Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pneumothora X: Spontaneous
Uploaded by
Lav0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
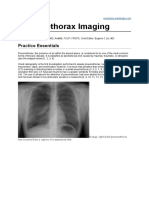
2 views14 pagesPneumothorax is the presence of air in the pleural space between the lungs and chest wall. It is commonly caused by trauma or medical procedures. On upright chest x-rays, it appears as a visceral pleural line separating from the chest wall. In supine views, air rises and is seen as a deep costophrenic sulcus or lucency in the upper chest. Hemothorax is blood in the pleural space, usually from blunt or penetrating trauma. It appears on chest x-rays as blunting of the costophrenic angle or blood layering in the chest cavity. Associated injuries like rib fractures are also common.
Original Description:
Radiology report
Original Title
Report-New Radiology
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPneumothorax is the presence of air in the pleural space between the lungs and chest wall. It is commonly caused by trauma or medical procedures. On upright chest x-rays, it appears as a visceral pleural line separating from the chest wall. In supine views, air rises and is seen as a deep costophrenic sulcus or lucency in the upper chest. Hemothorax is blood in the pleural space, usually from blunt or penetrating trauma. It appears on chest x-rays as blunting of the costophrenic angle or blood layering in the chest cavity. Associated injuries like rib fractures are also common.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views14 pagesPneumothora X: Spontaneous
Uploaded by
LavPneumothorax is the presence of air in the pleural space between the lungs and chest wall. It is commonly caused by trauma or medical procedures. On upright chest x-rays, it appears as a visceral pleural line separating from the chest wall. In supine views, air rises and is seen as a deep costophrenic sulcus or lucency in the upper chest. Hemothorax is blood in the pleural space, usually from blunt or penetrating trauma. It appears on chest x-rays as blunting of the costophrenic angle or blood layering in the chest cavity. Associated injuries like rib fractures are also common.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
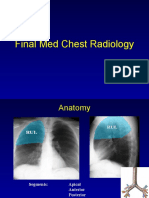
• The presence of air within the pleural space,
is one of the more common forms of thoracic
disease
Pneumothora • It is caused most often by trauma, either
x accidental or iatrogenic.
• In absence of such history, it is referred to as
spontaneous
• Spontaneous pneumothorax: Primary or
Secondary
• Primary: unassociated with clinical or
radiographic evidence of significant
pulmonary disease
• Secondary: in which significant pulmonary
disease is present
- Multifactorial pathogenesis
- MC in patients chronic obstructive
pulmonary disease (COPD)
• UPRIGHT
- radiologic diagnosis of pneumothorax can
Radiologic be made only after identifying the visceral
pleural line
Findings - pneumothorax is first evident near the
apex of the chest
- visceral pleural line is usually readily
identifiable
• If there is a strong suspicion clinically but
the pleural line is not identified, gas in the
pleural space can be detected by one of
the two procedures
Radiologic
Findings (1) Radiography in the erect position in full
expiration
(2) Radiography in the lateral decubitus
position with a horizonal x-ray beam
• SUPINE
- gas within the pleural space rises to the vicinity
of the diaphragm, the highest point in the
hemithorax in this position.
Radiologic -Depending on the size:
Findings • result can be an exceptionally deep radiolucent
costophrenic sulcus (deep sulcus sign)
• a lucency over the left or right upper quadrant
• much sharper than normal hemidiaphragm
with or without the presence of visceral pleural
line
• Right pneumothorax
• Portable AP supine
• (+) Deep Sulcus Sign
Hemothorax
• Hemothorax is the presence of blood within the pleural cavity and is
most frequently caused by blunt or penetrating trauma.
• The diagnosis is made on plain upright chest radiograph by the
visualization of fluid (blood) collecting in the right or left hemithorax
causing:
- blunting of the costophrenic angle
- larger hemithoraces: layering out of the blood occupying a portion of
the hemithorax
• Blood may also be seen tracking up the pleural margins of the chest
wall on radiographs
• Associated injuries such as rib fractures, pulmonary contusions, and
pneumothorax are common in the presence of hemothorax.
You might also like
- Pneumothorax: DR - Naveen Vennilavan R Pg-IiiDocument95 pagesPneumothorax: DR - Naveen Vennilavan R Pg-Iiinaveen vennilavanNo ratings yet
- Arthritis: by DR Samra Tahseen Registrar, Radiology LNHDocument86 pagesArthritis: by DR Samra Tahseen Registrar, Radiology LNHAngelic khanNo ratings yet
- JHA Lifting-Moving Heavy ObjectsDocument6 pagesJHA Lifting-Moving Heavy ObjectsMiguel AugustoNo ratings yet
- Unit IG2: Risk Assessment Part 1: BackgroundDocument23 pagesUnit IG2: Risk Assessment Part 1: Backgroundjimmy62% (13)
- Iliopsoas The Hidden Muscle - Anatomy, Diagnosis, and Treatment (2020)Document9 pagesIliopsoas The Hidden Muscle - Anatomy, Diagnosis, and Treatment (2020)yuliNo ratings yet
- EMPYEMA ReviewDocument95 pagesEMPYEMA ReviewBijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Pleural EffusionDocument3 pagesPleural EffusionRafahiah HaronNo ratings yet
- Emergency Point-of-Care UltrasoundFrom EverandEmergency Point-of-Care UltrasoundJames A. ConnollyNo ratings yet
- Imaging of The Respiratory SystemDocument105 pagesImaging of The Respiratory SystemMizrab Nadeem100% (1)
- Surgical Aspects of Pulmonary Infections: Kibrom Gebreselassie, MD, FCS-ECSA Cardiovascular and Thoracic SurgeonDocument60 pagesSurgical Aspects of Pulmonary Infections: Kibrom Gebreselassie, MD, FCS-ECSA Cardiovascular and Thoracic SurgeonVincent SerNo ratings yet
- L 5 - Lungs PathologyDocument128 pagesL 5 - Lungs PathologyDiana Popovici100% (1)
- Is.3786 2022Document18 pagesIs.3786 2022hamidNo ratings yet
- Read Between The Lines - Jo KnowlesDocument196 pagesRead Between The Lines - Jo KnowlesAndizazi NamNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Chest X Ray 2019Document11 pagesNeonatal Chest X Ray 2019Ahmad ApriansahNo ratings yet
- Chest Radiology Med Students2Document137 pagesChest Radiology Med Students2Mike Oluwaseun AmooNo ratings yet
- PneumothoraxDocument52 pagesPneumothoraxtrisna satrianaNo ratings yet
- Dr. Dicky SP.P Materi Gawat Darurat ParuDocument41 pagesDr. Dicky SP.P Materi Gawat Darurat ParuYuni SaviraNo ratings yet
- Gambaran Radiologis Pada Kegawatan Paru: Farah Fatma WatiDocument42 pagesGambaran Radiologis Pada Kegawatan Paru: Farah Fatma WatisabariaNo ratings yet
- Respirasi System ImagingDocument98 pagesRespirasi System ImagingRereNo ratings yet
- Pleural PathologiesDocument49 pagesPleural PathologiesIsaac ShirimaNo ratings yet
- Chest PainDocument15 pagesChest PainDwiky AmarullahNo ratings yet
- Pleural PathologiesDocument34 pagesPleural PathologiesAshwani RamawatNo ratings yet
- Pleural DiseasesDocument33 pagesPleural DiseasesDarawan MirzaNo ratings yet
- Pleural Effusion: Aarya PR Bds 3 YearDocument22 pagesPleural Effusion: Aarya PR Bds 3 YearThahseen TwzNo ratings yet
- Neonatal X Ray PDFDocument144 pagesNeonatal X Ray PDFnicuanumybabyNo ratings yet
- Basic Chest RadDocument112 pagesBasic Chest Radtesfayegermame95.tgNo ratings yet
- SGL6 - CoughDocument63 pagesSGL6 - CoughDarawan MirzaNo ratings yet
- Approach To Spontaneous PneumothoraxDocument25 pagesApproach To Spontaneous PneumothoraxMohdGhazaliAcoyNo ratings yet
- X Thorax BeoordelenDocument135 pagesX Thorax BeoordelenmtescasuraNo ratings yet
- PleuritisDocument48 pagesPleuritisMuhammad FhaliqNo ratings yet
- Radiology - Imaging of The ThoraxDocument49 pagesRadiology - Imaging of The Thoraxj.doe.hex_87No ratings yet
- Pleual ConditionsDocument61 pagesPleual ConditionsKandarp TrivediNo ratings yet
- The Radiology of PleuraDocument122 pagesThe Radiology of PleuraAimandu ShresthaNo ratings yet
- DR M Abdur Rahim M.D.:, Asst. Professor of MedicineDocument43 pagesDR M Abdur Rahim M.D.:, Asst. Professor of Medicinedr_abdurNo ratings yet
- What Is Ultrasound?Document15 pagesWhat Is Ultrasound?Al-Mukashfi TahaNo ratings yet
- Chest X Ray SessionDocument110 pagesChest X Ray SessionzakiyaNo ratings yet
- Topic 20. X-RayDocument4 pagesTopic 20. X-RayMadeline WanhartNo ratings yet
- PneumothoraxDocument30 pagesPneumothoraxnorhazirah hassanNo ratings yet
- ДД плеврального выпотаDocument26 pagesДД плеврального выпотаSriram Lakshmanan LNo ratings yet
- Chest Imaging PT 2Document70 pagesChest Imaging PT 2Andrei RomanNo ratings yet
- Nelson's Club - AtelectasisDocument22 pagesNelson's Club - AtelectasisAyen FornollesNo ratings yet
- Chest Trauma Management: Dr. Mariana UngurDocument81 pagesChest Trauma Management: Dr. Mariana UngurMariana UngurNo ratings yet
- DR Ahmed..thorasic SurgeryDocument20 pagesDR Ahmed..thorasic Surgeryمحمد رافد لطيفNo ratings yet
- Tension Pnemothorax 2022Document18 pagesTension Pnemothorax 2022DrKrishna ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Torso TraumaDocument37 pagesTorso TraumaFiza MushtaqNo ratings yet
- DR Ahmed - Surgery - Diseases of Pleura - 237Document18 pagesDR Ahmed - Surgery - Diseases of Pleura - 237Ahmed MohamadNo ratings yet
- Surgery TCVS SGD Guide KKDocument7 pagesSurgery TCVS SGD Guide KKFu Xiao ShanNo ratings yet
- Chest Radiography For InternsDocument42 pagesChest Radiography For InternsRose ValeNo ratings yet
- Fourth Problem: Group 3 Emergency Medicine Block 2018 Alvin RinaldoDocument93 pagesFourth Problem: Group 3 Emergency Medicine Block 2018 Alvin RinaldoSelly HerliaNo ratings yet
- Adult Chest X-RayDocument60 pagesAdult Chest X-RayAnil DasNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Reading EDEMA PARUDocument15 pagesJurnal Reading EDEMA PARUNatasena GpNo ratings yet
- Pneumothoraks Jurnal RadiologiDocument9 pagesPneumothoraks Jurnal RadiologiRachmi MerrinaNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Chest X-Ray-2019Document11 pagesNeonatal Chest X-Ray-2019madhu rathoreNo ratings yet
- Pleural EffusionDocument1 pagePleural EffusionElyas MehdarNo ratings yet
- Chest X-Rays: Phillip Smith, BA, RRTDocument29 pagesChest X-Rays: Phillip Smith, BA, RRTAlexandra PopaNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic TestsDocument70 pagesDiagnostic TestssimpforaiahNo ratings yet
- Lung UltrasoundDocument42 pagesLung UltrasoundBhaskar PendyalaNo ratings yet
- IImage Critique &pattern Recognition-1Document52 pagesIImage Critique &pattern Recognition-1Rabiu Salisu yunusaNo ratings yet
- Signs in Thoracic ImagingDocument100 pagesSigns in Thoracic ImagingMarcNicaNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Approach To TraumaDocument72 pagesDiagnostic Approach To TraumaJoher MendezNo ratings yet
- Pleural Effusion 23-24Document21 pagesPleural Effusion 23-24bazyan3aNo ratings yet
- Radiology Characteristics by Cell TypeDocument11 pagesRadiology Characteristics by Cell TypeCharm MeelNo ratings yet
- Dignostic Investigation in Respiratory SystemDocument99 pagesDignostic Investigation in Respiratory SystemGopi JaladiNo ratings yet
- NAME: Neema Tamang Roll No:-20 Subject:-Surgery Assignment Topic:-Pneumothorax Faculty: HA 2Document9 pagesNAME: Neema Tamang Roll No:-20 Subject:-Surgery Assignment Topic:-Pneumothorax Faculty: HA 2Shreekrishna BudhathokiNo ratings yet
- MKDDocument11 pagesMKDLavNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia Sample QuestionsDocument8 pagesAnesthesia Sample QuestionsLavNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia Drugs Part 1 and 2 CompiledDocument20 pagesAnesthesia Drugs Part 1 and 2 CompiledLavNo ratings yet
- Ecg ReadingDocument19 pagesEcg ReadingLavNo ratings yet
- Done - EDITED-HOPE1 - q1 - Mod5 - ObservesPersonalSafetyProtocolDocument24 pagesDone - EDITED-HOPE1 - q1 - Mod5 - ObservesPersonalSafetyProtocolMary Grace Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- Overview of Traumatic Upper Genitourinary Tract Injuries in Adults - UpToDateDocument22 pagesOverview of Traumatic Upper Genitourinary Tract Injuries in Adults - UpToDatecarlos.alberto.palacios.serratNo ratings yet
- DWN 1325Document8 pagesDWN 1325shourimitraNo ratings yet
- Foot ProtectionDocument29 pagesFoot ProtectionOmar RababaaNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of Wound Management - UpToDateDocument44 pagesBasic Principles of Wound Management - UpToDatePriscillaNo ratings yet
- Chest TrauDocument9 pagesChest TrauKaye CorNo ratings yet
- AC Voltage (V) #61-340 #61-342 Ranges & Accuracies: Digital Multimeter Instruction ManualDocument6 pagesAC Voltage (V) #61-340 #61-342 Ranges & Accuracies: Digital Multimeter Instruction Manualtallerleo551No ratings yet
- Canned Answer ExampleDocument3 pagesCanned Answer ExampleFaris YoungNo ratings yet
- O' Level Biology Notes: 2020-01-27 Mr. F.Moyo - 0733214032Document21 pagesO' Level Biology Notes: 2020-01-27 Mr. F.Moyo - 0733214032Dion MunyanyiNo ratings yet
- Module 3, Part A - Tort LawDocument50 pagesModule 3, Part A - Tort LawGian Tristan MadridNo ratings yet
- Mesa Puente - Stryker Tru-FitDocument37 pagesMesa Puente - Stryker Tru-FitJesus SilvaNo ratings yet
- Spinal Manual 20 August 2004Document235 pagesSpinal Manual 20 August 2004Forum PompieriiNo ratings yet
- 2023 USATKD Kyorugi Rules - Modified Head ContactDocument12 pages2023 USATKD Kyorugi Rules - Modified Head Contactyoussef mebarekNo ratings yet
- Latin MedicineDocument3 pagesLatin MedicineOmar El SamadNo ratings yet
- Management of Acute Severe Traumatic Brain Injury - UpToDate Jun 2019Document33 pagesManagement of Acute Severe Traumatic Brain Injury - UpToDate Jun 2019Johana Zamudio RojasNo ratings yet
- Review and Importance of Vajrasana in Daily LifeDocument6 pagesReview and Importance of Vajrasana in Daily LifeIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology 9Th Edition Martini Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument56 pagesFundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology 9Th Edition Martini Test Bank Full Chapter PDFgillanolympia4091253100% (10)
- Focal Peripheral NeuropathiesDocument6 pagesFocal Peripheral NeuropathiesSeptia P. Mayasari100% (1)
- Level 2 Risk Assessment Form - UTTM - Rev0Document2 pagesLevel 2 Risk Assessment Form - UTTM - Rev0Raznan RamliNo ratings yet
- Pe - Reviewer FinalsDocument5 pagesPe - Reviewer FinalsReign Helaena PardilloNo ratings yet
- Aoi 9 - Incident Reporting and Investigation v2-1Document10 pagesAoi 9 - Incident Reporting and Investigation v2-1chidinmaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - Teaching Vocab - English 11 Friends Global - Nga (Leader) - Tue123Document6 pagesLesson Plan - Teaching Vocab - English 11 Friends Global - Nga (Leader) - Tue123Khánh Ljnh TốngNo ratings yet
- Pathomechanics of Wrist and HandDocument16 pagesPathomechanics of Wrist and Handsonali tushamerNo ratings yet
- Biology Fluid RegulationDocument10 pagesBiology Fluid RegulationArcely EchaniqueNo ratings yet