Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Study Unit 5.5
Uploaded by
Mzingisi Tuswa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views19 pagesStephen needs to retrench 7 employees due to restructuring his business of over 100 employees. The document outlines the operational requirements and consultation process required for fair retrenchment. It defines operational requirements, discusses who to consult and topics for consultation. It addresses disclosure of information, fair selection criteria, severance pay, offers of reemployment, and the differences between small and large scale retrenchments as defined in Sections 189 and 189A of the Labour Relations Act.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentStephen needs to retrench 7 employees due to restructuring his business of over 100 employees. The document outlines the operational requirements and consultation process required for fair retrenchment. It defines operational requirements, discusses who to consult and topics for consultation. It addresses disclosure of information, fair selection criteria, severance pay, offers of reemployment, and the differences between small and large scale retrenchments as defined in Sections 189 and 189A of the Labour Relations Act.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views19 pagesStudy Unit 5.5
Uploaded by
Mzingisi TuswaStephen needs to retrench 7 employees due to restructuring his business of over 100 employees. The document outlines the operational requirements and consultation process required for fair retrenchment. It defines operational requirements, discusses who to consult and topics for consultation. It addresses disclosure of information, fair selection criteria, severance pay, offers of reemployment, and the differences between small and large scale retrenchments as defined in Sections 189 and 189A of the Labour Relations Act.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 19
IURI 222
STUDY UNIT 5.5
OPERATIONAL REQUIREMENTS
Su 5.5 Study outcomes
1. Define operational requirements
2. Know sections 189 and 189A
3. Distinguish between small and large scale retrenchments
4. Know ‘consultation’
5. Answer questions about disclosure of information
6. Discuss the following:
1. With who consults ER about what topics?
2. Fair selection criteria
3. Severance pay
4. Offer of re-employment
Due to the restructuring of his business (which employs over one hundred
employees), during which various departments were shuffled and some
functions ceased, Stephen has fifteen employees whose positions
ceased to exist. He could move eight of the employees to alternative
positions, but there is no longer place for the remaining seven
employees, thus they have now become redundant. What now?
Operational requirements
1. Economic, structural, technological and similar needs
2. S189 & S189A of the LRA
3. Small-scale and large-scale retrenchment
4. Sections indicate that dismissal should not take place if it can be avoided
5. If same results could be reached in another way without retrenchments –
dismissal not substantively fair
6. Reduction must be absolutely necessary – Johnson & Johnson and BMD
Knitting Mills
7. Thus, beware secret agenda!
Operational requirements
8. Substantive and procedural fairness in these cases?
SUBSTANTIVE: Was there truly a need of the business that could only
properly be addressed through retrenchments? Is the need
commercially justifiable?
PROCEDURAL: Did the employer follow the steps set out in the LRA?
9. S189 requires consultation, and subsection 2 indicates subjects for
consultation
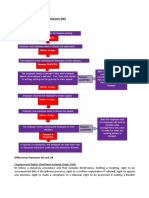
Pre-termination consultation
1. ‘Consultation’
1. “Meaningful joint -consensus seeking process”
2. Parties attempt to agree on certain aspects
3. Firstly attempt to avoid retrenchment altogether
4. If not – ameliorate the effects
5. Consultation must be exhaustive and all possibilities must be considered
– Johnson & Johnson; BEMAWU obo Mohapi (consult thoroughly on
every issue)
