0% found this document useful (0 votes)
51 views31 pagesWeek 4 LP
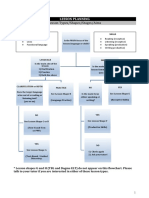
This document provides information about planning lessons. It discusses the importance of having clear objectives, formatting, and elements in a lesson plan. Common elements include objectives, pre-assessment, materials, warm-up, presentation, practice, evaluation, and application. It also describes the Presentation, Practice, Production (PPP) model for teaching grammar, which involves presenting new grammar, controlled practice, and free production. Finally, it recommends a lesson plan template that includes preparation, presentation, development, action, and closure phases to guide teaching a lesson.
Uploaded by
Daun PisangCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
51 views31 pagesWeek 4 LP
This document provides information about planning lessons. It discusses the importance of having clear objectives, formatting, and elements in a lesson plan. Common elements include objectives, pre-assessment, materials, warm-up, presentation, practice, evaluation, and application. It also describes the Presentation, Practice, Production (PPP) model for teaching grammar, which involves presenting new grammar, controlled practice, and free production. Finally, it recommends a lesson plan template that includes preparation, presentation, development, action, and closure phases to guide teaching a lesson.
Uploaded by
Daun PisangCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 31