0% found this document useful (0 votes)
81 views11 pagesUnderstanding Expert Systems in AI
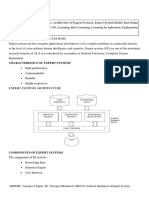
This document summarizes key aspects of expert systems in artificial intelligence. It describes expert systems as computer applications that solve complex problems in a particular domain at a level of human expertise. The major components of expert systems are the knowledge base, which contains domain knowledge, the inference engine, which manipulates the knowledge base to derive solutions, and the user interface. The document outlines the characteristics, capabilities, and limitations of expert systems, and describes the types of knowledge contained in the knowledge base and how it is acquired from human experts. It also discusses the strategies of forward and backward chaining used by the inference engine.
Uploaded by
Yousuf SheikhCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
81 views11 pagesUnderstanding Expert Systems in AI
This document summarizes key aspects of expert systems in artificial intelligence. It describes expert systems as computer applications that solve complex problems in a particular domain at a level of human expertise. The major components of expert systems are the knowledge base, which contains domain knowledge, the inference engine, which manipulates the knowledge base to derive solutions, and the user interface. The document outlines the characteristics, capabilities, and limitations of expert systems, and describes the types of knowledge contained in the knowledge base and how it is acquired from human experts. It also discusses the strategies of forward and backward chaining used by the inference engine.
Uploaded by
Yousuf SheikhCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd