0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views11 pagesChapter-1 Business Statistics
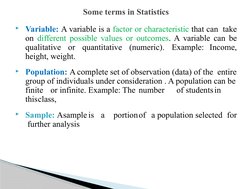
This document defines statistics and outlines its key stages and functions. It discusses the characteristics, limitations, and importance of statistics. It also describes some common statistical terms and the two main branches of statistics - descriptive and inferential. Finally, it provides examples of how statistics is applied in business and economics.
Uploaded by
Md. Anhar Sharif MollahCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views11 pagesChapter-1 Business Statistics
This document defines statistics and outlines its key stages and functions. It discusses the characteristics, limitations, and importance of statistics. It also describes some common statistical terms and the two main branches of statistics - descriptive and inferential. Finally, it provides examples of how statistics is applied in business and economics.
Uploaded by
Md. Anhar Sharif MollahCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd