Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Service Product Life Cycle
Uploaded by
Arun Mishra0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views20 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views20 pagesService Product Life Cycle
Uploaded by
Arun MishraCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 20
Unit – III
Service Product Life Cycle
Arun Kumar Mishra
9893686820
arunjimishra@gmail.com
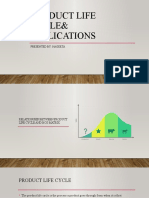
Service Product Life Cycle
• A service offer goes through stages of slow
acceptance, surge in popularity, steady
sales and sometimes drop in sales.
• The drop in sales can be due to many factors
including better substitute offers, product
obsolescence, changing preferences of the
consumers, etc.
Different Stage of Service Life Cycle
Stage 1: Conception/Incubation
• This is the incubation stage of a service product,
called New Product Development.
• It consists of the complete activities from
ideation, research and development and
product testing.
Stage 2: Introduction
• This is the stage soon after the launch of the
service offer.
• The public at large is not fully aware or exposed to
the offer.
• Sales growth or adoption by the market is
slow.
• The potential consumers display uncertainty
and resistance to any new products that are not
tried and tested.
• The service firm would be incurring heavy
expenditure, without any surge of revenue, only for
building up awareness through different types of
promotions.
Stage 3: Growth
• There will be a surge in demand for the service offer
when customers make repeat purchases.
• Potential customers come in due to
recommendations made by the formers and by the
generally positive publicity floating around.
• The peak of the profit curve does not coincide
with the peak of the sales curve.
• Surging sales, high voltage publicity, increasing
awareness & profits are all indications of success.
• The service marketer has to invest in
promotions to establish consumer attitudes,
increase market penetration and accessibility
through wider distribution reach.
Stage4: Maturity
• Sales at the maturity stage flatten & slow
down.
• Most possible product benefits are usually
developed & the market reaches the point of
saturation.
• More players in the market.
• Price cutting becomes norm for attracting
customers.
• The cost of doing business increases and the
market becomes stable.
• Sales growth can slow down to as low as zero
indicating complete saturation of the market.
Stage 5: Decline
• There is a downturn in revenues, customer
acquisition and retention.
• This could be due to a number of factors:
▫ Direct Competitors: could be doing a better job in
offering the same service with more value.
▫ Emergence of Substitute competition: The
market could witness other offers.
▫ Changing preference of the customers for the
service offer or the category.
▫ Technology obsolescence could make the
service offer redundant.
• The decline of the service offer can be permanent or
last for years.
Stage 6: Post-mortem
• This stage is an after-effect of the changing
environmental factors and the paradigm shift in
global managerial thinking.
• It implies that even after the service product and the
market have declined & the managers have stopped
any further investments, expenditures, or allocating
any responsibility & accountability, quality time is
spent in monitoring and servicing the
customers.
• Servicing of the customers & the service
products continue even if the product has been
withdrawn or the service firm has exited from the
market.
Marketing Responses to PLC
Different Marketing strategies applicable
during different stages of Service
Product Life Cycle
Introduction Stage
• The service marketer can choose from any of the
given four market entry alternatives.
Rapid Skimming
• It is an expensive initiative combining high
price and high promotion, directed at a low
aware, low willingness-to-buy market.
• This strategy is very useful if the market size
and potential is very high.
• When a service firm has a short-term goal of
profit maximization and increase in the
sales volume, it can resort to this strategy.
• The target markets are the Early Adopters &
Innovators who do not mind paying the high
price for the privilege of being the early users.
Slow Skimming
• Combination of high price & low promotion
• This strategy is used when the service firm is
confident that it can recover its investments in
sufficient time.
• This could be due to lack of competition,
requirement of heavy investments in technology
and systems to compete, etc.
• The target market, mostly business & industrial users
pays for the high price as the product is exclusive and
vital for their competitiveness.
• Five star hotels, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
and Supply Chain Management (SCM) System
providers like SAP, etc., used this strategy.
Rapid Penetration Strategy
• If the service firm has a long-term
objective of being a market leader, market
share and profit maximization, and
• If there exist entry barriers like intensive
competition, then this strategy is useful.
• The price of their offers is lower but there is
high visibility in the media.
• Big Bazaar, has successfully used this strategy
to make its mark.
• ICICI Bank is using rapid penetration strategy.
Slow Penetration Strategy
• When the market size is large, well aware of the
service offer and sensitive to price but the
competitive threats are almost non-existent, this
strategy is used.
• The long-term objective of the service firm is to
maximize sales or profits.
Growth Stage Strategies
• It is obvious that the Growth stage is a
battleground for survival.
• After achieving optimum awareness of the
service offer, the marketer should go all out in:
▫ Developing Customers
▫ Increasing Service Delivery Capability to
keep up with demand,
▫ Increasing Access and
▫ Making Distribution Effective.
▫ The advertising should emphasize on
features & image to create favourable attitudes.
Maturity Stage
• This stage will witness steady sales with frenetic
competition and price war.
• The marketer, therefore, concentrates on
▫ Maximizing profits,
▫ Seeks differentiation
▫ Offers wider range of products and
▫ Concentrates on building relationships and long-term
commitments with the customers.
• Product Line Modifications & Line Extensions can
be attempted here.
• The marketer should focus at consolidating the
position & maintaining the market share.
• The distribution should be the widest & multiple
channels can be looked into.
Decline Stage
• There is really nothing that the marketer can do if the
category of the offer itself is on the decline.
• Four strategies to tackle their products in decline:
▫ Leadership: When there is still potential in the market for
profit, the service firm can invest in product support to
strengthen it & emerge as a strong and competitive player.
▫ Niche: The service marketer can analyse & identify certain
specific segments that has potential for profitability.
▫ Harvest: The marketer is all set to totally exploit the offers.
Reduction of attributes in the augmented product level:
customer service, warranties, training etc.
▫ Divestment: If the marketer is savvy enough to detect the
symptoms of decline, the product line can be sold in the
latter part of maturity or earlier part of decline stages, at a
profit.
Any Questions?
You might also like
- The Corrs Runaway ChordsDocument8 pagesThe Corrs Runaway ChordsJessica AngelesNo ratings yet
- Setting Personal Selling ObjectivesDocument104 pagesSetting Personal Selling ObjectivesMir Mansoor Ali MagamiNo ratings yet
- Marketing Strategy For Small BusinessDocument4 pagesMarketing Strategy For Small BusinessChemical.AliNo ratings yet
- Joint VentureDocument23 pagesJoint VentureArun MishraNo ratings yet
- Vibrational Behaviour of The Turbo Generator Stator End Winding in CaseDocument12 pagesVibrational Behaviour of The Turbo Generator Stator End Winding in Casekoohestani_afshin50% (2)
- Marketing StrategyDocument40 pagesMarketing StrategyKAUSHIKNo ratings yet
- The Instruments of Trade Policy: Arun Mishra 9893686820Document13 pagesThe Instruments of Trade Policy: Arun Mishra 9893686820Arun MishraNo ratings yet
- Six Stages: Stage 1:the Mission StatementDocument36 pagesSix Stages: Stage 1:the Mission Statementparijatdubey100% (1)
- Proposals & Competitive Tendering Part 1: Strategy & Positioning to Win (Second Edition)From EverandProposals & Competitive Tendering Part 1: Strategy & Positioning to Win (Second Edition)No ratings yet
- Patterns of Entrepreneurship Management 4th Edition Kaplan Solutions Manual 1Document10 pagesPatterns of Entrepreneurship Management 4th Edition Kaplan Solutions Manual 1kathleenhutchinsonjrzoiyfbkt100% (22)
- Sales and Distribution ManagementDocument39 pagesSales and Distribution ManagementPrateek ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Ratio Method For Calculating A RatioDocument5 pagesRatio Method For Calculating A RatioFareeha KhanNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 (B)Document83 pagesUnit 2 (B)Alisha BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- Mounting Accessories 2017V03 - EN PDFDocument33 pagesMounting Accessories 2017V03 - EN PDFegalNo ratings yet
- Product Life Cycle Management: PLC Stages and StrategiesDocument17 pagesProduct Life Cycle Management: PLC Stages and StrategiessNo ratings yet
- Tao of Forgotten Food Diet - Taoist Herbology 2Document29 pagesTao of Forgotten Food Diet - Taoist Herbology 2ZioAngelNo ratings yet
- Reflection of Visit To The Museum of Natural HistoryDocument3 pagesReflection of Visit To The Museum of Natural Historyapi-302636182No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Franchise Market ProcessDocument19 pagesChapter 5 - Franchise Market ProcessGunther88% (8)
- Admin Case DigestDocument8 pagesAdmin Case DigestlenvfNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Neuroscience of MusicDocument13 pagesCognitive Neuroscience of MusicMitkoNo ratings yet
- Ansoff MatrixDocument25 pagesAnsoff Matrixrajisuma100% (1)
- Export Processing Zone Authority vs. CHRDocument1 pageExport Processing Zone Authority vs. CHRKling KingNo ratings yet
- Tourism PLC StrategiesDocument32 pagesTourism PLC StrategiesarushaNo ratings yet
- 11 Life Cycle StrategiesDocument7 pages11 Life Cycle StrategiesSarthak GuptaNo ratings yet
- Sales Strategy For PPE SegmentDocument31 pagesSales Strategy For PPE Segmentraman25100% (1)
- PLC Mktstrgy MktplanDocument40 pagesPLC Mktstrgy MktplanDEVASHISHNo ratings yet
- PLC StrategiesDocument14 pagesPLC StrategiesAkshat PanditNo ratings yet
- Product Life CycleDocument5 pagesProduct Life CyclevichuandiNo ratings yet
- Product Life Cycle: By: Aislinn E. SantanaDocument18 pagesProduct Life Cycle: By: Aislinn E. SantanaCombat GunneyNo ratings yet
- 1 Product Life CycleDocument16 pages1 Product Life Cycleveera kaurNo ratings yet
- PLC Stages & StrategiesDocument17 pagesPLC Stages & StrategiesNageeta BaiNo ratings yet
- Process of Sales PromotionDocument9 pagesProcess of Sales PromotionAniket MoolyaNo ratings yet
- Sales Management: Chapter - 02Document23 pagesSales Management: Chapter - 02Shariful IslamNo ratings yet
- The Product Life CycleDocument1 pageThe Product Life CycleSerena AboNo ratings yet
- PSM Chapter-2Document21 pagesPSM Chapter-2Shahed AhamedNo ratings yet
- Product Life CycleDocument3 pagesProduct Life Cyclekakaimraan025No ratings yet
- Managing Sales Promotions: Consumer, Trade & Salesforce TacticsDocument10 pagesManaging Sales Promotions: Consumer, Trade & Salesforce Tacticsp_charleNo ratings yet
- Planning, Sales Forecasting, and BudgetingDocument28 pagesPlanning, Sales Forecasting, and BudgetingVinay RaoNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Product Life Cycle in Rural MarketsDocument15 pagesUnderstanding the Product Life Cycle in Rural MarketsSneha Giji SajiNo ratings yet
- Franchise PERT Chart Marketing StrategiesDocument14 pagesFranchise PERT Chart Marketing StrategiesDanna Marie BanayNo ratings yet
- Sales Management Notes-1Document11 pagesSales Management Notes-1Shaurya SharmaNo ratings yet
- A Presentation ON Product Life Cycle BY: Abhinaw Pandey Dibyendu Mukherjee Subhraprova RoyDocument16 pagesA Presentation ON Product Life Cycle BY: Abhinaw Pandey Dibyendu Mukherjee Subhraprova RoyDibyendu MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Sales & Distribution ManagementDocument37 pagesUnit 1: Sales & Distribution Managementbhadauria99No ratings yet
- Unit II Strategy Formulation Value Chain AnalysisDocument19 pagesUnit II Strategy Formulation Value Chain AnalysisAmit Pandey100% (1)
- Product Life CycleDocument14 pagesProduct Life CycleAby MitNo ratings yet
- Product Life Cycle Stages & StrategiesDocument18 pagesProduct Life Cycle Stages & StrategiesDolly ParhawkNo ratings yet
- Product Life Cycle Stages & Marketing StrategiesDocument23 pagesProduct Life Cycle Stages & Marketing StrategiesUmairNo ratings yet
- Prestige Institute of Management and Research: Submitted ToDocument13 pagesPrestige Institute of Management and Research: Submitted ToAndrew WashingtonNo ratings yet
- 07 Target MarketingDocument5 pages07 Target MarketingSarthak GuptaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Management 7 - MarketingDocument50 pagesEngineering Management 7 - MarketingCraig PeriNo ratings yet
- Strategic Sales Management: A Boardroom Issue: Presented ByDocument31 pagesStrategic Sales Management: A Boardroom Issue: Presented Bysabyasachi sarkarNo ratings yet
- 4.5 The Four Ps of MarketingDocument121 pages4.5 The Four Ps of MarketingLUIS JEANPIER MARTINEZNo ratings yet
- Corona Virus IIDocument44 pagesCorona Virus IIBernadeth Siapo MontoyaNo ratings yet
- SDM G1 PresentationDocument16 pagesSDM G1 Presentationmohit rajputNo ratings yet
- Strategies for Managing a Product Life CycleDocument7 pagesStrategies for Managing a Product Life CycleRashmi Ranjan PanigrahiNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document32 pagesUnit 3Gouransh WadhwaniNo ratings yet
- MKT Rev Final ExamDocument39 pagesMKT Rev Final ExamclairecorfuNo ratings yet
- Market Segmentation, Targeting, and PositioningDocument6 pagesMarket Segmentation, Targeting, and PositioningChelsea MartinezNo ratings yet
- Chap 003Document45 pagesChap 003Alka FerrianNo ratings yet
- Marketing StrategiesDocument41 pagesMarketing StrategiesSairaj MohantyNo ratings yet
- Setting Personal Selling ObjectivesDocument104 pagesSetting Personal Selling ObjectivesMaruko ChanNo ratings yet
- Setting Media BudgetsDocument24 pagesSetting Media Budgetspirate85No ratings yet
- Pricing Strategies Over a Product's Life CycleDocument14 pagesPricing Strategies Over a Product's Life CycleMahak YadavNo ratings yet
- Business-Level Strategy Chapter SummaryDocument18 pagesBusiness-Level Strategy Chapter SummaryNando GontaniNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management IDocument10 pagesMarketing Management IDamodar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Amity School of Business: BBA V Semester Sales and Distribution ManagementDocument50 pagesAmity School of Business: BBA V Semester Sales and Distribution Managementpoojapanwar1_2587726No ratings yet
- Ch3 Planning, Sales Forecasting Phpapp01Document28 pagesCh3 Planning, Sales Forecasting Phpapp01Madhuri SheteNo ratings yet
- Sales and Distribution ManagementDocument52 pagesSales and Distribution ManagementfahdlyNo ratings yet
- Product Life CycleDocument12 pagesProduct Life CycleMohammad Rezwanur Rahman100% (8)
- Study of Rural Consumer Behavior Towards Rural Retail StoresDocument4 pagesStudy of Rural Consumer Behavior Towards Rural Retail StoresArun MishraNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Retailer Concentration and Store FormatDocument62 pagesThe Effect of Retailer Concentration and Store FormatArun MishraNo ratings yet
- Case of An Amusement ParkDocument1 pageCase of An Amusement ParkArun MishraNo ratings yet
- Impact of Packaging On The Buying Behaviour of ConsumersDocument12 pagesImpact of Packaging On The Buying Behaviour of ConsumersArun MishraNo ratings yet
- Consumer Survey QuestionnaireDocument2 pagesConsumer Survey QuestionnaireArun MishraNo ratings yet
- Marketing Mix and Branding Competitive Hypermarket StrategiesDocument19 pagesMarketing Mix and Branding Competitive Hypermarket StrategiesArun MishraNo ratings yet
- Unit III Decision Making ConceptsDocument16 pagesUnit III Decision Making ConceptsArun MishraNo ratings yet
- People in Services: Human Resources ManagementDocument15 pagesPeople in Services: Human Resources ManagementArun MishraNo ratings yet
- Exchange Rate Determination FactorsDocument21 pagesExchange Rate Determination FactorsArun MishraNo ratings yet
- Service Complaints & Recovery U5Document16 pagesService Complaints & Recovery U5Arun MishraNo ratings yet
- U3 Regional Integration & Trade ArrangementsDocument40 pagesU3 Regional Integration & Trade ArrangementsArun MishraNo ratings yet
- WTO's Importance for Indian BusinessDocument25 pagesWTO's Importance for Indian BusinessArun MishraNo ratings yet
- Physical EvidenceDocument27 pagesPhysical EvidenceArun MishraNo ratings yet
- Service Promotion Unit IIIDocument79 pagesService Promotion Unit IIIArun MishraNo ratings yet
- Theories of International Trade: Unit - IDocument24 pagesTheories of International Trade: Unit - IArun Mishra100% (1)
- Customer Satisfaction in ServicesDocument15 pagesCustomer Satisfaction in ServicesArun MishraNo ratings yet
- International Monetary Fund (IMF) Role and Function of Imf: Arun Mishra 9893686820Document27 pagesInternational Monetary Fund (IMF) Role and Function of Imf: Arun Mishra 9893686820Arun MishraNo ratings yet
- International Business Environment: Unit - IIDocument35 pagesInternational Business Environment: Unit - IIArun MishraNo ratings yet
- International Business: An Overview & Types: Unit - IDocument55 pagesInternational Business: An Overview & Types: Unit - IArun MishraNo ratings yet
- Decision Making TechDocument22 pagesDecision Making TechArun MishraNo ratings yet
- DBMS: An overview of database management systemsDocument31 pagesDBMS: An overview of database management systemsArun MishraNo ratings yet
- DSS - Relevance, Scope, Characteristics, Components: Dss & Mis - Unit IvDocument15 pagesDSS - Relevance, Scope, Characteristics, Components: Dss & Mis - Unit IvArun MishraNo ratings yet
- U3 Decision Making ConceptsDocument27 pagesU3 Decision Making ConceptsArun MishraNo ratings yet
- U5 Dialog Generation SystemDocument17 pagesU5 Dialog Generation SystemArun MishraNo ratings yet
- MNCs as Global IntermediariesDocument18 pagesMNCs as Global IntermediariesArun MishraNo ratings yet
- Unit V DSS Development: Arun Mishra 9893686820Document17 pagesUnit V DSS Development: Arun Mishra 9893686820Arun MishraNo ratings yet
- System Analysis & Design: Unit - IIDocument33 pagesSystem Analysis & Design: Unit - IIArun MishraNo ratings yet
- Dawn Ullmann - ReferenceDocument1 pageDawn Ullmann - Referenceapi-418750957No ratings yet
- UNITED STATES, Appellee, v. Joseph AITORO, Defendant, AppellantDocument14 pagesUNITED STATES, Appellee, v. Joseph AITORO, Defendant, AppellantScribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Assessment in Learning 1 Report (Formative Assessment)Document4 pagesAssessment in Learning 1 Report (Formative Assessment)Sampaga, Lovely Grace FerraroNo ratings yet
- Sept 2013 NewsletterDocument6 pagesSept 2013 NewsletterBKU1965No ratings yet
- Case Study EntDocument22 pagesCase Study Entnurul syafiqah yahyaNo ratings yet
- Partner With Rittal: It's Easy To Become A Rittal PartnerDocument10 pagesPartner With Rittal: It's Easy To Become A Rittal PartnerBhanu Uday SinghNo ratings yet
- Design Thinking What It Is Owen Korea05Document17 pagesDesign Thinking What It Is Owen Korea05DanijelBaraNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: Radhey ShyamDocument3 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Radhey ShyamGaurav SinghNo ratings yet
- Youth Stroke Education: 60min & 40min Lesson PlansDocument18 pagesYouth Stroke Education: 60min & 40min Lesson PlansShrishail ShreeNo ratings yet
- A Nurse's StoryDocument13 pagesA Nurse's StoryPeachee SolimanNo ratings yet
- Farm, George Orwell: Examples of AlliterationDocument4 pagesFarm, George Orwell: Examples of Alliterationruel_spideyNo ratings yet
- 5 Steps From Survey To Revenue InfographicDocument1 page5 Steps From Survey To Revenue InfographicBayCreativeNo ratings yet
- Is There a Batak HistoryDocument14 pagesIs There a Batak HistoryMWahdiniPurbaNo ratings yet
- Carte Tehnica Panou Solar Cu Celule Monocristaline SunPower 345 WDocument4 pagesCarte Tehnica Panou Solar Cu Celule Monocristaline SunPower 345 WphatdoggNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Saraf PDFDocument11 pagesJurnal Saraf PDFkade silabanNo ratings yet
- Thesis Jur ErbrinkDocument245 pagesThesis Jur Erbrinkgmb09140No ratings yet
- 100 Allowed FoodDocument2 pages100 Allowed Foodv_sharonNo ratings yet
- Graduation Day 2018 ScriptDocument3 pagesGraduation Day 2018 ScriptRiolyn Jhane Kho Ardena100% (1)
- TB CH 01 AppendixDocument15 pagesTB CH 01 AppendixtheplumberNo ratings yet
- 01 Lezione 1 Working LifeDocument18 pages01 Lezione 1 Working LifeVincenzo Di PintoNo ratings yet
- 2018 Sem 4Document8 pages2018 Sem 4shailesh latkarNo ratings yet