Professional Documents
Culture Documents
India Brochure
Uploaded by
Md. Tasnimul Hasan 20141716300 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views2 pagesIndia has several key exporting industries including mineral fuels, gems and precious metals, and pharmaceuticals. It has a factor endowment of a robust IT structure, high mineral fuels reserves, and favorable location for precious metals extraction. Key local companies in India include Reliance Industries, TATA Consultancy Services, HDFC Bank, Infosys, and ICICI Bank. India is located in South Asia with a population of over 1.4 billion people and borders several neighboring countries.
Original Description:
BROCHURE OF INDIA
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentIndia has several key exporting industries including mineral fuels, gems and precious metals, and pharmaceuticals. It has a factor endowment of a robust IT structure, high mineral fuels reserves, and favorable location for precious metals extraction. Key local companies in India include Reliance Industries, TATA Consultancy Services, HDFC Bank, Infosys, and ICICI Bank. India is located in South Asia with a population of over 1.4 billion people and borders several neighboring countries.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views2 pagesIndia Brochure
Uploaded by
Md. Tasnimul Hasan 2014171630India has several key exporting industries including mineral fuels, gems and precious metals, and pharmaceuticals. It has a factor endowment of a robust IT structure, high mineral fuels reserves, and favorable location for precious metals extraction. Key local companies in India include Reliance Industries, TATA Consultancy Services, HDFC Bank, Infosys, and ICICI Bank. India is located in South Asia with a population of over 1.4 billion people and borders several neighboring countries.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
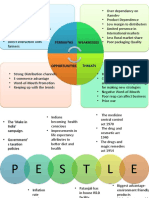
Porter’s Diamond Model
Exporting Industries:
• Mineral Fuels
• Gems & Precious Metals,
• Pharmaceuticals
Hofstede’s Cultural
Factor Endowment
• Robust IT Structure Dimensions India’s Regional Economic
• High Mineral Fuels Power Distance Integration
• Favourable Location for Precious • Score: 77 • India-Sri Lanka Free Trade Agreement
•
Metals
Cheap Labour in India
Relating & Supporting Industries
•
•
High Power Distance
Power Distance present in
Workplace
•
•
•
•
India-Bhutan Free Trade Agreement
India-Maldives Free Trade Agreement
South African Customs Union (SACU)
Global System of Trade Preferences
INDIA
• Availability of Capable Suppliers in
India
Individuality VS Collectivism
• Score: 48 •
(GSTP)
SAARC Preferential Trading
INB 372
Firm Strategy, Structure & Rivalry
• Investment in R&D and Changing
• Religion/Philosophy
Individualism
Arrangement (SAPTA)
SECTION 17
• Social & Workplace Collectivism 5 Interesting Facts about India
•
Locations for Expansion (Strategy)
Assembling a Huge Number of Masculinity VS Femininity
• India was the world's first diamond- GROUP 3
mining country.
Talented Workforce (Structure) • Score: 56
• • India boasts the world's second-
Using Innovations and Maintaining • Masculine Society
largest number of English Speakers.
Brand Value (Rivalry) • Gender Bias in India
• India is the greatest producer and
• Sexual Harassment in Workplace
Demand Conditions exporter of spices in the world.
• Expectation of Growing Demand for Uncertainty Avoidance • Sugar was refined and consumed for
Mineral Fuels • Score: 40 the first time in India.
• Increased Demand of Gems and • Low UAI • In Switzerland, there is a day
Precious Metals • Low Preferences dedicated to Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam
• High Demand in the Pharmaceutical • Not Compelled to Take Actions known as Science Day.
Industry Against Errors
Political Benefits Economic Benefits
• Policy Support to encourage FDI • Huge Market Size
Political Risks • Increased Future Wealth
• Conflict with the Neighbouring Economic Risks
Countries • Massive Debt Issues Due to
• Media Oppression Covid-19
Political Costs • Declining Living Standards Due to Consumer Price Index
• India’s Low Political Stability Covid-19 India is placed 86th in the 2020
Index Economic Costs Corruption Perception Index.
Geographical Location • World Trade Organisation (WTO) • Economic Loss Due to Covid-19
• Population Disputes • High Costs of Doing Business in Negative Impact of Corruption
1,400,000,000 (approx., 2021) India on FDI | Barrier
• Area • Unhealthy CPI
Technological Benefits Social Benefits •
3.287 million km² High levels of corruption deter FDI by
• 3rd Most Technologically • Huge Consumer Market
• Surrounding Countries imposing additional costs on investors
Advanced Country • Increasing Standards of Living and creating uncertainty about future
Afghanistan, Pakistan, China, • Leading IT Product Exporter Social Risks costs and revenues
Bhutan, Nepal, Myanmar, Technological Risks f
• Tensions in Communal • India's high percentage of corruption
Bangladesh, Maldives, and Sri • Cyber Risk has a detrimental influence on foreign
Harmony
Lanka Near to Sea/River • Information Privacy Risk
• Poverty direct investment.
India is bordered on the south by Technological Costs
Social Costs
the Indian Ocean, the Arabian Sea • Low App Development Costs Advantages of Economic
• Low Outsourcing Costs
• Rise in Pension Costs
on the west, the Lakshadweep Sea Integration
on the southwest, the Bay of • Nation Branding
Bengal on the east, and the Indian Key Local Companies Key Resources • Establishment of Alliances
Ocean on the south itself. • Reliance Industries • Minerals • Copper • Rise in Government Income
• TATA Consultancy Services • Coal • Marble • Fall in Unemployment due to Trading
• HDFC Bank • Gas • Diamond Companies
• Rise in Quality-of-Life Index
• Infosys • Gold • Oil • Improvement in Domestic
• ICICI Bank • Iron Ore Goods/Services
You might also like
- Case 9 - Maryam Namira 2403211017Document9 pagesCase 9 - Maryam Namira 2403211017Maryam NamiraNo ratings yet
- Entry and Growth in Two Emerging Markets: Harshil Sharma 20020346 Mba-BDocument9 pagesEntry and Growth in Two Emerging Markets: Harshil Sharma 20020346 Mba-BHarshil SharmaNo ratings yet
- A Case Study Analysis Of: Group No:1Document11 pagesA Case Study Analysis Of: Group No:1Nikhil RangariNo ratings yet
- Leveraging Talent: 6 Annual Conference - GEODocument22 pagesLeveraging Talent: 6 Annual Conference - GEOUmesh VashishthNo ratings yet
- Barriers To Entry: Presented by Group 8Document23 pagesBarriers To Entry: Presented by Group 8Devjani SealNo ratings yet
- CSR Project - Group 3Document19 pagesCSR Project - Group 3Aniruddha MajumderNo ratings yet
- Tesla Motors': Potential Market Expansion inDocument33 pagesTesla Motors': Potential Market Expansion inAnurag100% (1)
- Harley Davidson: Submitted By-Abhishek Pathak Faraz Khan Pratibha Yadav Rahul Pandey Sandeep Yadav Shubham SharmaDocument23 pagesHarley Davidson: Submitted By-Abhishek Pathak Faraz Khan Pratibha Yadav Rahul Pandey Sandeep Yadav Shubham Sharmapratibha087No ratings yet
- The Global India: Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Delhi IndiaDocument43 pagesThe Global India: Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Delhi Indiamohi_1513No ratings yet
- HZL Profiling OverviewDocument4 pagesHZL Profiling Overviewprakharsharma2208No ratings yet
- Mother Dairy Case Analysis: Group 18 PresentationDocument6 pagesMother Dairy Case Analysis: Group 18 PresentationAyaan ZaiNo ratings yet
- Himalayan Package Drinking WaterDocument34 pagesHimalayan Package Drinking WaterSheikh Zain UddinNo ratings yet
- Iia 2021Document55 pagesIia 2021Nikhil KakkarNo ratings yet
- Where Is India As An Innovation Country !!!Document17 pagesWhere Is India As An Innovation Country !!!maulikmotial200No ratings yet
- AL MA RT: GR Ou PaDocument22 pagesAL MA RT: GR Ou PaAnupam ChaplotNo ratings yet
- CRR-Tata Motors CaseDocument26 pagesCRR-Tata Motors CaseArnab ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Group Presentation May 2019Document35 pagesGroup Presentation May 2019nawaz khanNo ratings yet
- .Makerting PrestDocument27 pages.Makerting Prestsweety smileNo ratings yet
- Tech MahindraDocument9 pagesTech MahindraKUNAL KUMARNo ratings yet
- MACR - Group 6Document17 pagesMACR - Group 6SanchuNo ratings yet
- Cseet EbeDocument144 pagesCseet EbeAlka DubeyNo ratings yet
- Globalization & IndiaDocument16 pagesGlobalization & IndiaRishu Anand MridulaNo ratings yet
- BFRDocument14 pagesBFRJuhi MazumdarNo ratings yet
- Indian Pharmaceutical Industry: Evolution, Trends & OpportunitiesDocument121 pagesIndian Pharmaceutical Industry: Evolution, Trends & OpportunitiesHetal DubariaNo ratings yet
- Reliance Industries LimitedDocument7 pagesReliance Industries LimitedARYA BANERJEE PGP 2019-21 Batch0% (1)
- Horti Nursery B PlanDocument21 pagesHorti Nursery B PlanneoNo ratings yet
- Group 5 Aldi and LidlDocument29 pagesGroup 5 Aldi and LidlVershaNo ratings yet
- Milk MantraDocument18 pagesMilk MantraSidhant NayakNo ratings yet
- International Economics Trade IIFTDocument26 pagesInternational Economics Trade IIFTvipulhereNo ratings yet
- Group 1 - ABGDocument12 pagesGroup 1 - ABGshubhamNo ratings yet
- Group 4Document4 pagesGroup 4shivam sharmaNo ratings yet
- Management Trainee ProgrammeDocument39 pagesManagement Trainee Programmeshivanand_09No ratings yet
- MKTNG PatanjaliDocument4 pagesMKTNG PatanjaliShreya KadamNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of International Business & Its EnvironmentDocument29 pagesThe Evolution of International Business & Its EnvironmentDeepanshu KaushikNo ratings yet
- Herbalite Beverages Pvt. LTD.: Master Business Plan - Internal DraftDocument2 pagesHerbalite Beverages Pvt. LTD.: Master Business Plan - Internal DraftAnkit BalsaraNo ratings yet
- Integrating CMM & Six Sigma For A Competitive Edge: - Paddy Rao Associate VP, InfosysDocument18 pagesIntegrating CMM & Six Sigma For A Competitive Edge: - Paddy Rao Associate VP, InfosysNirmal ShahNo ratings yet
- Segmentation, Targeting and Positioning: What Is Segmentation, Anyone?Document5 pagesSegmentation, Targeting and Positioning: What Is Segmentation, Anyone?Batul KudratiNo ratings yet
- HBS Case Harley Davidson in India (A)Document20 pagesHBS Case Harley Davidson in India (A)Mayank Kumar100% (3)
- By Abhishek Dewangan K07002 SecbDocument10 pagesBy Abhishek Dewangan K07002 SecbPrasaad TayadeNo ratings yet
- Final CMMDocument31 pagesFinal CMMAkanksha PendharkarNo ratings yet
- Club Mahindra: Stock PitchDocument36 pagesClub Mahindra: Stock Pitchkrushna vaidyaNo ratings yet
- Assignment - CargillsDocument7 pagesAssignment - CargillsPradeep AthurugirigeNo ratings yet
- Inside Indian EconomyDocument8 pagesInside Indian EconomySumNo ratings yet
- SEM 2B - Strategy AnalysisDocument43 pagesSEM 2B - Strategy AnalysisSteffen HoNo ratings yet
- Chameli Devi Institute of Management and Research: Prepared byDocument59 pagesChameli Devi Institute of Management and Research: Prepared byLokesh JainNo ratings yet
- IBS Final ProjectDocument12 pagesIBS Final ProjectNishiGogiaNo ratings yet
- Harley Davidson: Submitted By-Abhishek Pathak Faraz Khan Pratibha Yadav Rahul Pandey Sandeep Yadav Shubham SharmaDocument22 pagesHarley Davidson: Submitted By-Abhishek Pathak Faraz Khan Pratibha Yadav Rahul Pandey Sandeep Yadav Shubham SharmaManish KapoorNo ratings yet
- Jindal Satainless LTD.: Presented By: Ravi Kant MBA-323-2k9Document31 pagesJindal Satainless LTD.: Presented By: Ravi Kant MBA-323-2k9Ravi BeniwalNo ratings yet
- Indian Institute of Finance & Management: Presentation On:-The Market Structure of Bharti AirtelDocument19 pagesIndian Institute of Finance & Management: Presentation On:-The Market Structure of Bharti AirtelAnkit AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Business Model Innovation: Sijoy Syriac Section A 180103214Document3 pagesBusiness Model Innovation: Sijoy Syriac Section A 180103214Sijoy SyriacNo ratings yet
- Introductions: - Name - Last GPA - Last Degree and Grade - Institution Attended - Organization - Planned MajorDocument60 pagesIntroductions: - Name - Last GPA - Last Degree and Grade - Institution Attended - Organization - Planned Majorforigner 157No ratings yet
- 3484-3204 Kotler MM 13e Media 21Document31 pages3484-3204 Kotler MM 13e Media 21aditiNo ratings yet
- Day 12Document11 pagesDay 12Ama De SilvaNo ratings yet
- Ford Motor Co.Document18 pagesFord Motor Co.Lucky SpinserNo ratings yet
- Session 1 What Is Strategy: - Nutshell:-Strategy Is Choosing To Perform Activities Differently Than Rivals DoDocument10 pagesSession 1 What Is Strategy: - Nutshell:-Strategy Is Choosing To Perform Activities Differently Than Rivals DoYash NaudiyalNo ratings yet
- SWOT Analysis: SourceDocument11 pagesSWOT Analysis: SourceJulie Berg RasmussenNo ratings yet
- International Expansion A Roadmap To Successful Growth For EntrepreneursDocument12 pagesInternational Expansion A Roadmap To Successful Growth For EntrepreneursVaishali KakadeNo ratings yet
- Armin Ravoof (TVS Motors)Document18 pagesArmin Ravoof (TVS Motors)armeena falakNo ratings yet
- Chahal Current Affairs August 2022 MagazineDocument138 pagesChahal Current Affairs August 2022 MagazineLame GamerNo ratings yet
- Walton PDFDocument24 pagesWalton PDFMd. Tasnimul Hasan 2014171630No ratings yet
- Entry Mode of NestleDocument2 pagesEntry Mode of NestleTasnimul HasanNo ratings yet
- Summer 2019 PHI-401 Sec: 08 Course Name: Business EthicsDocument23 pagesSummer 2019 PHI-401 Sec: 08 Course Name: Business EthicsMd. Tasnimul Hasan 2014171630No ratings yet
- An Argumentation Model of Deliberative Decision-Making: January 2010Document18 pagesAn Argumentation Model of Deliberative Decision-Making: January 2010Md. Tasnimul Hasan 2014171630No ratings yet
- Group:7 Topic: COVID-19 and Political Change in South AsiaDocument23 pagesGroup:7 Topic: COVID-19 and Political Change in South AsiaMd. Tasnimul Hasan 2014171630No ratings yet
- Group:7 Topic: COVID-19 and Political Change in South AishaDocument24 pagesGroup:7 Topic: COVID-19 and Political Change in South AishaMd. Tasnimul Hasan 2014171630No ratings yet
- Name: Md. Tasnimul Hasan ID: 2014171630 POL 101.25: Reflective JournalDocument8 pagesName: Md. Tasnimul Hasan ID: 2014171630 POL 101.25: Reflective JournalMd. Tasnimul Hasan 2014171630No ratings yet
- Ethocs & Ethical TheoryDocument5 pagesEthocs & Ethical TheoryMd. Tasnimul Hasan 2014171630No ratings yet
- Gender Inequality and Women in IndiaDocument8 pagesGender Inequality and Women in IndiatrishnuNo ratings yet
- Raj Gopal A ChariDocument13 pagesRaj Gopal A ChariakshaymnnitNo ratings yet
- महात्मा बुद्ध PDFDocument35 pagesमहात्मा बुद्ध PDFAmit GoriyanNo ratings yet
- Devil's Advocate (Interview With Jaswant Singh)Document14 pagesDevil's Advocate (Interview With Jaswant Singh)Moideen MuseemNo ratings yet
- Presentation ON Tirupati (Andhra Pradesh) : Submitted To:-Mam Submitted By: - Name: - Class: - Roll NoDocument13 pagesPresentation ON Tirupati (Andhra Pradesh) : Submitted To:-Mam Submitted By: - Name: - Class: - Roll NosanchitNo ratings yet
- E-Sbbj New Ifsc Details - 09052017Document108 pagesE-Sbbj New Ifsc Details - 09052017ssagrawal2000No ratings yet
- SSC Phase 10 Graduate Level Question Paper 5 August 2022 in EnglishDocument28 pagesSSC Phase 10 Graduate Level Question Paper 5 August 2022 in EnglishSateeshNo ratings yet
- Tel DirectoryDocument35 pagesTel DirectoryS ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Maruti Suzuki - WagonrDocument30 pagesMaruti Suzuki - WagonrKhushboo GuptaNo ratings yet
- 2 Constituent AssemblyDocument3 pages2 Constituent AssemblyGaurav ScribdNo ratings yet
- BTMVC PvtSecCoDocument21 pagesBTMVC PvtSecCojapani08No ratings yet
- High GrowthDocument88 pagesHigh GrowthPrakash Kc0% (1)
- Country Analysis: INDIA: A Framework To Identify and Evaluate The National Business EnvironmentDocument18 pagesCountry Analysis: INDIA: A Framework To Identify and Evaluate The National Business Environmentuzmas_3No ratings yet
- Crystal Super AdministrationDocument4 pagesCrystal Super AdministrationJagdeep ArryNo ratings yet
- 002 7th Social (EM) HistoryDocument34 pages002 7th Social (EM) HistoryEdagotti JyothiNo ratings yet
- The Coming of The British WorksheetDocument5 pagesThe Coming of The British Worksheetlavender2x2No ratings yet
- World Tamil CM SpeechDocument10 pagesWorld Tamil CM SpeechthulasiramaswamyNo ratings yet
- Rbi Releases 'Quarterly Statistics On Deposits and Credit of SCBS: December 2018'Document1 pageRbi Releases 'Quarterly Statistics On Deposits and Credit of SCBS: December 2018'Vivek ThakurNo ratings yet
- PAT Cycle 2Document72 pagesPAT Cycle 2Sohail PathanNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 (Khilafat Movement)Document6 pagesUnit 7 (Khilafat Movement)Ruqaya AhmadNo ratings yet
- 1st Merit List Ma SociologyDocument15 pages1st Merit List Ma Sociologyacct offr maduraiNo ratings yet
- 24 S Vijay Anand TourismDocument15 pages24 S Vijay Anand TourismKaran Berry100% (1)
- About DharwadDocument52 pagesAbout DharwadAkshay KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Manipur Bank Branches ListDocument17 pagesManipur Bank Branches ListKhundrakpam SatyabartaNo ratings yet
- Asian Paint Strategic ManagementDocument27 pagesAsian Paint Strategic Managementarushpratyush100% (2)
- Jay - GhandiDocument2 pagesJay - GhandiMary Joyce Bautista SilverioNo ratings yet
- Dr. Ram Manohar Lohiya National Law University, Lucknow: Affirmative Action Law Project OnDocument12 pagesDr. Ram Manohar Lohiya National Law University, Lucknow: Affirmative Action Law Project OnVipul GautamNo ratings yet
- MADURAI654782x PDFDocument254 pagesMADURAI654782x PDFRaghuNo ratings yet
- A Study On Performance of Mutual FundDocument25 pagesA Study On Performance of Mutual Fundanushakc1991No ratings yet
- Niira Radia TapesDocument12 pagesNiira Radia TapesselvamuthukumarNo ratings yet