Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Amino Acid New 1
Amino Acid New 1
Uploaded by
Sunny Khalifa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views14 pagesAmino acids are the building blocks of proteins and consist of an amino group, a carboxylic acid group, and an R group that varies between different amino acids. There are 20 standard amino acids, which are classified as essential or non-essential depending on whether the human body can synthesize them. Amino acids polymerize through peptide linkages between the amino and carboxyl groups to form polypeptides and proteins, which make up a major portion of the human body.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAmino acids are the building blocks of proteins and consist of an amino group, a carboxylic acid group, and an R group that varies between different amino acids. There are 20 standard amino acids, which are classified as essential or non-essential depending on whether the human body can synthesize them. Amino acids polymerize through peptide linkages between the amino and carboxyl groups to form polypeptides and proteins, which make up a major portion of the human body.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views14 pagesAmino Acid New 1
Amino Acid New 1
Uploaded by
Sunny KhalifaAmino acids are the building blocks of proteins and consist of an amino group, a carboxylic acid group, and an R group that varies between different amino acids. There are 20 standard amino acids, which are classified as essential or non-essential depending on whether the human body can synthesize them. Amino acids polymerize through peptide linkages between the amino and carboxyl groups to form polypeptides and proteins, which make up a major portion of the human body.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
Amino Acids
Made by Mudassar Zahoor Qureshi
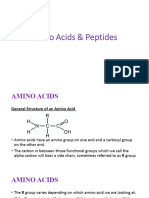
AMINO ACID
•Definition:
•Amino acids consists of one amino group and one
carboxyl group.
•The key elements of an amino acid are carbon,
hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen.
•General Formula:
Their general formula is given below
Types of Amino Acids
There are two types of amino acids
1. Essential amino acids
2. Non-essential amino acids
Essential amino acids
Those amino acids which our body cannot prepare but
are to be taken through diet. These amino acids are
required by our body.
Non-essential amino acids
Those amino acids which our body can prepare.
Function of Alkyl (R) Group
The difference in amino acids is due to the variation of R
group.
As R group varies, whole structure and function of
amino acid varies.
For Example
In above structures Glycine has only hydrogen atom in
R group, while Alanine has methyl group.
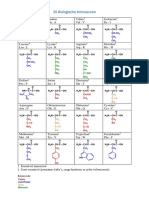
Classification
Amino acids are classified as follows:
Aliphatic
Aromatic
Polar
Non polar
Acidic
Basic
Acidic Amino Acid
Those amino acids which contain more than one
COOH group are called acidic amino acids.
For Example
Basic Amino Acid
Those amino acid which contain more than one group
of amino group in the molecule are called as basic
amino acids.
For example
Zwitter Ion
Some times amino acids contain a dionic structure i.e.
proton from carboxylic acid group is transferred to amino
group.
Such a structure is called Zwitter ion.
Resultant molecule is called to be a salt of amino acid.
Nomenclature of Amino Acid
Amino acids are named according to their trivial names
not according to their IUPAC names.
For example.
Glycine is derived from a word glycos meaning sweet.
Because of its sweet taste it is named as glycine.
For the sake of simplicity amino acids are represented
shortly by writing just first three letters of theair names.
i.e.
Valine is written as (Val)
Alanine is written as (Ala)
Glycine is written as (Gly) etc.
• Amino Acids are Building Blocks of
Proteins:
1. Thousands of amino acids polymerize to give
proteins.
2. Those proteins in turn form a major portion of our
body.
3. There are 20 amino acids which join to form all the
protein portion of our body.
Peptide Linkage
For protein formation, Amino acids link with each
other by the help of peptide linkage.
The special name given to the amide bond.
i.e. A bond between carboxyl group of one amino acid
and the amino group of other amino acid.
Formation of peptide linkage
Peptide linkage (bond) is formed by the elimination of
water molecule between the amino group of one
amino acid and carboxyl acid group of another.
The reaction is as follows:
Polypeptides
Polypeptides are chains of amino acids.
Polypeptides are essential portions of proteins in cells.
These can work together to form chains.
Thanks
You might also like
- Biochemistry FinalDocument71 pagesBiochemistry FinalJanie-Vi Gorospe100% (2)
- Prodew 400: Amino Acid Based Humectant For Skin CareDocument26 pagesProdew 400: Amino Acid Based Humectant For Skin CareKlara Miliktrisa KirbitievnaNo ratings yet
- Alanine Aminotransferase (Alt-Gpt)Document1 pageAlanine Aminotransferase (Alt-Gpt)Risqon Anjahiranda Adiputra50% (2)
- Amino Acids, Essential Amino Acids, Isoelectric Point, ZwitterionsDocument10 pagesAmino Acids, Essential Amino Acids, Isoelectric Point, ZwitterionsZafar IqbalNo ratings yet
- BCHM 201 Amino AcidDocument28 pagesBCHM 201 Amino AcidHabila OniNo ratings yet
- Iochemistry Roteins: Amino Acids As A Whole Are Represented by ThisDocument4 pagesIochemistry Roteins: Amino Acids As A Whole Are Represented by Thiskriss WongNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Amino Acids - ProteinsDocument81 pagesChemistry of Amino Acids - ProteinsgurmroadNo ratings yet
- BCH206 NURSING, Ana & PhysiologyDocument199 pagesBCH206 NURSING, Ana & PhysiologyjunaidukabirnabadeNo ratings yet
- Amino AcidsDocument24 pagesAmino AcidsAdam GawracdidNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Proteins and Amino Acids 1Document29 pagesLecture 3 Proteins and Amino Acids 1Caamir Dek HaybeNo ratings yet
- Appeton With Lysine Syrup: Harga: RP 81.900Document10 pagesAppeton With Lysine Syrup: Harga: RP 81.900ady-kresna-jaya-206No ratings yet
- Unit 1 Biochemistry Aminoacids & Proteins-1Document22 pagesUnit 1 Biochemistry Aminoacids & Proteins-1kamsjain6802No ratings yet
- Nitrogen Containing Compounds: Amino AcidsDocument10 pagesNitrogen Containing Compounds: Amino AcidsakshodhiniNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document76 pagesLecture 3salamnadanmustafaNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids Ms. Sarah ShakeelDocument35 pagesAmino Acids Ms. Sarah ShakeelRachna KhatriNo ratings yet
- Amino AcidDocument53 pagesAmino AcidRAJA AYYANo ratings yet
- PROTEIN (Biology Report) .PPTX FinalDocument20 pagesPROTEIN (Biology Report) .PPTX FinalHanz NazarenoNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids: ChemistryDocument6 pagesAmino Acids: ChemistryCarlosSchlozJuniorNo ratings yet
- Lif101 6Document34 pagesLif101 6Shubham MauryaNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid MetabolismDocument46 pagesAmino Acid Metabolismrsmbgss100% (1)
- Proteins and Amino AcidsDocument50 pagesProteins and Amino Acidsraddag100% (2)
- Amino Acid: Isoleucine Leucine Lysine Methionine Phenylalanine Threonine Tryptophan Valine HistidineDocument16 pagesAmino Acid: Isoleucine Leucine Lysine Methionine Phenylalanine Threonine Tryptophan Valine HistidineCrystal GarciaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Amino AcidDocument15 pagesChemistry of Amino AcidWay FarerNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Chapter 4Document16 pagesBiochemistry Chapter 4Jayson AguilarNo ratings yet
- M2.2 Demonstrating The Nature and Function of Biomolecules ProteinsDocument70 pagesM2.2 Demonstrating The Nature and Function of Biomolecules ProteinsCelestina JalemNo ratings yet
- ProteinDocument6 pagesProteinAbdullah Al MamunNo ratings yet
- Proteins: Amino AcidsDocument14 pagesProteins: Amino AcidsShivam KumarNo ratings yet
- Biochem LaibaDocument7 pagesBiochem LaibaLaiba ZulfiqarNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Chapter 4Document17 pagesBiochemistry Chapter 4Jayson AguilarNo ratings yet
- Amino AcidsDocument3 pagesAmino AcidsAya ShurrabNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument36 pagesBiomoleculesGaurav prajapatiNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids: Amino Acids: Are Organic Molecules That Are The Building Block ofDocument69 pagesAmino Acids: Amino Acids: Are Organic Molecules That Are The Building Block ofjkc collegeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 005 (Amino Acids and Peptides)Document43 pagesLecture 005 (Amino Acids and Peptides)Noel ManyiseNo ratings yet
- Protein and Amino Acid Chemistry: What Are PROTEINS?Document7 pagesProtein and Amino Acid Chemistry: What Are PROTEINS?Jayson AguilarNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids and PeptideDocument7 pagesAmino Acids and PeptideHƯNG LIÊU MẠNHNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 BIO201Document32 pagesLecture 3 BIO201Madiha Abu Saied Tazul Islam 1721217No ratings yet
- 3 - Biochemistry - 3rd Year Chem - Protein Structure and Function - Chapter-3Document21 pages3 - Biochemistry - 3rd Year Chem - Protein Structure and Function - Chapter-3MD. SAJID GHUFRANNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids: Structure and PropertiesDocument48 pagesAmino Acids: Structure and PropertiesOscar CruzNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids and Proteins: Larry Scheffler Lincoln High School Portland ORDocument35 pagesAmino Acids and Proteins: Larry Scheffler Lincoln High School Portland ORchuck55No ratings yet
- Amino Acids and ProteinDocument44 pagesAmino Acids and ProteinAliyu MohammedNo ratings yet
- Proteins TransesDocument7 pagesProteins TransesJamailah EncenzoNo ratings yet
- ProteinsDocument8 pagesProteins10m29satyamsinhaNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids and PeptidesDocument40 pagesAmino Acids and PeptidesDaniel LuchendoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6.1. Protein Structure and FunctionDocument18 pagesLesson 6.1. Protein Structure and FunctionCreeper RulezNo ratings yet
- CHY 47 Topic 4 2nd Sem 2018-2019 Protein Amino Acid PDFDocument129 pagesCHY 47 Topic 4 2nd Sem 2018-2019 Protein Amino Acid PDFHA RENo ratings yet
- Amino Acids StructureDocument7 pagesAmino Acids StructureBriziee xoNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids - Properties, Structure, Classification, FunctionsDocument6 pagesAmino Acids - Properties, Structure, Classification, Functionssattyadev95No ratings yet
- Protein DenaturationDocument12 pagesProtein DenaturationAhmed Elhakim100% (2)
- Lecture Protein and Amino AcidDocument47 pagesLecture Protein and Amino AcidDAVIE MATIASNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid 22Document12 pagesAmino Acid 22Ansh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistery:: Asparagine Is The 1Document12 pagesBiochemistery:: Asparagine Is The 1Naima AmjadNo ratings yet
- Activity No.1 in BIOCHEM BY CHRISTIAN JAMES B. CASJUPANG - 10 Newton NOV. 23Document2 pagesActivity No.1 in BIOCHEM BY CHRISTIAN JAMES B. CASJUPANG - 10 Newton NOV. 23Kerberos DelabosNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids and Protein 88Document32 pagesAmino Acids and Protein 88Omega ZuluNo ratings yet
- Final ProteinDocument57 pagesFinal ProteinmfernandezNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids 2018Document39 pagesAmino Acids 2018Elvie Gutierrez100% (1)
- CHAPTER II AMINO ACIDS and BCAADocument18 pagesCHAPTER II AMINO ACIDS and BCAAJohn TacordaNo ratings yet
- Proteins (Jigsaw)Document54 pagesProteins (Jigsaw)Milimo JingsawNo ratings yet
- All About ProteinsDocument16 pagesAll About ProteinsLenore ClyneNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids: Biocorp LLCDocument2 pagesAmino Acids: Biocorp LLCRica NorcioNo ratings yet
- AminoacidsDocument20 pagesAminoacidsChaudhary Sumit TatranNo ratings yet
- AminoacidsDocument63 pagesAminoacidsHamzaNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Engineering: Lect. 2Document43 pagesBiochemical Engineering: Lect. 2Mohamed AbdelaalNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 4 DK Spring 2024 Feb9Document3 pagesProblem Set 4 DK Spring 2024 Feb9Princess BellaNo ratings yet
- Protein Chemistry-1Document38 pagesProtein Chemistry-1Janhvi100% (1)
- Paper Chromatography: GROUP 5 (A2)Document38 pagesPaper Chromatography: GROUP 5 (A2)Zach Segmuel MiñanoNo ratings yet
- TGP Alt FluitestDocument4 pagesTGP Alt FluitestCristian LaraNo ratings yet
- B514ExamIIIA 10Document17 pagesB514ExamIIIA 10gunjan pratapNo ratings yet
- Carte Pediatrice NELSON BookDocument79 pagesCarte Pediatrice NELSON BookTRITEST TRITESTNo ratings yet
- GPT (Alt) : NADH. Kinetic UV. IFCC RecDocument1 pageGPT (Alt) : NADH. Kinetic UV. IFCC RecNawelNo ratings yet
- 20 Biologische Aminozuren: Asparaginezuur Asp DDocument2 pages20 Biologische Aminozuren: Asparaginezuur Asp Detienne.jooken8734No ratings yet
- Biomolecules Lecture CG Sir ALLENDocument54 pagesBiomolecules Lecture CG Sir ALLENJeevan KumarNo ratings yet
- ENVS 532: DR Assad Al-Thukair Associate ProfessorDocument17 pagesENVS 532: DR Assad Al-Thukair Associate ProfessorAbu Muhsin Al NgapakyNo ratings yet
- 9701 w03 QP 4Document12 pages9701 w03 QP 4Hubbak KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 - Amino Acid Oxidation and The Production of Urea PDFDocument10 pagesChapter 18 - Amino Acid Oxidation and The Production of Urea PDFpriyaprasad367792No ratings yet
- Coursebook Answers Chapter 28 Asal ChemistryDocument3 pagesCoursebook Answers Chapter 28 Asal ChemistryAditiNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid For NeonateDocument13 pagesAmino Acid For NeonateHerti PutriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Biochem ReviewerDocument5 pagesChapter 5 Biochem ReviewerCzarina Mae Quinones TadeoNo ratings yet
- Catabolic Activities of Aerobic HeterotrophsDocument26 pagesCatabolic Activities of Aerobic HeterotrophsSh SarkerNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Pearson EdexcelDocument36 pagesChemistry: Pearson EdexcelSanti DiazNo ratings yet
- Sintesis de N-Alquil Amino AcidsDocument45 pagesSintesis de N-Alquil Amino AcidsYbiedSalazarNo ratings yet
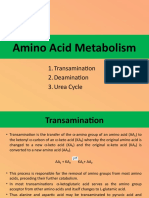
- Amino Acid Metabolism: 1. Transamination 2. Deamination 3. Urea CycleDocument14 pagesAmino Acid Metabolism: 1. Transamination 2. Deamination 3. Urea CycleDr. Subhadeep Sarker100% (1)
- Lecture Presentation - Protein MetabolismDocument8 pagesLecture Presentation - Protein Metabolismmr.avdheshsharma100% (1)
- Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 6th Ed Booksmedicos - Org (1) (0685-0755)Document71 pagesLehninger Principles of Biochemistry 6th Ed Booksmedicos - Org (1) (0685-0755)Ricky HerreraNo ratings yet
- Topic 19 HWDocument15 pagesTopic 19 HWNeetu BehalNo ratings yet
- Subjective QuestionsDocument5 pagesSubjective QuestionsAgustina MandasariNo ratings yet
- Catalogue EnglishDocument59 pagesCatalogue Englishbigweb100% (2)
- PROTEIN (Polypeptide) : Protein: Senyawa Organik Yang Merupakan Polimer Asam Amino Penyusun ProteinDocument79 pagesPROTEIN (Polypeptide) : Protein: Senyawa Organik Yang Merupakan Polimer Asam Amino Penyusun ProteinDwinur ChasanahNo ratings yet
- Human Metabolism Pathways and Clinical AspectsDocument8 pagesHuman Metabolism Pathways and Clinical AspectsSanjaya SenevirathneNo ratings yet
- Module (Amino Acids and Proteins)Document18 pagesModule (Amino Acids and Proteins)Edgie JunelaNo ratings yet