Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EIA Introduction and Significance
Uploaded by
Muneeb Yaqoob 010 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views14 pagesOriginal Title
Eia Concept and Significance
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views14 pagesEIA Introduction and Significance
Uploaded by
Muneeb Yaqoob 01Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
EIA introduction AND SIGNIFICANCE
Dept of Geography and Disaster Management
University Of Kashmir
Presented By: Muneeb Yaqoob
Roll No. 01
INTRODUCTION
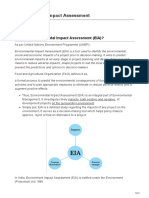
Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) is a process of
evaluating the likely environmental impacts of a proposed
project or development, taking into account inter-related
socio-economic, cultural and human-health impacts, both
beneficial and adverse.
UNEP defines Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) as a
tool used to identify the environmental, social and economic
impacts of a project prior to decision-making. It aims to
predict environmental impacts at an early stage in project
planning and design, find ways and means to reduce adverse
impacts, shape projects to suit the local environment and
present the predictions and options to decision-makers.
BRIEF HISTORY OF EIA
As the development continued in science and technology,
the various projects which were intended to provide benefits
to the people started to show negative effects in terms of
their effects on the environment , thus compelling us to
consider alternatives . Laws were introduced to counter such
effects from any project , thus highlighting the need for EIA .
The first country to give importance to EIA through its
National Environmental Protection Act of 1969 was the
United States
A large number of countries followed USA which were
having industries like Canada, Australia , Netherland , and
Japan adopted EIA legislation in 1973 , 1974, 1981 and 1984
respectively
After this the Columbia was the first developing country to
start the system of EIA in 1974 . EIA is developing in Africa
although some nations including Rwanda , Botswana and
Sudan have some experience of EIA
OECD issued recommendations of EIA to its states in 1974
and 79 . UNEP in 1987 set out goals and principles for the
number of countries and provide basic procedures for EIA
World Bank finally issued operational directive on EIA which
was revised and updated in October 1991.
ADB in 1990 issued guidelines for EIA
Importance of EIA was highlighted in the Bruntland report in
1987 and at United Nations Earth Summit on environment
and Development held at Rio De Jenerio in 1992
(UNCED,1992).
Worldwide, EIA is now practiced in more than 100 countries.
By the mid-1990s, some 110 countries applied EIA as a major
environmental policy.
HISTORY OF EIA IN INDIA
The Indian experience with Environmental Impact
Assessment began over 20 years back. It started in 1976-77
when the Planning Commission asked the Department of
Science and Technology to examine the river-valley projects
from an environmental angle.
Till 1994, environmental clearance from the Central
Government was an administrative decision and lacked
legislative support.
On 27 January 1994, the then Union Ministry of
Environment and Forests, under the Environmental
(Protection) Act 1986, promulgated an EIA notification
making Environmental Clearance (EC) mandatory for
expansion or modernization of any activity or for setting up
new projects listed in Schedule 1 of the notification.
The Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change
(MoEFCC) notified new EIA legislation in September
2006.
The notification makes it mandatory for various
projects such as mining, thermal power plants, river valley,
infrastructure (road, highway, ports, harbours and airports)
and industries including very small electroplating or foundry
units to get environment clearance.
However, unlike the EIA Notification of 1994, the new
legislation has put the onus of clearing projects on the state
government depending on the size/capacity of the project.
THE EIA PROCESS
EIA involves the steps mentioned below. However, the EIA process is
cyclical with interaction between the various steps.
Screening: The project plan is screened for scale of investment,
location and type of development and if the project needs
statutory clearance.
Scoping: The project’s potential impacts, zone of impacts, mitigation
possibilities and need for monitoring.
Collection of baseline data: Baseline data is the environmental
status of study area.
Impact prediction: Positive and negative, reversible and irreversible
and temporary and permanent impacts need to be predicted which
presupposes a good understanding of the project by the assessment
agency.
Mitigation measures and EIA report: The EIA report should
include the actions and steps for preventing, minimizing or by
passing the impacts or else the level of compensation for probable
environmental damage or loss.
Public hearing: On completion of the EIA report, public and
environmental groups living close to project site may be informed and
consulted.
Decision making: Impact Assessment Authority along with the experts
consult the project-in-charge along with consultant to take the final
decision, keeping in mind EIA and EMP (Environment Management
Plan).
Monitoring and implementation of environmental management
plan: The various phases of implementation of the project are monitored.
Assessment of Alternatives, Delineation of Mitigation Measures
and Environmental Impact Assessment Report: For every project,
possible alternatives should be identified, and environmental attributes
compared. Alternatives should cover both project location and process
technologies.
Once alternatives have been reviewed, a mitigation plan should be drawn up
for the selected option and is supplemented with an Environmental
Management Plan (EMP) to guide the proponent towards environmental
improvements.
Risk assessment: Inventory analysis and hazard probability
and index also form part of EIA procedures.
STAKEHOLDERS IN EIA
The Project Proponent
Government Authorities
Pollution Control Board (State or National)
Expert appraisal committee
Affected community
Social activist group
Regional centre of the MoEFCC
IMPORTANCE OF EIA
EIA links environment with development for
environmentally safe and sustainable development.
EIA provides a cost effective method to eliminate or
minimize the adverse impact of developmental projects.
EIA enables the decision makers to analyze the effect of
developmental activities on the environment well before the
developmental project is implemented.
EIA encourages the adaptation of mitigation strategies in the
developmental plan.
EIA makes sure that the developmental plan is
environmentally sound and within the limits of the capacity
of assimilation and regeneration of the ecosystem.
You might also like
- EIA notesDocument32 pagesEIA notesimabhiraj19No ratings yet
- Introduction to Environmental Impact AssessmentsDocument24 pagesIntroduction to Environmental Impact AssessmentsaddcdfsdfNo ratings yet
- Environmental Impact Assessment ProcessDocument6 pagesEnvironmental Impact Assessment Processsiva ramanNo ratings yet
- Eia 2020Document6 pagesEia 2020Aditi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Impact AssessmentDocument8 pagesEnvironmental Impact Assessmentjunaid khanNo ratings yet
- Environmental Impact Assessment 1Document6 pagesEnvironmental Impact Assessment 1Mrīgendra Narayan UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Environmental Impact AssessmentDocument15 pagesEnvironmental Impact AssessmentGAUTAM NATHNo ratings yet
- Environmental Law: End-Term AssignmentDocument18 pagesEnvironmental Law: End-Term AssignmentSadhvi SinghNo ratings yet
- EIA REPORT SUMMARYDocument54 pagesEIA REPORT SUMMARYPalak JoshiNo ratings yet
- EIA Ba LLB Revised 22-11-2019Document54 pagesEIA Ba LLB Revised 22-11-2019Palak JoshiNo ratings yet
- Environmental Law: End-Term AssignmentDocument18 pagesEnvironmental Law: End-Term AssignmentSadhvi SinghNo ratings yet
- Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) and Construction: Review PaperDocument4 pagesEnvironmental Impact Assessment (EIA) and Construction: Review PaperfaizNo ratings yet
- EIA 01 - Introduction and Overview of EIADocument28 pagesEIA 01 - Introduction and Overview of EIAAhanafNo ratings yet
- History of EIA in IndiaDocument31 pagesHistory of EIA in IndiaanaghaNo ratings yet
- EIADocument17 pagesEIAkonakala25_789833571No ratings yet
- Environmental Impact AssessmentDocument13 pagesEnvironmental Impact AssessmentPooja KishanpuriaNo ratings yet
- UNIT-I (1)Document86 pagesUNIT-I (1)ShrutiNo ratings yet
- Environment Impact AssessmentDocument5 pagesEnvironment Impact AssessmentSuresh ManiNo ratings yet
- Environmental Impact AssesmentDocument8 pagesEnvironmental Impact Assesmentnaman guptaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Impact AssessmentDocument20 pagesEnvironmental Impact AssessmentDanish RaisNo ratings yet
- EIA Process GuideDocument19 pagesEIA Process GuidebbnNo ratings yet
- Environment (Protection) Act, 1986Document7 pagesEnvironment (Protection) Act, 1986Shivangi BajpaiNo ratings yet
- Environmental Impact Assessment (Eia) : CHACHA Lilian G THOMAS Mugwe Lufyagila Ibrahim H MAGOHE StephenDocument34 pagesEnvironmental Impact Assessment (Eia) : CHACHA Lilian G THOMAS Mugwe Lufyagila Ibrahim H MAGOHE StephenEba EbaNo ratings yet
- EIA Process: 8 Key Steps for Environmental Impact AssessmentDocument3 pagesEIA Process: 8 Key Steps for Environmental Impact AssessmentAnand Krishna G Unni hs18h007No ratings yet
- EIA Process Session 13 1Document59 pagesEIA Process Session 13 1Vaishnavi JayakumarNo ratings yet
- Environmental Management and Co OverviewDocument6 pagesEnvironmental Management and Co Overviewstella njeriNo ratings yet
- Environment Project Sem6Document15 pagesEnvironment Project Sem6Amit RawlaniNo ratings yet
- Roll No 140 Environment LawDocument19 pagesRoll No 140 Environment Lawdnyanesh177No ratings yet
- EIA Scheme-Version 3 - Jun. 2015 - HRDocument20 pagesEIA Scheme-Version 3 - Jun. 2015 - HRRutuja GameyNo ratings yet
- EIA Process OverviewDocument16 pagesEIA Process OverviewAbu Zafor100% (3)
- EST Assignment 2, 1812055Document8 pagesEST Assignment 2, 1812055DEEPJYOTI DEKANo ratings yet
- Eia Lecture MdsDocument33 pagesEia Lecture MdsNamwangala Rashid NatinduNo ratings yet
- EIA - Environmental Impact Assessment Guide for Development ProjectsDocument15 pagesEIA - Environmental Impact Assessment Guide for Development ProjectsAyush BhadauriaNo ratings yet
- EiaDocument6 pagesEiaDIPAK KUMAR GUPTANo ratings yet
- Environmental Law - VII SemDocument15 pagesEnvironmental Law - VII SemShivam SinghNo ratings yet
- Understanding EIA Process and Its EvolutionDocument13 pagesUnderstanding EIA Process and Its EvolutionMeharuNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On Environmental Impact Assessment and Management IV B. Tech II Semester (JNTU (A) - R13)Document9 pagesLecture Notes On Environmental Impact Assessment and Management IV B. Tech II Semester (JNTU (A) - R13)mekalaNo ratings yet
- Transpo ReportDocument12 pagesTranspo ReportRanZky MercadoNo ratings yet
- GEE11ADocument74 pagesGEE11ANICHOLEANDREA MARTINNo ratings yet
- Components of Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) - Environment NotesDocument8 pagesComponents of Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) - Environment NotesAminullah HamidiNo ratings yet
- EIADocument32 pagesEIAHershita SinghNo ratings yet
- Understanding EIADocument8 pagesUnderstanding EIAPranzalNo ratings yet
- Environment Impact Assessment 123Document83 pagesEnvironment Impact Assessment 123Sudip ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Impact Assessment and Emss: An IntroductionDocument17 pagesEnvironmental Impact Assessment and Emss: An IntroductionMunashe Josiah ChipatisoNo ratings yet
- EIA Process OverviewDocument44 pagesEIA Process OverviewAbdul Aziz100% (1)
- Understanding the Process and History of Environmental Impact AssessmentsDocument12 pagesUnderstanding the Process and History of Environmental Impact AssessmentsAarathi ManojNo ratings yet
- Eia 1Document42 pagesEia 1abhijeetNo ratings yet
- Environmental Impact Assesment PRESENTATIONDocument16 pagesEnvironmental Impact Assesment PRESENTATIONchurail khan100% (1)
- Teesta RiverDocument16 pagesTeesta RiverArvind NegiNo ratings yet
- ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ASSESSMENT (MSM3208) LECTURE NOTES 1-What Is EIADocument8 pagesENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ASSESSMENT (MSM3208) LECTURE NOTES 1-What Is EIAmamat88100% (12)
- EIA Lecture for Project Management CourseDocument33 pagesEIA Lecture for Project Management Courseg4goharNo ratings yet
- Eia Q & ADocument10 pagesEia Q & AAnkur YashNo ratings yet
- Environment Impact Assessment Process in India and The Drawbacks-1Document30 pagesEnvironment Impact Assessment Process in India and The Drawbacks-1Saurabh ChhabraNo ratings yet
- EIA As Per UNEPDocument8 pagesEIA As Per UNEPvinaykumar paidiNo ratings yet
- Valuation Note - Environmental IssuesDocument14 pagesValuation Note - Environmental IssuesEmmanuel OladeleNo ratings yet
- GALANG (M4-Elective1)Document4 pagesGALANG (M4-Elective1)jerkNo ratings yet
- Safeguarding the Environment in Mining Development ProjectsFrom EverandSafeguarding the Environment in Mining Development ProjectsNo ratings yet
- Environmental Policy Under Reagan's Executive Order: The Role of Benefit-Cost AnalysisFrom EverandEnvironmental Policy Under Reagan's Executive Order: The Role of Benefit-Cost AnalysisNo ratings yet
- A Model Environmental Code: The Dubai Environment LawFrom EverandA Model Environmental Code: The Dubai Environment LawNo ratings yet
- Hazardous Substances and Human Health: Exposure, Impact and External Cost Assessment at the European ScaleFrom EverandHazardous Substances and Human Health: Exposure, Impact and External Cost Assessment at the European ScaleNo ratings yet
- Technical Data Sheet: Product NameDocument3 pagesTechnical Data Sheet: Product NameAndres DelaCruzNo ratings yet
- Sagittarius Season WorkbookDocument50 pagesSagittarius Season Workbookmaevadrouot52No ratings yet
- Quadratics Unit Quiz #1Document3 pagesQuadratics Unit Quiz #1hix8073No ratings yet
- Logical FallaciesDocument15 pagesLogical FallaciesLouis Marvil AbalaNo ratings yet
- Green MarketingDocument20 pagesGreen MarketingMukesh PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- SDD GROUP (Zuhaira, Zikry, Athirah, Ariff, Aiman)Document11 pagesSDD GROUP (Zuhaira, Zikry, Athirah, Ariff, Aiman)MUHAMMAD HARITH IKHWAN ROSMAEININo ratings yet
- Danny Debois: Tips for Effective Whip Speeches in DebateDocument2 pagesDanny Debois: Tips for Effective Whip Speeches in DebateJOSE FRANCISCO VERGARA MUÑOZNo ratings yet
- Ilham Shalabi, Imam Muhammad Bin Saud Islamic UniversityDocument20 pagesIlham Shalabi, Imam Muhammad Bin Saud Islamic Universityaron victoryNo ratings yet
- CO2 Declaration Summary - Template - 1.2Document3 pagesCO2 Declaration Summary - Template - 1.2Musa GürsoyNo ratings yet
- Élan VitalDocument3 pagesÉlan Vitalleclub IntelligenteNo ratings yet
- Research Leadership As A Predictor of Research CompetenceDocument7 pagesResearch Leadership As A Predictor of Research CompetenceMonika GuptaNo ratings yet
- APC Easy UPS 1000VA Floor/Wall Mount 230V UPS Spec SheetDocument3 pagesAPC Easy UPS 1000VA Floor/Wall Mount 230V UPS Spec SheetÁrea de IngenieríaNo ratings yet
- An Empirical Investigation of Organizational Citizenship Behavior Ocb The Way To Improve Performance in Higher Education InstitutionsDocument3 pagesAn Empirical Investigation of Organizational Citizenship Behavior Ocb The Way To Improve Performance in Higher Education Institutionsሻሎም ሃፒ ታዲNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Conducting Condition Assessment of Education FacilitiesDocument200 pagesGuidelines For Conducting Condition Assessment of Education FacilitiesMichael MatshonaNo ratings yet
- (Reuters Institute For The Study of Journalism) James Painter - Climate Change in The Media - Reporting Risk and Uncertainty-I. B. Tauris (2013)Document192 pages(Reuters Institute For The Study of Journalism) James Painter - Climate Change in The Media - Reporting Risk and Uncertainty-I. B. Tauris (2013)Thomas Ravelly Batista dos SantosNo ratings yet
- Adequacy and Utilization of Instructional Resources For Skills Acquisiton in BrickDocument5 pagesAdequacy and Utilization of Instructional Resources For Skills Acquisiton in BrickSaidu NingiNo ratings yet
- ADVANCED PRACTICE TEST 2Document7 pagesADVANCED PRACTICE TEST 2phươngNo ratings yet
- Avinash Adluri PTE JourneyDocument6 pagesAvinash Adluri PTE Journeydarpan.groverNo ratings yet
- Budget of Work English 7: Quarter Competencies No. of Sessions First QuarterDocument3 pagesBudget of Work English 7: Quarter Competencies No. of Sessions First QuarterEllane Jean DeniegaNo ratings yet
- 13.ionic Equilibria NotesDocument37 pages13.ionic Equilibria Notesgeoboom12100% (15)
- Sow English Year 5 2021Document14 pagesSow English Year 5 2021AZRINA ZARIFAH BINTI ZAINAL MoeNo ratings yet
- PRINCIPLES OF DETERMINING WATER'S FORMULADocument1 pagePRINCIPLES OF DETERMINING WATER'S FORMULAMominul HaqueNo ratings yet
- m2 Arithmetic SequenceDocument9 pagesm2 Arithmetic Sequenceedmund roseteNo ratings yet
- Innovative Solution For Biomedical Waste ManagementDocument5 pagesInnovative Solution For Biomedical Waste Managementaysh2383No ratings yet
- 8. Abandoned, LostDocument11 pages8. Abandoned, LostValeria BotacheNo ratings yet
- Parts 1 and 2 Notes On The Coinage of Julian The ApostateDocument9 pagesParts 1 and 2 Notes On The Coinage of Julian The ApostateΣπύρος ΑNo ratings yet
- Excellent Student Achieves High MarksDocument2 pagesExcellent Student Achieves High MarksKhalid MeitaniNo ratings yet
- Functions in Real-Life SituationsDocument16 pagesFunctions in Real-Life SituationsJim Lloyd SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Leadership and Management ModuleDocument6 pagesLeadership and Management ModuleMichael AngelesNo ratings yet
- The Range and Application of Phast and Safeti Explosion Models For Facility Siting Work - 3 December - PresentationDocument60 pagesThe Range and Application of Phast and Safeti Explosion Models For Facility Siting Work - 3 December - PresentationsushantNo ratings yet