6. Employees or trade unions must make suggestions
Pre-termination consultation
7. Employer must not have made a final decision before the
consultation
8. Approach consultation with open mind and give each suggestion
reasonable consideration
9. Final decision rests with employer
10. Must not rush the process
11. All parties have to work together to find a solution
Pre-termination consultation
2. When must consultation commence?
1. When employer first contemplates retrenchment
2. Final decision must not have already been made
3. Employees informed as soon as it is realised that certain
circumstances at work may lead to retrenchments
Pre-termination consultation
3. Notice of consultation
1. Employer give proper notice to employees or trade unions of
need for retrenchment
2. Notice in writing
3. Notice should contain important information, ex.
- Reasons for retrenchment
- Number of employees affected
- When
- Selection criteria
- Severance packages
- Possibility of future re-employment
Pre-termination consultation
4. Who are consulted?
1. Anyone in terms of a collective agreement
2. If no such collective agreement exists – workplace forum
3. If no workplace forum – trade union
4. If no trade union – employees directly
5. Consult only employees affected by the retrenchment –
therefore not independent contractors
Pre-termination consultation
5. Topics for consultation
1. Measures taken to avoid dismissals
2. Measures taken to minimise number of employees
affected
3. Measures taken to change the time of dismissals
4. Measures taken to mitigate the adverse effects of the
dismissals
5. Selection criteria
6. Severance pay
Disclosure of information
1. Employer disclose information to employees/trade unions to be
able to make proper suggestions
2. Relevant information:
Reasons for retrenchment
Number of employees
Method of selection
Re-employment
When
Severance pay
3. Relevance sometimes difficult to determine
4. If employer refuses, prove lack in relevance
5. Certain information not obligated to provide: Which?
Final decision
1. Rests with employer
2. Only after the consultation process has been exhausted
3. NB - Employer can return to consultation after the decision to
address certain overlooked aspects
4. Can therefore revoke the final decision – has to be bona fide
Fair selection criteria
1. Use criteria agreed upon by
parties
2. If no such agreement – fair and objective criteria
3. Fairness forbid possible automatically unfair dismissal – specific groups
for impermissible reasons
4. LIFO best option – must not stray too far
5. LIFO not mandatory if it could lead to loss in necessary skills
6. Other acceptable criteria?
See item 9 of Code (Operational requirements)
7. CWIU v Latex Surgical Products and NUMSA v Columbus Stainless
Severance pay
1. Severance pay at 1 week salary for every year of continuous
service
2. If agreed on higher amount – use that
3. If lower – use legislation
4. Soften blow of circumstances – compensation
5. Amount unlimited
6. Limitations
Only for continuous service
Short break in service will not have affect
Only with operational requirements
Severance pay
7. When are employees not entitled?
8. Employee who accepts severance package can still open a case
for unfair dismissal
9. Service not interrupted during the transfer of a business –
service delivered at old employer are added to the total years of
service
Offers of re-employment
1. Employer inform parties of the possibility
2. Under no obligation – but if employer re-employ only a select
few – regarded as dismissal
3. Employer must defend his actions
4. If employer made a promise by way of an agreement – bound by
that agreement
S 189A Retrenchments
1. Large scale retrenchment – 10% and more
2. Employers with more than 50 employees but less than 200 – only if at least
ten are earmarked for retrenchment
3. More than 200 employees – 10% thereof retrenched, ex. 20 (on a scale as
from 200)
4. Difference between 189 and 189A – employees can strike
5. Employers must give notice of retrenchment
6. Facilitator plays a role here
7. Summarise the procedure for yourself from the text book and Act
Retrenchment of individual
1. Such employee can refer case for arbitration or to Labour Court
2. Employee has a choice
3. Requirements
Only one employee affected
For operational requirements
You might also like
- MCQs The Employees' Provident Funds Act, 1952 PDFDocument65 pagesMCQs The Employees' Provident Funds Act, 1952 PDFsrirama rao50% (8)
- c64 TE12 Secondment GuidelinesDocument11 pagesc64 TE12 Secondment GuidelinesNorjiella Binti Mohd Nurdin100% (1)
- Karnataka Minimum Wage 2016-17 PDFDocument133 pagesKarnataka Minimum Wage 2016-17 PDFSanthosh Prabhu100% (2)
- Unit 5.5 - Operational RequirementsDocument22 pagesUnit 5.5 - Operational RequirementsDylan BanksNo ratings yet
- Questions Chapter 04 Q&ADocument10 pagesQuestions Chapter 04 Q&AJane StoneNo ratings yet
- Discipline & Grievance CourseDocument47 pagesDiscipline & Grievance CoursesheldonNo ratings yet
- Employement Law2Document10 pagesEmployement Law2ampriestNo ratings yet
- Managing Poor Performance Policy Procedures For SCS April2023Document32 pagesManaging Poor Performance Policy Procedures For SCS April2023Rustam KoshelevNo ratings yet
- UKRI Ways of Working PolicyDocument7 pagesUKRI Ways of Working PolicyanupkrajakNo ratings yet
- Temporary Employee Contract ChecklistDocument2 pagesTemporary Employee Contract ChecklistHesham HassaanNo ratings yet
- 6 - Dismissal - Operational Requirements PDFDocument15 pages6 - Dismissal - Operational Requirements PDFTeboho Tebu MofokengNo ratings yet
- Nebosh Past Q August 2020Document32 pagesNebosh Past Q August 2020Taiwo100% (2)
- HRM13-Employee GrievancesDocument6 pagesHRM13-Employee GrievancesAnnalene BantilanNo ratings yet
- Strategies Taken During ConflictDocument2 pagesStrategies Taken During ConflictJada ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Example of A Disciplinary ProcedureDocument3 pagesExample of A Disciplinary ProcedureLAARNI SOTTONo ratings yet
- Study Unit 5.1 - The Meaning of Dismissals-1Document18 pagesStudy Unit 5.1 - The Meaning of Dismissals-1honwanaamanda1No ratings yet
- Managing Flexible Working Requests NIDocument20 pagesManaging Flexible Working Requests NIJade CraigNo ratings yet
- BA 101 Diwata GoldDocument2 pagesBA 101 Diwata GoldRexbelleNo ratings yet
- 09 Employment LawDocument7 pages09 Employment LawkketlenNo ratings yet
- Grievance HandlingDocument9 pagesGrievance HandlingLipika haldarNo ratings yet
- LAW604 - Week 10 (Redundancy The Law)Document14 pagesLAW604 - Week 10 (Redundancy The Law)Shareen ChandNo ratings yet
- What Are The Pros and Cons of EmploymentDocument4 pagesWhat Are The Pros and Cons of EmploymentKaguraNo ratings yet
- Industrial RelationsDocument12 pagesIndustrial RelationsRoisinNo ratings yet
- HR Managing Redundancy - 20230327T223951Document15 pagesHR Managing Redundancy - 20230327T223951Lamya AkoudNo ratings yet
- HRMG 3205 Topic 4Document9 pagesHRMG 3205 Topic 4ChristinaNo ratings yet
- Apl4802 Study Unit 4 The Ulp 2Document13 pagesApl4802 Study Unit 4 The Ulp 2tempeleNo ratings yet
- Pad363 Note CHP 5Document37 pagesPad363 Note CHP 5shandaardinaanakjontanNo ratings yet
- Lay OffDocument13 pagesLay OffsaakshibaggaNo ratings yet
- Unjust Dismissal - Canada Labour CodeDocument20 pagesUnjust Dismissal - Canada Labour CodeSarahNo ratings yet
- Sample COMPANY POLICY - RESIGNATIONDocument4 pagesSample COMPANY POLICY - RESIGNATIONNUR SARAH SALLEHNo ratings yet
- How To Dismiss For Poor PerformanceDocument3 pagesHow To Dismiss For Poor PerformanceLea HcimNo ratings yet
- Employment Law TaskDocument5 pagesEmployment Law TaskadNo ratings yet
- Grievances Final Group 01 NMP 23Document2 pagesGrievances Final Group 01 NMP 23floamiyaNo ratings yet
- IURI 222 Study Unit 6 Unfair Labour Practices - 2023Document13 pagesIURI 222 Study Unit 6 Unfair Labour Practices - 2023Sandiswa MazwiNo ratings yet
- Grievance RedressalDocument41 pagesGrievance RedressalJads GogoiNo ratings yet
- Grievance ProcedureDocument12 pagesGrievance Procedureshubh bhansali100% (1)
- Tutorial Week 5 Employment Law: By: Nurul Ashiqin Shamsuri Nurulashiqin@ucsiuniversity - Edu.myDocument41 pagesTutorial Week 5 Employment Law: By: Nurul Ashiqin Shamsuri Nurulashiqin@ucsiuniversity - Edu.myKheng How LimNo ratings yet
- Week 11 Reading Comprehension QuestionsDocument3 pagesWeek 11 Reading Comprehension QuestionsGabi CristinaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Law Impacting On Human Resources ManagementDocument20 pagesUnit 2: Law Impacting On Human Resources ManagementAthandile Silence DlaukanaNo ratings yet
- Averaging Hours Permit ApplicationDocument11 pagesAveraging Hours Permit ApplicationTravis BattingNo ratings yet
- Study Unit 6Document13 pagesStudy Unit 6Mzingisi TuswaNo ratings yet
- 2010 Employment Law Outline YurackoDocument33 pages2010 Employment Law Outline YurackofiskieNo ratings yet
- HRMG 3205 Topic 5Document6 pagesHRMG 3205 Topic 5ChristinaNo ratings yet
- How To Handle Employee GrievanceDocument12 pagesHow To Handle Employee GrievanceJitesh ChawlaNo ratings yet
- LMS DisciplinaryCode&ProcedureDocument18 pagesLMS DisciplinaryCode&ProcedureD HOLNo ratings yet
- LLA152 AdamsDocument9 pagesLLA152 AdamsVincentius KrigeNo ratings yet
- Grievance Handling and DisciplineDocument15 pagesGrievance Handling and DisciplineVinoth KumarNo ratings yet
- Law Chapter 5 Employee LawDocument10 pagesLaw Chapter 5 Employee LawYap AustinNo ratings yet
- DR Reddy DraftDocument2 pagesDR Reddy DraftKunal RautNo ratings yet
- How To Write A Business Report: Important Points To RememberDocument2 pagesHow To Write A Business Report: Important Points To Rememberno4russoNo ratings yet
- Employeegrievances PPT 111014093929 Phpapp01 120118075812 Phpapp01Document39 pagesEmployeegrievances PPT 111014093929 Phpapp01 120118075812 Phpapp01ricky_soni32No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Disciplinary System and Termination of ServiceDocument35 pagesChapter 7 - Disciplinary System and Termination of Serviceezzah dhysNo ratings yet
- Labor Review Final Exams 2022Document17 pagesLabor Review Final Exams 2022Shane JardinicoNo ratings yet
- Disciplinary GrievanceDocument28 pagesDisciplinary Grievancesiva100% (4)
- Grievance and Dispute Resolution ProceduresDocument7 pagesGrievance and Dispute Resolution ProceduresTayyabaNo ratings yet
- NEBOSH IG1 Open Book Exam August 2020Document19 pagesNEBOSH IG1 Open Book Exam August 2020Robert Gyebi Kofi100% (1)
- Summary of NegotiationsDocument7 pagesSummary of NegotiationsRidhima GuptaNo ratings yet
- CHP 10 - Internal Employee RelationsDocument20 pagesCHP 10 - Internal Employee RelationsFarah FarhathunNo ratings yet
- General Theme For Regulating/Not Regulating:: Employees v. Independent ContractorDocument32 pagesGeneral Theme For Regulating/Not Regulating:: Employees v. Independent ContractorMarissa MajorNo ratings yet
- Prepare to Impress: —Job Hunting for the Ambitious, Frustrated, Unemployed and Those Facing RedundancyFrom EverandPrepare to Impress: —Job Hunting for the Ambitious, Frustrated, Unemployed and Those Facing RedundancyNo ratings yet
- Steps Academics Can Take Now to Protect and Grow Their PortfoliosFrom EverandSteps Academics Can Take Now to Protect and Grow Their PortfoliosNo ratings yet
- Scenario 3 Surrebuttal PDFDocument3 pagesScenario 3 Surrebuttal PDFMzingisi TuswaNo ratings yet
- Study Unit 1 - IURI 376-2Document23 pagesStudy Unit 1 - IURI 376-2Mzingisi TuswaNo ratings yet
- Study Unit 1 Updated T. Viljoen - Includes Criminal LiabilityDocument28 pagesStudy Unit 1 Updated T. Viljoen - Includes Criminal LiabilityMzingisi TuswaNo ratings yet
- B. The Legal Practice Act 28 of 2014-1Document26 pagesB. The Legal Practice Act 28 of 2014-1Mzingisi TuswaNo ratings yet
- IURI 221 - 2022 - Study Unit 1Document36 pagesIURI 221 - 2022 - Study Unit 1Mzingisi TuswaNo ratings yet
- Mca 1944232Document116 pagesMca 1944232Mzingisi TuswaNo ratings yet
- Study Unit 1Document19 pagesStudy Unit 1Mzingisi TuswaNo ratings yet
- pvl1501 Law Persons Notes Cases 2008Document73 pagespvl1501 Law Persons Notes Cases 2008Mzingisi TuswaNo ratings yet
- Study Unit 6Document13 pagesStudy Unit 6Mzingisi TuswaNo ratings yet
- Iuri311 - PC Welcome - AdminDocument12 pagesIuri311 - PC Welcome - AdminMzingisi TuswaNo ratings yet
