Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ECG-EKG Presentation - Gunda G
Uploaded by
Gadzika0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views21 pagesEKG
Original Title
ECG-EKG Presentation- Gunda g
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentEKG
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views21 pagesECG-EKG Presentation - Gunda G
Uploaded by
GadzikaEKG
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 21
ECG/EKG
By: Gunda Gadzika (RN)
Introduction
• Welcome this afternoons
presentation on ECG/EKG. I hope
we have a wonderful discussion
and your participation in the
discussion of outmost
importance to a productive
presentation.
GENERAL OBJECTIVE
• By the end of this Discussion, we
as a team must have a basic
understanding of an ECG and its
interpretation.
SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES
• Definition of terms
• Review of the A&P of the Conduction system
of the heart and how it relates to ECG.
• Understanding the 3, 5 and 12 lead ECGs.
• Interpretation of an ECG.
• Disorders Related to ECG Abnormalities
(Abnormal ECG). Why ECG?
DEFINITON OF TERMS
• Electrocardiography: A radiological examination of the heart to
show the electrical activity of the heart. It is simply process of
producing an electrocardiogram.
• Electrograph: A machine used for electrocardiography.
• Electrocardiogram: A record or Display of someone's heartbeat
produced by electrocardiography.
• PQRST: The P Wave: QRS Complex and a T Wave.
• Conduction System of the heart: The normal physiology
process of the impulse movement through the heart.
• SA/AV Nodes: The Sino atrial and the Atrioventricular Nodes,
the nodes responsible for the electrical activities of the heart.
CONDUCTION SYSTEM OF THE HEART
• The sinoatrial node located on the upper right
side of the right atrium produces primary
impulses at a rate of 60-80 times per minute
in an adult and so it is known as the pace
maker of the heart because the rate at which
the SA node fires impulses correlates with the
heartbeat
• The impulses fired move through the
Buchman's bundle to the left atrium causing
atrial systole.
• Other impulses go through the
atrioventricular node into the bundle of his
and are distributed thought the myocardium
by purkinje fibers branching off the bundle of
his. Thereby causing Ventricular Systole
• The electrocardiography is meant to pick up
this process of the hearts conduction system
and displays it to us in a language that we are
able to understand in from of a pattern on an
electrocardiogram.
ECG VARIATIONS
• The standard ECG is the 12 lead ECG but there
are other variations such as the 3 and the 5
lead ECG.
3 LEAD ECG
• A 3 Lead ECG uses 3 electrodes that are
labeled White, Black and Red. The colors are
not standard as there are two coloring
methods for an ECG. These 3 leads monitor
rhythm but does not reveal sufficient
information on ST elevation activity.
5 Lead ECG
• A 5 lead ECG uses 4 limb leads and 1 chest
lead. It helps improve the ST elevation reading
but its still inferior to the 12 lead ECG.
12 LEAD ECG
• In a 12 lead ECG there are 12 leads calculated
using 10 electrodes. 4 leads placed to the right
and left of the body appropriately and the 6
placed evenly and as per standard on the
chest. The 12 lead ECG is detailed and gives
complete detailed information of the heart
electrical activity which is off course displayed
to us on a graph.
12 Lead Chest
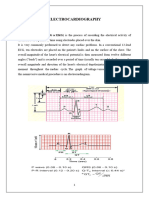
INTERPRETATION OF AN ECG
• The P wave represents depolarization of the
right and left atria.
• The QRS complex represent the spread of a
stimulus through the ventricles. However not
every ECG reading contains these variables and
so at times it might be a little confusing.
• The initial deflection of the QRS complex is
NEGATIVE (below the baseline) and it is called Q
Wave.
• The first positive deflection in the QRS
complex is an R wave.
• A negative deflection following the R wave is
called an S Wave.
• If the P wave is
WHY ECG?
• An ECG can help detect the following,
• Arrhythmias: This is where the heart beats irregular, too
fast or too slow.
• Coronary Heart Disease: Where a hearts blood supply is
interrupted.
• Heart Attacks: Sudden Blockage of blood supply to the
heart.
• Cardiomyopathies: Heart walls become too thick or too
thin.
• Electrolyte imbalances
You might also like
- Basic EKG RefresherDocument210 pagesBasic EKG RefresherAaron D. Phoenix100% (6)
- EKG and ECG Interpretation: Learn EKG Interpretation, Rhythms, and Arrhythmia Fast!From EverandEKG and ECG Interpretation: Learn EKG Interpretation, Rhythms, and Arrhythmia Fast!No ratings yet
- 12 Lead EKG 101: A Guide to Interpreting EKGs and Treating Cardiac PatientsDocument84 pages12 Lead EKG 101: A Guide to Interpreting EKGs and Treating Cardiac Patientszul fatmah100% (1)
- Dubin ECG Reference SheetsDocument13 pagesDubin ECG Reference SheetsEllie100% (1)
- ECG & EKG Interpretation: How to interpret ECG & EKG, including rhythms, arrhythmias, and more!From EverandECG & EKG Interpretation: How to interpret ECG & EKG, including rhythms, arrhythmias, and more!No ratings yet
- ECG: A Noob's Guide to Understanding ElectrocardiographyDocument103 pagesECG: A Noob's Guide to Understanding ElectrocardiographyGhaidaa Sadeq100% (1)
- Basic Principles of ECGDocument53 pagesBasic Principles of ECGSmita Jain100% (1)
- Basic Ecg Interpretation and Arrhythmia Recognition By: Ma. Victoria E. Martinez Er - RNDocument34 pagesBasic Ecg Interpretation and Arrhythmia Recognition By: Ma. Victoria E. Martinez Er - RNMavic Martinez BuntalesNo ratings yet
- ECG InterpretationDocument5 pagesECG InterpretationRichelle Dianne Ramos-Giang100% (3)
- Pharmacological Tools: Doses, Routes, and Uses of Common DrugDocument1 pagePharmacological Tools: Doses, Routes, and Uses of Common DrugApuntesdemedicinaa blogNo ratings yet
- Basic EKG InterpretationDocument48 pagesBasic EKG InterpretationAimee Ann Pauco MacaraegNo ratings yet
- EKG 12 Lead GuideDocument59 pagesEKG 12 Lead GuideM Lukman HakimNo ratings yet
- Ecg Treadmill and Holter TestDocument77 pagesEcg Treadmill and Holter TestRiteka Singh100% (1)
- ECG InterpretationDocument73 pagesECG Interpretationsultan khabeebNo ratings yet
- EKG | ECG: An Ultimate Step-By-Step Guide to 12-Lead EKG | ECG Interpretation, Rhythms & Arrhythmias Including Basic Cardiac DysrhythmiasFrom EverandEKG | ECG: An Ultimate Step-By-Step Guide to 12-Lead EKG | ECG Interpretation, Rhythms & Arrhythmias Including Basic Cardiac DysrhythmiasRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (5)
- ECG Analysis of Coronary CirculationDocument155 pagesECG Analysis of Coronary CirculationDeepika PatelNo ratings yet
- Avnrt AvrtDocument21 pagesAvnrt AvrtRima Rovanne Wenas100% (1)
- Santosh DevDocument45 pagesSantosh Devdevdsantosh100% (1)
- Utmc - Utoledo.edu Depts Nursing Pdfs Basic EKG RefresherDocument210 pagesUtmc - Utoledo.edu Depts Nursing Pdfs Basic EKG RefresherTrish HồNo ratings yet
- EKG Interpretation Basics Guide: Electrocardiogram Heart Rate Determination, Arrhythmia, Cardiac Dysrhythmia, Heart Block Causes, Symptoms, Identification and Medical Treatment Nursing HandbookFrom EverandEKG Interpretation Basics Guide: Electrocardiogram Heart Rate Determination, Arrhythmia, Cardiac Dysrhythmia, Heart Block Causes, Symptoms, Identification and Medical Treatment Nursing HandbookNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Investigations of Cardiovascular System: A Presentation by Tejaswini MDocument70 pagesDiagnostic Investigations of Cardiovascular System: A Presentation by Tejaswini MDea Amelia YolandaNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Arrythmias in The ED Menbeu Edited From AnaDocument106 pagesCardiac Arrythmias in The ED Menbeu Edited From AnaTemesgen Geleta100% (1)
- ECG1Document67 pagesECG1Farhan RosliNo ratings yet
- EKG | ECG Interpretation. Everything You Need to Know about 12-Lead ECG/EKG InterpretationFrom EverandEKG | ECG Interpretation. Everything You Need to Know about 12-Lead ECG/EKG InterpretationRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Ecg 01Document103 pagesEcg 01Bandar al ghamdi100% (1)
- NCM 112 MidtermDocument25 pagesNCM 112 MidtermJan Charlie Sophia100% (1)
- ECG Basics: A Guide to ElectrocardiographyDocument18 pagesECG Basics: A Guide to ElectrocardiographyArnab Guin100% (1)
- Basic ECG ReadingDocument41 pagesBasic ECG ReadingBenj100% (3)
- Drug Study CARDIODocument17 pagesDrug Study CARDIODiannetotz Morales100% (1)
- Atrial FlutterDocument16 pagesAtrial Flutterapi-527603714100% (1)
- Basic of ECG: Prepared By: Zahid HussainDocument38 pagesBasic of ECG: Prepared By: Zahid HussainZahid Hussain100% (1)
- Differential Diagnosis of CHDDocument42 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of CHDDr Piyush100% (1)
- ECG Guide: Understanding Heart Rhythms & EKG TestDocument10 pagesECG Guide: Understanding Heart Rhythms & EKG TestSilver Villota Magday Jr.No ratings yet
- ECG Self Study BookDocument390 pagesECG Self Study BookChandramohan SettyNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Arrest: April B. Perez, RN, Man, PHD, FpchaDocument50 pagesCardiac Arrest: April B. Perez, RN, Man, PHD, Fpchayuuki konnoNo ratings yet
- Group 4 - Baseline Heart Rate & EcgDocument38 pagesGroup 4 - Baseline Heart Rate & EcgTimothy John Bautista100% (2)
- Tomasz WikarekDocument95 pagesTomasz Wikareknamar13766No ratings yet
- Lecure-6 The Heat & Electrocardiogram (ECG)Document72 pagesLecure-6 The Heat & Electrocardiogram (ECG)Noor AhmedNo ratings yet
- 12 Lead EKG 101Document84 pages12 Lead EKG 101Clarke KrugmanNo ratings yet
- ECG Guide: Everything You Need to Know About ElectrocardiogramsDocument72 pagesECG Guide: Everything You Need to Know About ElectrocardiogramsGaras AnnaBerniceNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Tests for Heart ConditionsDocument70 pagesDiagnostic Tests for Heart ConditionsKusum RoyNo ratings yet
- ECG Complete LectureDocument33 pagesECG Complete LectureDr. SUVA NATHNo ratings yet
- Ecg or Electro Cardiogram and ElectrocardiographDocument20 pagesEcg or Electro Cardiogram and ElectrocardiographsureshNo ratings yet
- APEC 611 Scientific and Industrial Instrumentation: Electrocardiogram (ECG)Document22 pagesAPEC 611 Scientific and Industrial Instrumentation: Electrocardiogram (ECG)Faisal Bin KashemNo ratings yet
- MUCLecture 2021 1292271Document34 pagesMUCLecture 2021 1292271Kouka MahfoudiNo ratings yet
- ECG Interpretation: Prepared byDocument16 pagesECG Interpretation: Prepared bypipoahmed51No ratings yet
- Electrical Activity of The HeartDocument156 pagesElectrical Activity of The HeartNIRANJANA SHALININo ratings yet
- ElectrocardiogramDocument29 pagesElectrocardiogrammahnoorNo ratings yet
- ECG Basics: Understanding Waves, Intervals and LeadsDocument12 pagesECG Basics: Understanding Waves, Intervals and LeadsAprina RosyadahNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiogram: Electrocardiogram EKG Heart Heart's Electrical Activity DiagnosisDocument38 pagesElectrocardiogram: Electrocardiogram EKG Heart Heart's Electrical Activity DiagnosislorhenzsoNo ratings yet
- Ecg Reading PresntDocument101 pagesEcg Reading PresntbasilielnasirNo ratings yet
- ECG 22septDocument53 pagesECG 22septA ScribbbNo ratings yet
- ECG FILEDocument29 pagesECG FILEneha miriNo ratings yet
- Cardiology Teaching PackageDocument13 pagesCardiology Teaching Packagesarah morleyNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiogram (Ecg/Ekg) : Presented By: Elgeene E. DizonDocument41 pagesElectrocardiogram (Ecg/Ekg) : Presented By: Elgeene E. DizonElgeene DizonNo ratings yet
- ECGs The Basics (Part 1) LectureDocument32 pagesECGs The Basics (Part 1) Lectureliudmyla zakordonetsNo ratings yet
- Ecg 1Document198 pagesEcg 1hibaNo ratings yet
- ECGs The Basics (Part 1) LectureDocument33 pagesECGs The Basics (Part 1) Lectureliudmyla zakordonetsNo ratings yet
- How To Read An EcgDocument86 pagesHow To Read An EcgmajdNo ratings yet
- DrAbnet ECG - BasicsDocument99 pagesDrAbnet ECG - BasicsAbnet WondimuNo ratings yet
- Electro Cardiograph yDocument94 pagesElectro Cardiograph ykajonasfoodproductsNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiograph Y (ECG / Ekg) : Rose Dyane F - Nunag, RMT, MPHDocument52 pagesElectrocardiograph Y (ECG / Ekg) : Rose Dyane F - Nunag, RMT, MPHClaire GonoNo ratings yet
- Electro PhysiologyDocument108 pagesElectro PhysiologyGUTIERREZ, CRISHA ANDREA M.No ratings yet
- ECG Basics for CardiologistsDocument37 pagesECG Basics for CardiologistsLan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Muscle Contractions & Heart FunctionDocument22 pagesCardiac Muscle Contractions & Heart FunctionFransiska Anggreni SihotangNo ratings yet
- ECG EKG: BasicsDocument191 pagesECG EKG: BasicsSabio DenmenNo ratings yet
