0% found this document useful (0 votes)
261 views24 pagesReal Time Clock
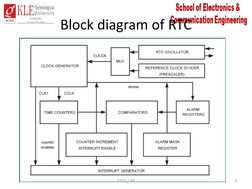
The document describes the real-time clock (RTC) in the LPC2148 microcontroller. The RTC keeps track of time even when the system is powered off by using ultra-low power circuitry. It provides values for seconds, minutes, hours, date, month, year, day of week, and day of year. The RTC functions using a set of registers that are split into groups for miscellaneous functions, time counting, alarms, and clock prescaling. It can generate interrupts on increments to the stored time values. The clock is interfaced by selecting ports, enabling the clock, loading time values, and converting to ASCII for display.
Uploaded by
Kedar BikkCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
261 views24 pagesReal Time Clock
The document describes the real-time clock (RTC) in the LPC2148 microcontroller. The RTC keeps track of time even when the system is powered off by using ultra-low power circuitry. It provides values for seconds, minutes, hours, date, month, year, day of week, and day of year. The RTC functions using a set of registers that are split into groups for miscellaneous functions, time counting, alarms, and clock prescaling. It can generate interrupts on increments to the stored time values. The clock is interfaced by selecting ports, enabling the clock, loading time values, and converting to ASCII for display.
Uploaded by
Kedar BikkCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- RTC Introduction: Provides an overview of RTC, explaining its timing functions and design goal of supporting powered and non-powered operations.
- Block Diagram of RTC: Explains the logical flow and component architecture of the RTC through a block diagram.
- Register Description: Covers the categorization of registers used in RTC by functionality.
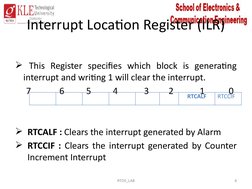
- Miscellaneous Register Group: Lists and describes registers related to miscellaneous functions including interrupt location and clock tick.
- Reference Clock Divider: Outlines the operation of the prescaler used to maintain consistent RTC rate despite varying clock speeds.
- Prescalar Integer Registers: Details the integer portion of the prescalar value for frequency management.
- RTC Interfacing: Details the interfacing steps to configure RTC with other modules.
- Reference Clock Divider Implementations: Explains practical implementations with examples for prescalar settings.
- References: Lists reference manuals relevant to the LPC2148 and RTC configurations.