Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Senior School Year 2
Uploaded by
Derinsola Oduwole0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
112 views21 pagesHelps if you want to learn authentication
Original Title
ICT
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentHelps if you want to learn authentication
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
112 views21 pagesSenior School Year 2
Uploaded by
Derinsola OduwoleHelps if you want to learn authentication
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 21
SENIOR SCHOOL YEAR 2
7TH WEEK
Security of Data con’td
Additional Security of data Online
• Firewalls
• Security protocols
• Encryption
FIREWALLS
• Firewall can be software or hardware. It sits
between user's computer and an external
network(internet) and filters information
coming in and out of the user’s computer.
Tasks carried out by firewalls
• To examine the traffic between a user’s computer (internal
network) and a public network(internet).
• Checks whether incoming or outgoing data meets a given a set
of given criteria, if the data fails the criteria, the firewall block
the traffic.
• It can be used to log all incoming and outgoing traffic to allow
later interrogation by the network manager.
• Criteria can be set so that the firewall prevents access to certain
undesirable sites.
• It is possible for firewall to help prevent hackers gaining access
to the user’s computer or network.
• The user is warned if some software on their system is trying to
access an external data source(automatic software upgrade).
• The firewall can be a hardware interface that
is located somewhere between the computer
and the internet connection, in which case is
often referred to as GATEWAY.
• Alternately, the firewall can be software
installed on a computer, in some cases it is
part of the operating system(Windows
firewall).
Certain circumstances where the firewall
can’t prevent potential harmful traffic.
• It cannot prevent individuals, on the internal
networks using their own modems to bypass
the firewall.
• Employee misconduct or carelessness cannot
be controlled by firewalls e.g control of
passwords or user accounts).
• Users on stand-alone computers can choose to
disable the firewall.
Security Protocols
• Communicate with one another over the
internet requires these two forms of security
protocols (set of rules used by computers)
1) Secure Socket Layer (SSL)
2) Transport Layer Security (TLS)
Secure Socket Layer (SSL)
Secure Socket Layer (SSL): is a type of protocol that
allows data to be sent and received securely/safely
over the internet.
• When a user logs on to a website, SSL secures and
encrypts the data – only the user’s computer and
the web server are able to make sense of what is
being transmitted.
• A user will know if SSL is being applied when they
see https (as part of the web address) or a small
padlock in the status bar at the top of the screen.
Secure Socket Layer (SSL)
• SSL is used on (e-commerce) websites where we
use bank or credit card details in order to make
purchases.
• Examples:
Secure websites start with https and have an icon of
a padlock.
Non-secure websites start with http.
• Buying products over the internet is known as e-
commerce. Examples of e-commerce websites
include Amazon, Ebay, Jumia, Konga, Walmart
e.t.c.
How to identified secure and non-secure
websites
Transport Layer Security
• Transport Layer Security (TLS): is similar to SSL,
but is more recent security system.
• TLS is a form of protocol that ensures the
security and privacy of a data between devices
and users when communicating over the
internet.
• It is essentially designed to provide encryption,
authentication and data integrity.
Layers of Transport Layer Security (TLS)
• Record Protocol: This part of communication
can be used with or without encryption. It is also
responsible for securing application data and
verifying its integrity and origin/source)
• Handshake protocol: this permits the website
and the user to authenticate each other and to
make use of encryption algorithms (a secure
session between user and website is
established).
Differences between SSL and TLS
• TLS is possible to be extended by adding new
authentication method.
• TLS make use of session caching, which
improves the overall performance compared
to SSL.
Session caching
• Session caching: when opening a TLS session,
it requires a lot of computer time due to the
complex encryption key being used.
• The use of session caching can avoid the need
to utilize so much computer time for each
connection.
• TLS can either establish a new session or
attempt to resume an existing session.
ENCRYPTION
• Encryption is used to protect data in case it has
been hacked and accessed illegally.
• Encryption doesn’t prevent hacking, it makes
the data meaningless or un-readable unless the
recipient has the necessary decryption tools.
• Whenever you use a computer device that is
connected to the internet, you are potentially
vulnerable to hackers.
Encryption turns data into scrambled and unreadable
nonsense.
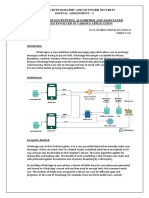
An example of encryption
• Bob wants to send a personal message to Mary.
• Bob wants to encrypt the message so that it can
only be read by Mary.
• Go to the next slide to see the encryption
process.
The example below explains how the encryption
process works
1) Bob first needs to create an encryption key.
The key will usually be a very long random
number.
2) Bob will now give Mary a copy of the
encryption key.
3) Bob can now encrypt (lock) the personal
message using encryption software and the
encryption key.
Once encrypted, the message will just look
like scrambled nonsense.
4) Bob can now send the encrypted message to Mary
via the internet.
5) When Mary receives the message, she will use her
copy of the encryption key to decrypt (unlock) the
message.
6) Mary can now read the message sent by Bob
When should you use encryption?
It is a good idea to use encryption and stop
unauthorised people from reading your data in the
following circumstances.
• Any files containing bank account or credit card
data.
• When buying items on the internet using
credit/bank cards
• Any data containing confidential medical records
• Emails that you wish to remain private.
• Any data that could be used to commit identity
fraud (social security numbers, insurance
numbers etc.).
You might also like
- Simple Steps to Data Encryption: A Practical Guide to Secure ComputingFrom EverandSimple Steps to Data Encryption: A Practical Guide to Secure ComputingNo ratings yet
- Security FundamentalsDocument19 pagesSecurity FundamentalsJenny AndresNo ratings yet
- Cybersecurity Enforcement and Monitoring Solutions: Enhanced Wireless, Mobile and Cloud Security DeploymentFrom EverandCybersecurity Enforcement and Monitoring Solutions: Enhanced Wireless, Mobile and Cloud Security DeploymentNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Security and Ethics Computer Science IgcseDocument7 pagesChapter 8 Security and Ethics Computer Science IgcseDesire KandawasvikaNo ratings yet
- REMOTE ACCESS VPN- SSL VPN: A deep dive into SSL VPN from basicFrom EverandREMOTE ACCESS VPN- SSL VPN: A deep dive into SSL VPN from basicRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Security and EthicsDocument6 pagesSecurity and EthicssramsahaNo ratings yet
- Encrypting Data GuideDocument29 pagesEncrypting Data GuideAra Jane T. PiniliNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document7 pagesLecture 4Code SolutionNo ratings yet
- DeviceMgmtSecDocument49 pagesDeviceMgmtSecvenkatsai elethNo ratings yet
- Safety and Security - SummaryDocument7 pagesSafety and Security - SummaryReda Zuhair AlQasimNo ratings yet
- 3com - A Simple Guide To FirewallsDocument8 pages3com - A Simple Guide To Firewallssohailmeer80No ratings yet
- Networ AssignmentDocument44 pagesNetwor Assignmentmargaa bacuraaNo ratings yet
- Encryption LfM4p0YDocument7 pagesEncryption LfM4p0YtannnnNo ratings yet
- Part A-Theoretical Questions: CybersecurityDocument42 pagesPart A-Theoretical Questions: Cybersecurityadikesa100% (1)
- U NetworkSecurity4Document10 pagesU NetworkSecurity4api-3798998No ratings yet
- FALLSEM2021-22 CSE3501 ETH VL2021220103874 Reference Material I 30-08-2021 Lect 9Document21 pagesFALLSEM2021-22 CSE3501 ETH VL2021220103874 Reference Material I 30-08-2021 Lect 9wurdigNo ratings yet
- Mis - Privacy IssuesDocument24 pagesMis - Privacy IssuesJeffin Jose0% (1)
- Network Security A Simple Guide To FirewallsDocument3 pagesNetwork Security A Simple Guide To FirewallsSergeyNo ratings yet
- Computer and Network Security Organizational ControlsDocument12 pagesComputer and Network Security Organizational ControlsMihir RathodNo ratings yet
- Security: Refer Chapter-10 From Gary P. SchneiderDocument60 pagesSecurity: Refer Chapter-10 From Gary P. Schneidernancy bhatiaNo ratings yet
- VAPT QuestionsDocument46 pagesVAPT Questionspepal38750No ratings yet
- UNIT 10 SecurityDocument44 pagesUNIT 10 SecurityBonaventure MasekoNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2023-24 BCSE354E ETH VL2023240501599 2024-02-24 Reference-Material-IIDocument29 pagesWINSEM2023-24 BCSE354E ETH VL2023240501599 2024-02-24 Reference-Material-IILet's Hear it the other wayNo ratings yet
- Organizational Security Environment - Technical CountermeasuresDocument34 pagesOrganizational Security Environment - Technical CountermeasuresSameer QuadriNo ratings yet
- 20BCA1335 Ashish-Yadav AssinmentDocument4 pages20BCA1335 Ashish-Yadav AssinmentimyadashuNo ratings yet
- Part A-Theoretical Questions: 1. What Is Cryptography?Document14 pagesPart A-Theoretical Questions: 1. What Is Cryptography?Emran HossainNo ratings yet
- Afroz FinalDocument11 pagesAfroz FinalMohd JunedNo ratings yet
- Most Common Security Threats in The E-Commerce EnvironmentDocument22 pagesMost Common Security Threats in The E-Commerce EnvironmentKunal ObhraiNo ratings yet
- Security Issues Unit 2Document10 pagesSecurity Issues Unit 2Richa GargNo ratings yet
- E-Business in Hospitality 7Document15 pagesE-Business in Hospitality 7Tsea CaronNo ratings yet
- Security Plus NotesDocument21 pagesSecurity Plus NotesJosh Garcia100% (1)
- Browse Web Basics & Security ConceptsDocument21 pagesBrowse Web Basics & Security ConceptsTavisLeaNo ratings yet
- Interview Preparation For Cyber SecurityDocument114 pagesInterview Preparation For Cyber SecurityAhmed Ajmal100% (2)
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Network SecurityDocument26 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Network SecurityMuhammad NashriqNo ratings yet
- Nad Ns Unit 4 Part 2Document23 pagesNad Ns Unit 4 Part 2Akshay UtaneNo ratings yet
- Security in E-CommerceDocument29 pagesSecurity in E-CommerceAlex T BinoyNo ratings yet
- A Seminar Report ON FirewallDocument35 pagesA Seminar Report ON FirewallSuresh KumarNo ratings yet
- 2) Host Level Threats and VulnerabilitiesDocument19 pages2) Host Level Threats and VulnerabilitiesBhanu NaikNo ratings yet
- Types of Computer MisuseDocument10 pagesTypes of Computer MisuseSamNo ratings yet
- Computer Security: - DefinitionDocument38 pagesComputer Security: - Definitionarchana_sree13No ratings yet
- Web Security and ProtocolsDocument35 pagesWeb Security and ProtocolsFarhan KhurshidNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce Chapter 4Document34 pagesE-Commerce Chapter 4THABISILE MBATHANo ratings yet
- CH5-6 CS LectureDocument17 pagesCH5-6 CS LecturepyramidmistreNo ratings yet
- A) What Is A Hacker?Document2 pagesA) What Is A Hacker?ANDREI VNo ratings yet
- Security and Privacy On The InternetDocument6 pagesSecurity and Privacy On The InternetBùi Tuấn MinhNo ratings yet
- E-business Security EssentialsDocument38 pagesE-business Security EssentialsKavitha PalaniNo ratings yet
- Cs Lab6 B19CSE025Document15 pagesCs Lab6 B19CSE025Ankur BorkarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document70 pagesChapter 5masnun mareebNo ratings yet
- Dire Dawa University: College of Computing Department of Computer ScienceDocument8 pagesDire Dawa University: College of Computing Department of Computer ScienceAhadu techNo ratings yet
- Ece4013 A2Document10 pagesEce4013 A2Praveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Information SecurityDocument11 pagesInformation Securitys_asmathNo ratings yet
- Network Quality and Cyber SecurityDocument18 pagesNetwork Quality and Cyber Securitytylerd2506No ratings yet
- Security: Table of ContentDocument5 pagesSecurity: Table of ContentMihir PatelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document26 pagesLecture 3Jasbindar SinghNo ratings yet
- Network Security FUndamentalsDocument22 pagesNetwork Security FUndamentalspetercoolish108No ratings yet
- How Encryption Works: in The Key Of..Document5 pagesHow Encryption Works: in The Key Of..tksctr1No ratings yet
- IT Note2Document17 pagesIT Note2yoyoNo ratings yet
- SC-900 Security, Compliance and Identity FundamentalsDocument68 pagesSC-900 Security, Compliance and Identity FundamentalsJoseph ChenNo ratings yet
- VPNDocument13 pagesVPNAndreea IftodeNo ratings yet
- RuPay Chip Issuer HOST Implementation Requirements Guide - v2 0Document53 pagesRuPay Chip Issuer HOST Implementation Requirements Guide - v2 0Mohammed Abdul KhuddoosNo ratings yet
- St12a1-Performance Task 2 - Group 10Document13 pagesSt12a1-Performance Task 2 - Group 10Godsend AlertaNo ratings yet
- 1.5 IGCSE ICT Impact of Emerging Technologies Topic Question Paper 1 Set 1 WMDocument5 pages1.5 IGCSE ICT Impact of Emerging Technologies Topic Question Paper 1 Set 1 WMmahaNo ratings yet
- Top 10 SAP Audit and Security Risks: 2. Insecure ConfigurationDocument3 pagesTop 10 SAP Audit and Security Risks: 2. Insecure ConfigurationTARA_23No ratings yet
- 7 Creating A CertificateDocument66 pages7 Creating A CertificateSanya VongmackNo ratings yet
- Hot Joe Online 8-2Document29 pagesHot Joe Online 8-2renmincvphNo ratings yet
- Watchman AIR User Guide UG-0000-0001.3 (CX)Document41 pagesWatchman AIR User Guide UG-0000-0001.3 (CX)MILTON CÉSAR AGUILAR DE AZAMBUJANo ratings yet
- Linux System Administration Part-3Document1 pageLinux System Administration Part-3AtaurRahmanNo ratings yet
- Essay of CybercrimeDocument3 pagesEssay of Cybercrimekaladevi21No ratings yet
- Sangfor NGAF Report 20211026154432Document11 pagesSangfor NGAF Report 20211026154432Alzi Al-LailNo ratings yet
- Formation FortiGate Infrastructure v6.2-23-08-2019Document159 pagesFormation FortiGate Infrastructure v6.2-23-08-2019Amani YAO N'GORANNo ratings yet
- WAF01 Barracuda Web Application Firewall - Foundation - Lab GuideDocument19 pagesWAF01 Barracuda Web Application Firewall - Foundation - Lab GuideneoaltNo ratings yet
- QuizDocument2 pagesQuizAkhila ChinniNo ratings yet
- Gautam Buddha University: ID Card Form (Please Fill Up The Form in Block Letters)Document1 pageGautam Buddha University: ID Card Form (Please Fill Up The Form in Block Letters)ATUL SAXENANo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Security Privacy and Data IntegrityDocument91 pagesChapter 6 Security Privacy and Data IntegrityUsman ShaukatNo ratings yet
- The Fight Against Cybercrime in Tanzania - ReportDocument14 pagesThe Fight Against Cybercrime in Tanzania - ReportYusuph KileoNo ratings yet
- Firewall MKDocument3 pagesFirewall MKArman NthreeNo ratings yet
- 703 Sophos-managers-guide-to-UTM-NGFW FirewallsDocument10 pages703 Sophos-managers-guide-to-UTM-NGFW FirewallsVinay AroraNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument18 pagesSeminar Reportcrazyshyam3100% (2)
- Cyber Safe Girl 3.0 Book (19-05-2020)Document100 pagesCyber Safe Girl 3.0 Book (19-05-2020)Satya Prakash BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Ethical Hacking Firefox Plugin by Srikanta SenDocument131 pagesEthical Hacking Firefox Plugin by Srikanta SenSrikanta SenNo ratings yet
- Encryption and Decryption Process Using Quaternion and Farey Fractions For Secure TransmissionDocument9 pagesEncryption and Decryption Process Using Quaternion and Farey Fractions For Secure TransmissionIRJCS-INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF COMPUTER SCIENCENo ratings yet
- Part I Debit Credit Application OverviewDocument94 pagesPart I Debit Credit Application OverviewMai Nam ThangNo ratings yet
- Securing Networks With Cisco Firepower Next Generation Firewall SSNGFWDocument5 pagesSecuring Networks With Cisco Firepower Next Generation Firewall SSNGFWkalidNo ratings yet
- ExamDocument48 pagesExamFercoNo ratings yet
- Web Application Security Master ThesisDocument6 pagesWeb Application Security Master Thesistrinasimmonssavannah100% (2)
- Airtel Info....Document1 pageAirtel Info....Ravi Kiran KandimallaNo ratings yet
- Reversing Android AppsDocument72 pagesReversing Android AppsjoseNo ratings yet
- Possessive Pilot Flara Deviana PDF FreeDocument463 pagesPossessive Pilot Flara Deviana PDF FreeRafika DewiNo ratings yet
- The Most Marketable ICT Courses in KenyaDocument3 pagesThe Most Marketable ICT Courses in KenyaJOSEPHNo ratings yet