- ECG Interpretation & Dysrhythmia Identification: by Naaim AliDocument47 pagesECG Interpretation & Dysrhythmia Identification: by Naaim AliMohamed ElkadyNo ratings yet
- Electrocardiogram: What Is An ECG?Document8 pagesElectrocardiogram: What Is An ECG?Ali dhyaa100% (1)
- Biochem BSC 2010Document19 pagesBiochem BSC 2010GadzikaNo ratings yet
- Intro Lines of DefenseDocument15 pagesIntro Lines of DefenseGadzikaNo ratings yet
- CamScanner Document CollectionDocument103 pagesCamScanner Document CollectionGadzikaNo ratings yet
- The 17 Drawings You NEED and MUST Know by Heart by Gunda Gadzika (RN)Document1 pageThe 17 Drawings You NEED and MUST Know by Heart by Gunda Gadzika (RN)GadzikaNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Vascular DisordersDocument27 pagesPeripheral Vascular DisordersGadzikaNo ratings yet
- SilicosisDocument21 pagesSilicosisGadzikaNo ratings yet
- Inflammatory Conditions of the Urinary Tract: Cystitis, Pyelitis, Nephritis & Pyelonephritis (39Document9 pagesInflammatory Conditions of the Urinary Tract: Cystitis, Pyelitis, Nephritis & Pyelonephritis (39GadzikaNo ratings yet
- Properties of Water GundaDocument15 pagesProperties of Water GundaGadzikaNo ratings yet
- Understanding biochemistry basicsDocument16 pagesUnderstanding biochemistry basicsGadzikaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Education Roles QADocument25 pagesNursing Education Roles QAGadzikaNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy The Gastrointestinal TractDocument53 pagesHuman Anatomy The Gastrointestinal TractGadzikaNo ratings yet
- Position Paper: A B C D e F G H CDocument11 pagesPosition Paper: A B C D e F G H CNico IonaşcuNo ratings yet
- Direct Current Shock and Digitalis: A Clinical and Experimental StudyDocument6 pagesDirect Current Shock and Digitalis: A Clinical and Experimental StudyNur JanahNo ratings yet
- Congestive - Cardiac-FailureDocument38 pagesCongestive - Cardiac-FailureAkhil R KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Sinhala PPT CPRDocument54 pagesSinhala PPT CPRsl zam zam100% (1)
- Clinical Characteristic and Outcome of Acute Lower Respiratory Tract Infection in Children With Congenital Heart DiseaseDocument6 pagesClinical Characteristic and Outcome of Acute Lower Respiratory Tract Infection in Children With Congenital Heart DiseaseYenieMaciechESweteNo ratings yet
- PALS Precourse Self-AssessmentDocument3 pagesPALS Precourse Self-AssessmentMarsya Julia RiyadiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Amiodaron HydrochlorideDocument4 pagesDrug Study - Amiodaron HydrochlorideTwinkle SalongaNo ratings yet
- First Description of TVD in Basset HoundDocument4 pagesFirst Description of TVD in Basset HoundFlorencia SeneseNo ratings yet
- ACLS AHA Guidelines 2006 PosterDocument1 pageACLS AHA Guidelines 2006 PosterJeane SuyantoNo ratings yet
- Atrial Fibrillation: Racheal James Heart Rhythm Specialist Nurse UHWDocument37 pagesAtrial Fibrillation: Racheal James Heart Rhythm Specialist Nurse UHWAman ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Abnormal ECGDocument4 pagesWorksheet Abnormal ECGKarthik SNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Heart and Neck VesselsDocument10 pagesAssessment of The Heart and Neck VesselsJasmin MolanoNo ratings yet
- IAS AneurysmDocument13 pagesIAS AneurysmE'len HamidahNo ratings yet
- Cardiopulmonary ResuscitationDocument10 pagesCardiopulmonary ResuscitationZacchariah Zeref CaraigNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document2 pagesWeek 2Elaine Marie SemillanoNo ratings yet
- Defibrillation - Basic 55 For DistributorDocument14 pagesDefibrillation - Basic 55 For DistributorchanlalNo ratings yet
- Premature Ventricular Contractions: Reassure or Refer?: ReviewDocument7 pagesPremature Ventricular Contractions: Reassure or Refer?: ReviewFahmi RaziNo ratings yet
- AirwayDocument25 pagesAirwayKURIMAONGNo ratings yet
- Successful Resuscitation of VF Cardiac Arrest with Early CPR and DefibrillationDocument1 pageSuccessful Resuscitation of VF Cardiac Arrest with Early CPR and DefibrillationAfdhalia Khairunnisa SyammarhanNo ratings yet
- Accelerated Idioventricular RhythmDocument4 pagesAccelerated Idioventricular RhythmnasimhsNo ratings yet