- Delport 2020 NewEntrepreneurialLaw-3Document1 pageDelport 2020 NewEntrepreneurialLaw-3Mzingisi TuswaNo ratings yet
- Pension Interest CaseDocument21 pagesPension Interest CaseMzingisi TuswaNo ratings yet
- Su 5 Criminal ProcedureDocument11 pagesSu 5 Criminal ProcedureMzingisi TuswaNo ratings yet
- World University RankingsDocument80 pagesWorld University RankingsMzingisi TuswaNo ratings yet
- IURI273 - Test - 4 - MEMO - Updated - 5.10.22 - 1Document7 pagesIURI273 - Test - 4 - MEMO - Updated - 5.10.22 - 1Mzingisi TuswaNo ratings yet
- R V Geddes 1964 RLR 288 AD Mistake in Criminal LawDocument10 pagesR V Geddes 1964 RLR 288 AD Mistake in Criminal LawMzingisi TuswaNo ratings yet
- 213 NotesDocument5 pages213 NotesMzingisi TuswaNo ratings yet
- Distinction Between Real Rights and Personal RightsDocument1 pageDistinction Between Real Rights and Personal RightsMzingisi TuswaNo ratings yet
- Conceptualising Exceptional CircumstanceDocument18 pagesConceptualising Exceptional CircumstanceMzingisi TuswaNo ratings yet
- MRL3702-Retrenchment in Terms of S189aDocument1 pageMRL3702-Retrenchment in Terms of S189aMzingisi TuswaNo ratings yet
- PVL3703-delict Notes 2 2006Document6 pagesPVL3703-delict Notes 2 2006Mzingisi TuswaNo ratings yet
- Revolutionizing IHRM With People AnalyticsDocument17 pagesRevolutionizing IHRM With People Analyticsshweta JainNo ratings yet
- Organizational StructuresDocument18 pagesOrganizational Structuresjapv_pasNo ratings yet
- altMBA BrochureDocument36 pagesaltMBA BrochureAlexei Diaz-Paz100% (1)
- TD - Outsourcing PDFDocument17 pagesTD - Outsourcing PDFrajaNo ratings yet
- Employees: Stakeholder AnalysisDocument3 pagesEmployees: Stakeholder AnalysisSamrin HassanNo ratings yet
- Stebleton IRM 0135023289-136014Document135 pagesStebleton IRM 0135023289-136014tofik2No ratings yet
- Crisis at MarcopoloDocument18 pagesCrisis at Marcopoloruts2611No ratings yet
- Tvet Glossary Acs Afd 2015Document25 pagesTvet Glossary Acs Afd 2015Carmen Rosa PerezNo ratings yet
- Human Resource ManagementDocument34 pagesHuman Resource ManagementItchigo KorusakiNo ratings yet
- Asos Vs PNCCDocument12 pagesAsos Vs PNCCpiptipaybNo ratings yet
- Romney AIS15 SM ch16Document22 pagesRomney AIS15 SM ch16Jonathan SinagaNo ratings yet
- Manila Terminal Company Vs CIRDocument2 pagesManila Terminal Company Vs CIRKirsten Denise B. Habawel-VegaNo ratings yet
- Quotation For Security Guards and Housekeeping Lpersons-340270102Document11 pagesQuotation For Security Guards and Housekeeping Lpersons-340270102ajaysharma.npcilNo ratings yet
- Gross Income (Tax)Document52 pagesGross Income (Tax)HOOPE JISONNo ratings yet
- Policy TemplateDocument2 pagesPolicy TemplateMelisaRoseNo ratings yet
- HRM6 TH EditionDocument17 pagesHRM6 TH EditionVarsha N kumarNo ratings yet
- Employers ObligationsDocument7 pagesEmployers ObligationsMohamed MeeranNo ratings yet
- A Research Assignment On: "Contemporary Issues On Labour Law Reform in India"Document13 pagesA Research Assignment On: "Contemporary Issues On Labour Law Reform in India"kritikaNo ratings yet
- MKTGDocument173 pagesMKTGYoga RajNo ratings yet
- Primera Lengua Extranjera Inglés IIDocument2 pagesPrimera Lengua Extranjera Inglés IIDepartamento InglésNo ratings yet
- Best Template For Training Needs AssessmentDocument115 pagesBest Template For Training Needs AssessmentMikealayNo ratings yet
- Levels of Students Satisfaction in Sma CDocument41 pagesLevels of Students Satisfaction in Sma CRJ Ladublan GalloNo ratings yet
- Charges of Civil Engineering ServicesDocument14 pagesCharges of Civil Engineering ServicesAgrawalAnurag100% (1)
- 5 6167848430359019603 CompressedDocument226 pages5 6167848430359019603 CompressedRafiq NadafNo ratings yet
- Employee Handbook 2016 Eddies PDFDocument41 pagesEmployee Handbook 2016 Eddies PDFMohammad Abd Alrahim ShaarNo ratings yet
- 2customer Service Satisfaction Among Senior Citizens in ChowkingDocument13 pages2customer Service Satisfaction Among Senior Citizens in ChowkingItsboi BoiyahNo ratings yet
- Opwdd MemoDocument5 pagesOpwdd MemoRick KarlinNo ratings yet