0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3K views55 pagesUnderstanding Fiscal Management in Governance
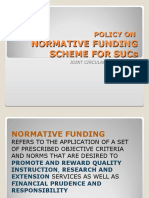
Fiscal management refers to the efficient use of capital funds and procurement of funds to effectively utilize in business operations. It is important for monitoring capital expenditures and cash flow, planning to minimize taxes, reducing operating expenses, and increasing overall efficiency. Effective fiscal management provides the foundation for strategic planning, decision making, and controlling budgets. It is practiced in both public and private sectors, with the goals of ensuring profitability, protecting financing, enabling economic growth, and environmental stewardship. Nations aim to adequately, efficiently, and equitably finance education, which consumes a significant portion of resources.
Uploaded by
Hadijah Limos Ali AbutazilCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3K views55 pagesUnderstanding Fiscal Management in Governance
Fiscal management refers to the efficient use of capital funds and procurement of funds to effectively utilize in business operations. It is important for monitoring capital expenditures and cash flow, planning to minimize taxes, reducing operating expenses, and increasing overall efficiency. Effective fiscal management provides the foundation for strategic planning, decision making, and controlling budgets. It is practiced in both public and private sectors, with the goals of ensuring profitability, protecting financing, enabling economic growth, and environmental stewardship. Nations aim to adequately, efficiently, and equitably finance education, which consumes a significant portion of resources.
Uploaded by
Hadijah Limos Ali AbutazilCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Introduction to Fiscal Management
- Overview of Fiscal Management
- Meaning and Importance of Fiscal Management
- Importance of Fiscal Management
- Public Financial Management
- Private Financial Management
- National Perspective on Financing Education
- Public and Private Sectors in Economic Development
- References