0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views21 pagesOWAS
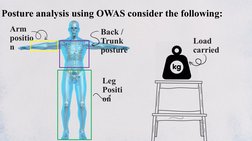
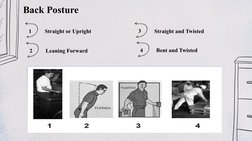
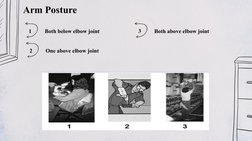
The Ovako Working Posture Analysis System (OWAS) was created in the 1970s by a Finnish steel company to evaluate working postures. It analyzes postures of the back, arms, legs, and carried loads on a scale of 1 to 4, with 4 being the most harmful. OWAS provides a simple but effective method for identifying problematic postures and evaluating ergonomic interventions. While easy to use, it does not capture posture duration or distinguish between left and right sides. Overall, OWAS remains a useful tool for job analysis and research.
Uploaded by
MarianneC.TaboadaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views21 pagesOWAS
The Ovako Working Posture Analysis System (OWAS) was created in the 1970s by a Finnish steel company to evaluate working postures. It analyzes postures of the back, arms, legs, and carried loads on a scale of 1 to 4, with 4 being the most harmful. OWAS provides a simple but effective method for identifying problematic postures and evaluating ergonomic interventions. While easy to use, it does not capture posture duration or distinguish between left and right sides. Overall, OWAS remains a useful tool for job analysis and research.
Uploaded by
MarianneC.TaboadaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd