in 20th Century America, GreenWood Pressscience.dataNo ratings yet
- Time Line Home EconomicsDocument8 pagesTime Line Home Economicsfaker koreaNo ratings yet
- Social Consequences of UnemploymentDocument3 pagesSocial Consequences of UnemploymentvillafuerteviNo ratings yet
- What Is A Family?Document9 pagesWhat Is A Family?anubhav_singh_26No ratings yet
- How Does Industrialization Affects Family System and RelationshipDocument5 pagesHow Does Industrialization Affects Family System and RelationshipMomina JavedNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Home EconomicsDocument5 pagesEvolution of Home EconomicsAlthea Grace AbalaNo ratings yet
- Family and Culture:: Functions of The FamilyDocument19 pagesFamily and Culture:: Functions of The Familyrocelle marbellaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 EconomicsDocument5 pagesChapter 1 Economicsjordan cedeñoNo ratings yet
- Week 7Document2 pagesWeek 7EdwardNo ratings yet
- 0521847567Document453 pages0521847567Sybella Antonucci Antonucci100% (1)
- Houses Transformed: Anthropological Perspectives on Changing Practices of Dwelling and BuildingFrom EverandHouses Transformed: Anthropological Perspectives on Changing Practices of Dwelling and BuildingJonathan AldermanNo ratings yet
- Quick Revise: Defining Key Terms of Family StructuresDocument9 pagesQuick Revise: Defining Key Terms of Family StructuresKashif AminNo ratings yet
- Fcs Timeline 1Document4 pagesFcs Timeline 1api-534370181No ratings yet
- Names: Abas, Amani SDocument4 pagesNames: Abas, Amani SAmani AbasNo ratings yet
- Children in English-Canadian Society: Framing the Twentieth-Century ConsensusFrom EverandChildren in English-Canadian Society: Framing the Twentieth-Century ConsensusNo ratings yet
- Addison and Steele EssaysDocument46 pagesAddison and Steele EssaysafhbexrciNo ratings yet
- Breastfeeding, Subjugation and Empowerment in Rural GuatemalaDocument11 pagesBreastfeeding, Subjugation and Empowerment in Rural GuatemalaWuqu' KawoqNo ratings yet
- Ephemeral Modern FamilyDocument10 pagesEphemeral Modern FamilySheen Junio VisdaNo ratings yet
- Home Economics - A History - SutoriDocument26 pagesHome Economics - A History - SutoriLhon Drake Marco ReguyalNo ratings yet
- James S. Coleman - Families and SchoolsDocument8 pagesJames S. Coleman - Families and SchoolsJorgeA GNNo ratings yet
- Notes3 (Family & Gender)Document8 pagesNotes3 (Family & Gender)christykoNo ratings yet
- Cultures Change Through TimeDocument3 pagesCultures Change Through TimeLimbani KabiniNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Close Relations An Introduction To The Sociology of Families Canadian 5th Edition Mcdaniel Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Close Relations An Introduction To The Sociology of Families Canadian 5th Edition Mcdaniel Solutions Manual PDFmalinsjavitai100% (11)
- Close Relations An Introduction To The Sociology of Families Canadian 5th Edition Mcdaniel Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesClose Relations An Introduction To The Sociology of Families Canadian 5th Edition Mcdaniel Solutions Manualbedwarfratitemmg4100% (26)
- Social Institutions - FamilyDocument49 pagesSocial Institutions - FamilybascilloattliaNo ratings yet
- Sociology Lecture No 8 FamilyDocument4 pagesSociology Lecture No 8 FamilySafiullah mirzaNo ratings yet
- P01 M21200217090902021313Document9 pagesP01 M21200217090902021313chanlyn carlosNo ratings yet
- The Pro To Industrial Family Economy The Structural Function of Household and Family During The Transition From Peasant Society To IndustrialDocument26 pagesThe Pro To Industrial Family Economy The Structural Function of Household and Family During The Transition From Peasant Society To IndustrialhelenaNo ratings yet
- Family Patterns Gender Relations 180-208Document29 pagesFamily Patterns Gender Relations 180-208Riddhi DananiNo ratings yet
- AS Unit 1 Acquiring CultureDocument18 pagesAS Unit 1 Acquiring CultureAgnis Dwi Ratna PuspitasariNo ratings yet
- King Concepts of ChildhoodDocument38 pagesKing Concepts of ChildhoodTomislav SmolčićNo ratings yet
- General ScienceDocument305 pagesGeneral SciencekyratagboNo ratings yet
- W2 Reading Task STUDENT (Koray Nedim Özdemir)Document5 pagesW2 Reading Task STUDENT (Koray Nedim Özdemir)Koray Nedim ÖzdemirNo ratings yet
- International Medieval CongressDocument352 pagesInternational Medieval CongressYvonneRayNo ratings yet
- HRM - Workplace Social PartnershipDocument26 pagesHRM - Workplace Social Partnershipagenisus1No ratings yet
- Strategic Human Resource Management (SHRM)Document16 pagesStrategic Human Resource Management (SHRM)agenisus1No ratings yet
- Human Resource Management: Payment Systems in The New EconomyDocument13 pagesHuman Resource Management: Payment Systems in The New Economyagenisus1No ratings yet
- Lesson 10 Act 2Document2 pagesLesson 10 Act 2je raldNo ratings yet
- Psychology Key TermsDocument4 pagesPsychology Key TermskirushanthNo ratings yet
- 2020 Blitz Brochure Final 02042020Document11 pages2020 Blitz Brochure Final 02042020Javier CamposNo ratings yet
- Government Should Forbid SameDocument3 pagesGovernment Should Forbid SameKIMBERLEY SICATNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Marriage - Shaykh DR Mohammad Akram NadwiDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Marriage - Shaykh DR Mohammad Akram NadwiniazmhannanNo ratings yet
- Vol 2 Issue 5 AKRITI KASHYAPDocument11 pagesVol 2 Issue 5 AKRITI KASHYAPAkritiNo ratings yet
- MCN GND Prenatal and Stages of DevelopmentDocument5 pagesMCN GND Prenatal and Stages of DevelopmentKristal Jane RuedasNo ratings yet
- Social Issues of The ChurchDocument12 pagesSocial Issues of The ChurchLee SuarezNo ratings yet
- A Study of Maintenance Under Hindu Marriage Act: S.Manoj VasanthDocument14 pagesA Study of Maintenance Under Hindu Marriage Act: S.Manoj Vasanthmr dharniNo ratings yet
- CB-Unit 03-External Influences PDFDocument87 pagesCB-Unit 03-External Influences PDFVivek Lal KarnaNo ratings yet
- Teen PregnancyDocument2 pagesTeen PregnancyMaria Paula Uribe VargasNo ratings yet
- The Perinatal Paradigm - Klaus y KennellDocument13 pagesThe Perinatal Paradigm - Klaus y KennellAna CorderoNo ratings yet
- Divorce Prohibition in The PhilippinesDocument1 pageDivorce Prohibition in The PhilippinesgandalngmariaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Sains Kebidanan: Perawatan Metode Kanguru Pada Bayi Berat Lahir RendahDocument4 pagesJurnal Sains Kebidanan: Perawatan Metode Kanguru Pada Bayi Berat Lahir Rendahumy fadhillahNo ratings yet
- State-By-State Pregnancy and Leave LawsDocument109 pagesState-By-State Pregnancy and Leave LawsLegal MomentumNo ratings yet
- Princess Shoebelyn CDocument5 pagesPrincess Shoebelyn CPrincess Shoebelyn Cañete MauricioNo ratings yet
- Interacial MarriageDocument12 pagesInteracial Marriageboyfromdaheaven100% (4)
- (Continuity of Care Midwifery) Di Wilayah KerjaDocument7 pages(Continuity of Care Midwifery) Di Wilayah KerjaNafisha HaifaNo ratings yet
- Teenage Parents and Their Educational AttainmentDocument13 pagesTeenage Parents and Their Educational AttainmentKatzkie NeriNo ratings yet
- 2 PDFDocument232 pages2 PDFSandeep KakkarNo ratings yet
- Annulment and Declaration of Nullity of MarriageDocument3 pagesAnnulment and Declaration of Nullity of MarriageJee JeeNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Marriage and Family The Quest For Intimacy 8th Edition Lauer Test Bank PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Marriage and Family The Quest For Intimacy 8th Edition Lauer Test Bank PDFrainbow.basque1cpq100% (10)
- Introduction To Sociology - BBA 2ndDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Sociology - BBA 2ndAdnan AhmadNo ratings yet