0% found this document useful (0 votes)
692 views21 pagesMajor Accident Hazards Control in India
This document discusses India's Major Accident Hazards (MAH) control system. [1] It outlines the rules and regulations developed since 1988 to prevent and mitigate major industrial accidents, including the Manufacture, Storage and Import of Hazardous Chemicals Rules and Chemical Accidents Emergency Planning Rules. [2] It describes the identification of MAH installations and responsibilities of sites handling hazardous chemicals above threshold limits. [3] It also explains the different crisis group levels from local to central and their functions in emergency preparedness and response.
Uploaded by
Holly SmithCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
692 views21 pagesMajor Accident Hazards Control in India
This document discusses India's Major Accident Hazards (MAH) control system. [1] It outlines the rules and regulations developed since 1988 to prevent and mitigate major industrial accidents, including the Manufacture, Storage and Import of Hazardous Chemicals Rules and Chemical Accidents Emergency Planning Rules. [2] It describes the identification of MAH installations and responsibilities of sites handling hazardous chemicals above threshold limits. [3] It also explains the different crisis group levels from local to central and their functions in emergency preparedness and response.
Uploaded by
Holly SmithCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Major Accident Hazards Control: Introduction to major accident hazards control measures and framework in India.
- Development of MAH System in India: Overview of the development of the Major Accident Hazards (MAH) system and associated projects from 1988 to 1990.
- MAHC System in India: Details of the rules related to the Manufacture Storage & Import of Hazardous Chemicals (MSIHC) and management practices.
- Regulatory Components: Explanation of the regulatory rules for chemical accident management by the Ministry of Environment and Forests.
- CIMAH Rules: Description of the Control of Industrial Major Accident Hazards (CIMAH) rules aligned with EC directives.
- MAH Installation: Definition and criteria for identifying Major Accident Hazards installations and their inspection protocols.
- Major Hazards Control: Strategies for controlling major hazards through proactive and reactive approaches.
- MAHC System in India (Contd.): Continuation of the MAHC system detailing accident reporting, safety audits, and emergency planning.
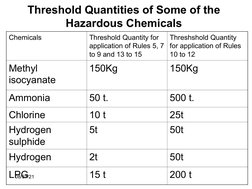
- Threshold Quantities: Table detailing threshold quantities for various hazardous chemicals relevant to MAH regulations.
- Chemical Accidents Rules 1996: Information on the Chemical Accidents (EPP&R) Rules of 1996 including crisis group constitution.
- Major Accident Hazards Control (Approaches): Emphasizes proactive and reactive approaches to managing major accident hazards.
- Responsibilities of MAH Installations: Outlines the responsibilities of MAH installations including emergency plan preparation and accident notification.
- Crisis Group Levels: Describes the hierarchical structure of crisis groups from central to local levels.
- Chairmen of Crisis Groups: Lists the leadership roles for various crisis group levels in managing chemical hazards.
- Meeting Periodicity: Schedule of meetings for different levels of crisis groups to manage ongoing chemical safety tasks.
- Local Crisis Groups - Functions: Functions and duties of local crisis groups in preparing and implementing emergency plans.
- Functions of DCG: Responsibilities of the District Crisis Groups in overseeing chemical accidents and emergency preparedness.
- State Crisis Group - Functions: The role of state crisis groups in managing offsite emergency plans and post-accident reviews.
- Central Crisis Group - Functions: Central Crisis Group tasks including post-accident analysis and infrastructural assistance.
- Conclusion: Concludes the presentation with thanks, indicating the end of the major accident hazards control training.