Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Control: Control: Budgetary Control, Non-Financial Control, Human Aspects of Control
Control: Control: Budgetary Control, Non-Financial Control, Human Aspects of Control
Uploaded by
Yad0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views14 pagesThis document discusses various aspects of controlling, including:
1. Controlling involves evaluating actual performance against plans and taking corrective actions as needed. It is a managerial, dynamic, continuous, action-oriented, and both forward-looking and backward-looking process.
2. The controlling process involves establishing objectives and standards, measuring actual performance, comparing results to objectives and standards, and taking corrective actions.
3. Budgetary control compares actual results to budget data to identify differences and rectify causes of mismatch. Types of budgets include functional, master, capital/revenue, short-term/long-term, and fixed/flexible budgets.
Original Description:
Original Title
z.1 Conrol
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses various aspects of controlling, including:
1. Controlling involves evaluating actual performance against plans and taking corrective actions as needed. It is a managerial, dynamic, continuous, action-oriented, and both forward-looking and backward-looking process.
2. The controlling process involves establishing objectives and standards, measuring actual performance, comparing results to objectives and standards, and taking corrective actions.
3. Budgetary control compares actual results to budget data to identify differences and rectify causes of mismatch. Types of budgets include functional, master, capital/revenue, short-term/long-term, and fixed/flexible budgets.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views14 pagesControl: Control: Budgetary Control, Non-Financial Control, Human Aspects of Control
Control: Control: Budgetary Control, Non-Financial Control, Human Aspects of Control
Uploaded by
YadThis document discusses various aspects of controlling, including:
1. Controlling involves evaluating actual performance against plans and taking corrective actions as needed. It is a managerial, dynamic, continuous, action-oriented, and both forward-looking and backward-looking process.
2. The controlling process involves establishing objectives and standards, measuring actual performance, comparing results to objectives and standards, and taking corrective actions.
3. Budgetary control compares actual results to budget data to identify differences and rectify causes of mismatch. Types of budgets include functional, master, capital/revenue, short-term/long-term, and fixed/flexible budgets.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
CONTROL
Control : Budgetary control, non-financial control, human aspects of
control.
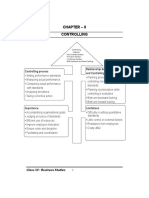
CONTROLLING
• Process of evaluating actual performance & if necessary, taking corrective actions so that the performance
is in accordance with planned performance.
Nature:
• A Managerial function
• Dynamic process: it sets & changes standard as per situational requirements
• Continuous process : not one time action
• Action oriented : as it indicates the areas of performance in which control actions can be taken
• Control as Forward looking : as one can control future happenings not the past. In light of past
performance mangers suggest corrective actions for future period.
• Control as Backward looking : as control action is based on past performance.
CONTROLLING PROCESS
Step 1 — Establish objectives and standards.
Step 2 — Measure actual performance.
Step 3 — Compare results with objectives and standards.
Step 4 — Take corrective action as needed
Budgetary control
• Budgetary control is a process of comparing the actual results with the
corresponding budget data in order to identify whether both match or
differ and rectify factors causing mismatch.
• Types of Budgets
1. Based on coverage of functions –
Functional Budgets :
Master Budget:
• Based on Nature of activities covered – Capital & Revenue
Budget.
• Based on Time period - Short Term, & Long Term.
• Based on flexibility adopted- Fixed Budget &Flexible Budgets.
Other techniques of control
• Break even analysis
• ABC Analysis
• EOQ
• PERT & CPM
• FINANCIAL RATIO ANALYSIS
QUALITY CONTROL THROUGH QUALITY
CIRCLES
Human Resource Accounting
• human resource is most precious resource . Organization has taken
measures to not only develop but measure the value of this resource.
• American Accounting Association has defined Human Resource
Accounting as : it is a process of identifying & measuring data about
human resources & communicating this information to interested parties.
• Thus, HR accounting is primary involved in measuring the various
aspects related to human assets.
Objectives
Methods of valuation of human assets
• historical cost
• Replacement cost
• Standard cost
• Present value of future earnings
• Expected realizable value
Problems in HR Accounting
You might also like
- Controlling Techniques 2Document14 pagesControlling Techniques 2Dipen Ashokkumar KadamNo ratings yet
- Elements of Management Planning & Control SystemsDocument15 pagesElements of Management Planning & Control Systemsyakarim100% (1)
- Chapter 7 ControllingDocument17 pagesChapter 7 ControllingAmeer Muhaymin AbbasNo ratings yet
- HSE Auditors TrainingDocument66 pagesHSE Auditors Trainingparadigman100% (4)
- Apply The Concept and Nature of Different Control Methods and Techniques in AccoDocument22 pagesApply The Concept and Nature of Different Control Methods and Techniques in AccoJoebert LomotosNo ratings yet
- SUMMARY - Managerial ControlDocument38 pagesSUMMARY - Managerial ControlSilmy AlfatirNo ratings yet
- Skw-Ppm-Module 4Document32 pagesSkw-Ppm-Module 4sharang IngawaleNo ratings yet
- ControllingDocument40 pagesControllingsharanashutoshNo ratings yet
- ControlDocument12 pagesControlKunal singh RajpurohitNo ratings yet
- ControllingDocument10 pagesControllingkhaabishayarNo ratings yet
- UNIT - I Basic Concepts of MCSDocument19 pagesUNIT - I Basic Concepts of MCSsagar029No ratings yet
- ControllingDocument31 pagesControllingMehbub Bihan SajinNo ratings yet
- 10 Fundamentals of ControllingDocument32 pages10 Fundamentals of ControllingasegidhaileNo ratings yet
- UNIT V PomDocument55 pagesUNIT V PomVandhana PramodhanNo ratings yet
- In The Name of Allah, The Most Beneficent, The Most MercifulDocument40 pagesIn The Name of Allah, The Most Beneficent, The Most MercifulMuhammad SaadNo ratings yet
- ControllingDocument21 pagesControllingAyush GoelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 ControllingDocument22 pagesChapter 5 ControllingWalaa ElsharifNo ratings yet
- Management Theory Chapter 9Document31 pagesManagement Theory Chapter 9AddiNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 8 Controlling: Class XII: Business Studies 1Document6 pagesChapter - 8 Controlling: Class XII: Business Studies 1Mahlet100% (1)
- MBA-Fourth Semester-Management Control System - Organisation StructureDocument14 pagesMBA-Fourth Semester-Management Control System - Organisation StructureMadhu RakshaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 (MGT Concepts and Practices)Document24 pagesChapter 7 (MGT Concepts and Practices)waleNo ratings yet
- Ch12 Guan CM AiseDocument40 pagesCh12 Guan CM AiseKarina RinaNo ratings yet
- Chapt08 3Document22 pagesChapt08 3Samartha SamtheDonNo ratings yet
- Session 6 (Management Essentials - BBA I)Document30 pagesSession 6 (Management Essentials - BBA I)Neha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Six - The Controlling FunctionsDocument11 pagesChapter Six - The Controlling Functionshaftom arayaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 PomDocument32 pagesUnit 5 PomDebasis BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- ControllingDocument31 pagesControllingElleNo ratings yet
- Accounting & Control: Cost ManagementDocument40 pagesAccounting & Control: Cost ManagementArisky AndrinaldoNo ratings yet
- MGTFunction8 - CONTROLLING 2Document29 pagesMGTFunction8 - CONTROLLING 2Nicholas Bonn SingNo ratings yet
- Unit VDocument25 pagesUnit VLionel Bharath RazerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document17 pagesChapter 7Gizaw BelayNo ratings yet
- Control: Made By: Vivek TyagiDocument6 pagesControl: Made By: Vivek TyagiSamaira JainNo ratings yet
- ControllingDocument44 pagesControllingFAIZAAN MARFANINo ratings yet
- Control Function of ManagementDocument14 pagesControl Function of ManagementOscar PozadasNo ratings yet
- Controlling: DR S Patnaik Lecturer Clothing & Textiles Department Cape Peninsula University of Technology EmailDocument16 pagesControlling: DR S Patnaik Lecturer Clothing & Textiles Department Cape Peninsula University of Technology EmailMamello Meme BolofoNo ratings yet
- Macc Maksi - How Management Accounting Information Support Decision MakingDocument31 pagesMacc Maksi - How Management Accounting Information Support Decision MakinglovianicyndiNo ratings yet
- Chapter Seven 2022Document19 pagesChapter Seven 2022abdiimohammedadamNo ratings yet
- 6 ControllingDocument47 pages6 ControllingKOFI BROWNNo ratings yet
- UNIT-5 ControllingDocument49 pagesUNIT-5 ControllingPrathyusha ReddyNo ratings yet
- Control Governance and Risk ManagementDocument11 pagesControl Governance and Risk ManagementJack Daniel PaduraNo ratings yet
- Chapter Seven Controlling FunctionDocument24 pagesChapter Seven Controlling FunctionBiniam Tesfay MeresaNo ratings yet
- ControllingDocument39 pagesControllingJosvin JoshyNo ratings yet
- ControlDocument7 pagesControlrishisaxena92No ratings yet
- CHP 12 - BBCDocument36 pagesCHP 12 - BBCjayrjoshiNo ratings yet
- Fourth Management FunctionDocument36 pagesFourth Management FunctionJames OwusuNo ratings yet
- BBFD 2014 LEC 14 - Internal Control SystemsDocument29 pagesBBFD 2014 LEC 14 - Internal Control SystemsCT LeeNo ratings yet
- Controlling: Principles & Practices of ManagementDocument33 pagesControlling: Principles & Practices of ManagementAdityaNo ratings yet
- Proj Implementation - ControllingDocument72 pagesProj Implementation - ControllingBhawesh SthaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 5 ControllingDocument21 pagesUNIT 5 ControllingbuviaroNo ratings yet
- MGMT6072 Introduction To Management and Business: Week 5Document32 pagesMGMT6072 Introduction To Management and Business: Week 5SofyyNo ratings yet
- Group 2Document23 pagesGroup 2bad geniusNo ratings yet
- Control: Correction & PreventionDocument13 pagesControl: Correction & PreventionRaj VermaNo ratings yet
- Lecuture Notes 1Document58 pagesLecuture Notes 1fbicia218No ratings yet
- Unit-5 PomDocument41 pagesUnit-5 PomSiranjeevi PNo ratings yet
- Acc215 01Document52 pagesAcc215 01lukumay stevenNo ratings yet
- Controlling & LeadershipDocument55 pagesControlling & LeadershipSaurabh PednekarNo ratings yet
- MODULE 5 - ControllingDocument10 pagesMODULE 5 - ControllingJoshua Roberto GrutaNo ratings yet
- Strategy Evaluation and ControlDocument41 pagesStrategy Evaluation and ControlVaibhav GuptaNo ratings yet
- An Improved Accounting and Control System For Pipeline Integrity DepartmentDocument26 pagesAn Improved Accounting and Control System For Pipeline Integrity DepartmentMona AlkhatibNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Business Environment MBA Semester I (Batch: 2020-22)Document2 pagesLesson Plan: Business Environment MBA Semester I (Batch: 2020-22)YadNo ratings yet
- "Fera and FemaDocument32 pages"Fera and FemaYadNo ratings yet
- PM To Address Valedictory Function of 2nd National Youth Parliament Festival On 12 JanuaryDocument2 pagesPM To Address Valedictory Function of 2nd National Youth Parliament Festival On 12 JanuaryYadNo ratings yet
- MdiaDocument24 pagesMdiaYadNo ratings yet
- M.S Patel Nstitute Faculty of Management Studies (M.S. University of Baroda)Document2 pagesM.S Patel Nstitute Faculty of Management Studies (M.S. University of Baroda)YadNo ratings yet
- TX Ls MimDocument3 pagesTX Ls MimYadNo ratings yet
- Gadaet Calculator: Questions CompulsoryDocument3 pagesGadaet Calculator: Questions CompulsoryYadNo ratings yet
- Operations TasksDocument31 pagesOperations TasksYadNo ratings yet