Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Enzymes: - Definition of Enzyme - Properties of Enzymes - Lock and Key Mechanism
Uploaded by
Maris0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views12 pagesOriginal Title
Enzymes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views12 pagesEnzymes: - Definition of Enzyme - Properties of Enzymes - Lock and Key Mechanism
Uploaded by
MarisCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
Enzymes
• Definition of enzyme
• Properties of enzymes
• Lock and Key Mechanism
03/12/2022 Created by E. Humel
Enzymes
Enzymes are biological catalysts produced by all living cells.
They speed up chemical reactions occurring in living organisms without
being changed themselves.
03/12/2022 Created by E. Humel
Enzymes
Enzymes are proteins that living cells produce from amino acids
obtained from the diet in animals, or manufactured in plants.
Without enzymes, chemical reactions would occur too slowly to
maintain life.
03/12/2022 Created by E. Humel
Examples
Amylase catalyses the breakdown of starch into sugars, mainly maltose.
It is present in saliva, pancreatic juice and germinating seeds.
03/12/2022 Created by E. Humel
Example
Catalase catalyses the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide into water and
oxygen:
Catalase is found in most cells.
It prevents the build-up of harmful hydrogen peroxide which is
produced as a by-product of many chemical reactions occurring incells.
03/12/2022 Created by E. Humel
Properties of Enzymes
All enzymes have similar properties:
• Enzymes are specific, i.e. each type of enzyme catalyses only one type
of reaction.
• Enzymes work best at a particular temperature known as the
optimum temperature. This is about37 °C for human enzymes.
03/12/2022 Created by E. Humel
Properties of Enzymes
The effect of temperature on the rate of a reaction catalysed by
enzymes.
03/12/2022 Created by E. Humel
Properties of Enzymes
High temperatures denature enzymes, i.e. the shape of the enzyme
molecules changes so that they are inactivated.
Enzymes start to be denatured at about 40 °C to 45 °C.
03/12/2022 Created by E. Humel
Properties of Enzymes
Enzymes work best at a particular pH known as the optimum pH. This is about pH7 for most enzymes.
The effect of pH on the rate of a reaction catalysed by enzymes.
03/12/2022 Created by E. Humel
Properties of Enzymes
• Extremes of acidity or alkalinity denature most enzymes.
• The action of enzymes is helped by certain vitamins and minerals, e.g.
vitamin B1 helps the action of respiratory enzymes.
• The action of enzymes is inhibited by certain poisons, e.g. arsenic and
cyanide.
03/12/2022 Created by E. Humel
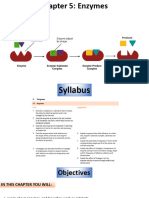
Lock and Key Mechanism
03/12/2022 Created by E. Humel
Effects of pH on the rate of a reaction
catalyzed by enzymes
03/12/2022 Created by E. Humel
You might also like
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- EnzymesDocument6 pagesEnzymesADEEL AHMADNo ratings yet
- Biology OlevelsDocument6 pagesBiology OlevelsMuhammad Usman AjmalNo ratings yet
- ENZYMESDocument2 pagesENZYMESSaadFarooqiNo ratings yet
- Structure and Functions in Living Things: Biological MoleculesDocument41 pagesStructure and Functions in Living Things: Biological MoleculesPooya ZargariNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument2 pagesEnzymesSabita SinghNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument5 pagesBiology NotesNoah RileyNo ratings yet
- Module 6 in BiochemistryDocument19 pagesModule 6 in BiochemistryjeromeNo ratings yet
- What Are Enzymes?Document6 pagesWhat Are Enzymes?eugene_970418755No ratings yet
- General Science: - Assignment No-8Document13 pagesGeneral Science: - Assignment No-8Prerna AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Alwadi International School Biology Grade 9 5. Enzymes NotesDocument43 pagesAlwadi International School Biology Grade 9 5. Enzymes NotesMohammed HelmyNo ratings yet
- Biologicalmolecules Grade 10 IgcseDocument46 pagesBiologicalmolecules Grade 10 IgcseShubh KakraniyaNo ratings yet
- Prelab 4Document6 pagesPrelab 4Trần Xuân QuỳnhNo ratings yet
- ENZYMES For MedicineDocument127 pagesENZYMES For MedicinefikaduNo ratings yet
- Gas Aqueous Solution: CatalaseDocument1 pageGas Aqueous Solution: CatalaseRochel CaduyacNo ratings yet
- Biology GCSE Unit 2 Part 4 Enzymes and DigestionDocument3 pagesBiology GCSE Unit 2 Part 4 Enzymes and DigestiontahamidNo ratings yet
- ENZYMES, This Is It!Document47 pagesENZYMES, This Is It!Myrian V. LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Enzymes (Biological Catalyst) : CatalaseDocument3 pagesEnzymes (Biological Catalyst) : CatalaseRayonesh RayanaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: The Chemistry of LifeDocument21 pagesBiochemistry: The Chemistry of LifeShahabNo ratings yet
- Enzymes IntroDocument49 pagesEnzymes IntroIcha AmandaNo ratings yet
- Ngorima Bio NotesDocument189 pagesNgorima Bio Notesluengwenya16No ratings yet
- Enzymes Quiz AnswersDocument2 pagesEnzymes Quiz AnswerslatteNo ratings yet
- Folio Biology EnzymeDocument10 pagesFolio Biology EnzymeIzZati YazidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 EnzymeDocument37 pagesChapter 5 Enzymejzdf2d9nnvNo ratings yet
- Folio Biology: Name: Abd Majid Bin MaarofDocument14 pagesFolio Biology: Name: Abd Majid Bin MaarofZeti Ahtar Abdullah SaparNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical BiochemistryDocument52 pagesPharmaceutical BiochemistryCherryl ValeraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Life NotesDocument8 pagesChemistry of Life Noteskolejose88No ratings yet
- ENZYMESDocument6 pagesENZYMESJumana ElkhateebNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of ProteinsDocument10 pagesPhysical Properties of Proteinsaditi_joshee419No ratings yet
- AQA GCSE Biology - Unit 2 Summary NotesDocument10 pagesAQA GCSE Biology - Unit 2 Summary NotesRajashree MuNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument18 pagesEnzymesDRMEHUL DAVE100% (1)
- Food BasicsDocument30 pagesFood BasicsRupini SinnanPandian100% (1)
- Enzymes and Biotechnology: See Also Rates Notes at End of 2. Extra Organic ChemistryDocument4 pagesEnzymes and Biotechnology: See Also Rates Notes at End of 2. Extra Organic ChemistryYusra RasoolNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument25 pagesEnzymesmymimi100% (1)
- Nutrients: Unit 3: Environmental ChemistryDocument28 pagesNutrients: Unit 3: Environmental ChemistrynithitheyellowstarNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: Natures Chemical WorkforceDocument17 pagesEnzymes: Natures Chemical Workforcescribd1No ratings yet
- Biological Molecules 2021Document5 pagesBiological Molecules 2021lowkeydeadNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument19 pagesEnzymesKimCharlsO. EstradaNo ratings yet
- Pre-Lab 3: 1. What Is A Catalyst and A Catalysis Reaction?Document3 pagesPre-Lab 3: 1. What Is A Catalyst and A Catalysis Reaction?Trần NguyênNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Fermentation 2Document10 pagesAssignment On Fermentation 2WALEXCELLENT ANo ratings yet
- R11. Enzymes and Other Proteins: Henedina A. Maini, RPH LecturerDocument33 pagesR11. Enzymes and Other Proteins: Henedina A. Maini, RPH LecturerChyra OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Enzyme: Enzymatic Reaction and TerminologyDocument6 pagesEnzyme: Enzymatic Reaction and TerminologySidra NosheenNo ratings yet
- Units Covered Objectives: Biological MoleculesDocument8 pagesUnits Covered Objectives: Biological MoleculesVibhor PandeyNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 9 ENZYMESDocument5 pagesExperiment No. 9 ENZYMESMissy Arabella PameNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument26 pagesEnzymesMichaella Denise San PedroNo ratings yet
- 04 Life Processes of Cell ArDocument72 pages04 Life Processes of Cell ArsheelaNo ratings yet
- NoteDocument18 pagesNotevarel rcNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: Catalytic ActionDocument13 pagesEnzymes: Catalytic ActionTemesgen MuletaNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document11 pagesModule 4yiyiyi7699No ratings yet
- Assymetric Organic CatalysisDocument24 pagesAssymetric Organic Catalysisnavaneetha santhoshNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: The Enzyme ActionDocument4 pagesEnzymes: The Enzyme ActionUmar AliNo ratings yet
- The Place Where These Molecules Fit Is Called The Active SiteDocument10 pagesThe Place Where These Molecules Fit Is Called The Active SiteNushrat KaziNo ratings yet
- GCSE EnzymesDocument32 pagesGCSE EnzymesFrankie BarnesNo ratings yet
- 2.4 Exploring EnzymesDocument17 pages2.4 Exploring EnzymesIsaacNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 4 The Chemicals of Life: There Are 7 Types of Nutrients, These AreDocument8 pagesChapter - 4 The Chemicals of Life: There Are 7 Types of Nutrients, These AreVandana Gupta SinglaNo ratings yet
- ENZYMEDocument19 pagesENZYMEImtiaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- How Enzymes WorkDocument15 pagesHow Enzymes WorkJXNo ratings yet
- 2 2-ProteinsDocument17 pages2 2-Proteinshero samilinNo ratings yet
- AS Biology Unit 1 EnzymesDocument42 pagesAS Biology Unit 1 EnzymesSany FahymNo ratings yet
- ReservationDocument7 pagesReservationMarisNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of LifeDocument23 pagesThe Chemistry of LifeMarisNo ratings yet
- Cells: - Definition of A Cell - Types of Cells - Examples of CellsDocument31 pagesCells: - Definition of A Cell - Types of Cells - Examples of CellsMarisNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Social Studies Week 10Document6 pagesGrade 10 Social Studies Week 10MarisNo ratings yet
- Total: CELEBRITY Family FeudDocument2 pagesTotal: CELEBRITY Family FeudMarisNo ratings yet
- Dahleh, 2021 PDFDocument13 pagesDahleh, 2021 PDFFani araujoNo ratings yet
- Composition and Properties of Apis Mellifera HoneyDocument34 pagesComposition and Properties of Apis Mellifera HoneyrestuniawNo ratings yet
- PH Control in Fermentation PlantsDocument2 pagesPH Control in Fermentation PlantssrshahNo ratings yet
- Biologi T4 Kertas 3Document14 pagesBiologi T4 Kertas 3nizampermaiNo ratings yet
- Desizing: Steeping For Affecting The Swelling and Softening of The Polyvinyl Alcohol FilmDocument6 pagesDesizing: Steeping For Affecting The Swelling and Softening of The Polyvinyl Alcohol FilmFarhana LaeeqNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument14 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationValentina RumhizhaNo ratings yet
- Ug Botany HonoursDocument73 pagesUg Botany Honoursbarlafrancis0No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument8 pagesUntitledQudsia AbrarNo ratings yet
- Senior Five BiologyDocument452 pagesSenior Five BiologyApuuli Kara100% (2)
- Catalysis Notes PDFDocument12 pagesCatalysis Notes PDFbbtbadal100% (2)
- Lab Report BioDocument9 pagesLab Report BioArissa SyaminaNo ratings yet
- Catalysis and Physical Organic ChemistryDocument49 pagesCatalysis and Physical Organic ChemistryAnandarup GoswamiNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: KM 0.5 M, Vmax 5nmol/minDocument5 pagesThis Study Resource Was: KM 0.5 M, Vmax 5nmol/minRickNo ratings yet
- Amit Kumar Sinha - Nutrizyme - Aquaculture HealthDocument40 pagesAmit Kumar Sinha - Nutrizyme - Aquaculture HealthMitshutopNo ratings yet
- Types of Catalysts - Arrhenius Equation and Reaction Mechanisms - Kinetics - Chemistry - Khan Academy PDFDocument9 pagesTypes of Catalysts - Arrhenius Equation and Reaction Mechanisms - Kinetics - Chemistry - Khan Academy PDFJohn Rene DalidaNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Organic ChemistryDocument6 pagesEnzymes Organic Chemistryمحمد الكبيسيNo ratings yet
- She29 PDFDocument124 pagesShe29 PDFfitashah2634100% (1)
- Pharmacology - Chapter 4Document5 pagesPharmacology - Chapter 4GILLAN KIN ROBLESNo ratings yet
- SIM Biochemistry ULO8Document34 pagesSIM Biochemistry ULO8Darl MalazarteNo ratings yet
- Journal of Bioremediation & Biodegradation: Trigonopsis VariabilisDocument7 pagesJournal of Bioremediation & Biodegradation: Trigonopsis VariabilisAvissauliaNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Summary NotesDocument12 pagesCell Biology Summary NotesQuesyNo ratings yet
- Bio Enzymes BoardworksDocument23 pagesBio Enzymes Boardworksjt75% (4)
- Cell Biology GlossaryDocument55 pagesCell Biology GlossaryEmrul HasanNo ratings yet
- Lab02 PDFDocument12 pagesLab02 PDFSiddharth KumraNo ratings yet
- Lab 8 Enzyme KineticsDocument5 pagesLab 8 Enzyme KineticsSiti Mastura Abdul RahmanNo ratings yet
- Yearly Lesson Plan Biology Form 4 YEAR 2022Document36 pagesYearly Lesson Plan Biology Form 4 YEAR 2022SITI NURSYIFA BINTI ROZALI Moe100% (1)
- Enzymes Lab ReportDocument11 pagesEnzymes Lab Reportcodybearden100% (2)
- 8464 B 1H MS Trilogy Specimen (Set 2) v1.0Document16 pages8464 B 1H MS Trilogy Specimen (Set 2) v1.0balkesalslkadi4No ratings yet
- FISHER. T - Traditional Detoxification Processes of Poisonous Foods in Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander CulturesDocument14 pagesFISHER. T - Traditional Detoxification Processes of Poisonous Foods in Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander CulturesTJNo ratings yet
- Ib Course PlannerDocument11 pagesIb Course PlannerTijana Tosic100% (1)