0% found this document useful (0 votes)
157 views45 pagesCircle Geometry Basics
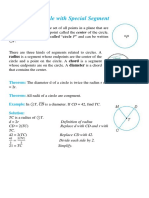
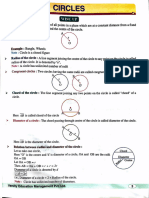
1. An inscribed angle is an angle whose vertex lies on the circle and whose sides contain chords of the circle.
2. Theorem 115 states that the measure of an inscribed angle is equal to half the measure of its intercepted arc.
3. The intercepted arc is the arc between the two chords that form the sides of the inscribed angle.
Uploaded by
Roselle G. FernandezCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
157 views45 pagesCircle Geometry Basics
1. An inscribed angle is an angle whose vertex lies on the circle and whose sides contain chords of the circle.
2. Theorem 115 states that the measure of an inscribed angle is equal to half the measure of its intercepted arc.
3. The intercepted arc is the arc between the two chords that form the sides of the inscribed angle.
Uploaded by
Roselle G. FernandezCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd