Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3) Stack
Uploaded by
Lol Telr0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views9 pagesOriginal Title
3) Stack.pptx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views9 pages3) Stack
Uploaded by
Lol TelrCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
What is a Stack?
A Stack is a linear data structure that follows the LIFO (Last-In-First-Out)
principle. Stack has one end, whereas the Queue has two ends (front
and rear). It contains only one pointer top pointer pointing to the
topmost element of the stack. Whenever an element is added in the
stack, it is added on the top of the stack, and the element can be
deleted only from the stack. In other words, a stack can be defined as a
container in which insertion and deletion can be done from the one
end known as the top of the stack.
Some key points related to stack
It is called as stack because it behaves like a real-world stack, piles of
books, etc.
A Stack is an abstract data type with a pre-defined capacity, which
means that it can store the elements of a limited size.
It is a data structure that follows some order to insert and delete the
elements, and that order can be LIFO or FILO.
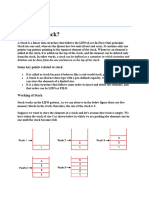
• Working of Stack
• Stack works on the LIFO pattern. As we can observe in the below
figure there are five memory blocks in the stack; therefore, the size
of the stack is 5.
• Suppose we want to store the elements in a stack and let's assume
that stack is empty. We have taken the stack of size 5 as shown below
in which we are pushing the elements one by one until the stack
becomes full.
• Since our stack is full as the size of the stack is 5. In the above cases,
we can observe that it goes from the top to the bottom when we
were entering the new element in the stack. The stack gets filled up
from the bottom to the top.
• When we perform the delete operation on the stack, there is only
one way for entry and exit as the other end is closed. It follows the
LIFO pattern, which means that the value entered first will be
removed last. In the above case, the value 5 is entered first, so it will
be removed only after the deletion of all the other elements.
• Standard Stack Operations
• The following are some common operations implemented on the
stack:
• push(): When we insert an element in a stack then the operation is
known as a push. If the stack is full then the overflow condition
occurs.
• pop(): When we delete an element from the stack, the operation is
known as a pop. If the stack is empty means that no element exists
in the stack, this state is known as an underflow state.
• isEmpty(): It determines whether the stack is empty or not.
• isFull(): It determines whether the stack is full or not.'
• peek(): It returns the element at the given position.
• count(): It returns the total number of elements available in a stack.
• change(): It changes the element at the given position.
• display(): It prints all the elements available in the stack.
• PUSH operation
• The steps involved in the PUSH operation is given below:
• Before inserting an element in a stack, we check whether the stack is full.
• If we try to insert the element in a stack, and the stack is full, then the
overflow condition occurs.
• When we initialize a stack, we set the value of top as -1 to check that the
stack is empty.
• When the new element is pushed in a stack, first, the value of the top gets
incremented, i.e., top=top+1, and the element will be placed at the new
position of the top.
• The elements will be inserted until we reach the max size of the stack.
• POP operation
• The steps involved in the POP operation is given below:
• Before deleting the element from the stack, we check whether the stack is
empty.
• If we try to delete the element from the empty stack, then the underflow
condition occurs.
• If the stack is not empty, we first access the element which is pointed by the
top
• Once the pop operation is performed, the top is decremented by 1, i.e.,
top=top-1.
• Implementing Stack functionalities using Linked List
• Push an element into Stack
Now, our Stack and Node class is ready. So, we will proceed to Push
operation on Stack. We will add a new element at the top of Stack.
• Algorithm
• Create a new node with the value to be inserted.
• If the Stack is empty, set the next of the new node to null.
• If the Stack is not empty, set the next of the new node to top.
• Finally, increment the top to point to the new node.
The method for Push will look like this.
internal void Push(int value)
{
Node newNode = new Node(value);
if (top == null)
{
newNode.next = null;
}
else
{
newNode.next = top;
}
top = newNode;
Console.WriteLine("{0} pushed to stack", value);
}
• Pop an element from Stack
We will remove the top element from Stack.
• Algorithm
• If the Stack is empty, terminate the method as it is Stack underflow.
• If the Stack is not empty, increment top to point to the next node.
• Hence the element pointed by top earlier is now removed.
The method for Pop will be like following.
void Pop()
{
if (top == null)
{
Console.WriteLine("Stack Underflow. Deletion not possible");
return;
}
Console.WriteLine("Item popped is {0}", top.data);
top = top.next;
}
• Uses of Stack
• Stack can be used to implement back/forward button in the browser.
• Undo feature in the text editors are also implemented using Stack.
• It is also used to implement recursion.
• Call and return mechanism for a method uses Stack.
• It is also used to implement backtracking.
Program of Stack
Menu Driven program in C implementing all the stack operations usin
g linked list :
You might also like
- StackDocument3 pagesStacksabbirsafi08No ratings yet
- Unit 3 StackDocument7 pagesUnit 3 StackShrijeshNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document43 pagesUnit 2Rohan AjeeNo ratings yet
- Stack OperationsDocument5 pagesStack OperationsMohammed Razid LathifNo ratings yet
- Stack OperationsDocument5 pagesStack OperationsMohammed Razid LathifNo ratings yet
- DS Module3Document54 pagesDS Module3Sreekesh GiriNo ratings yet
- StackDocument8 pagesStacksrujan koppunooriNo ratings yet
- What Is A Stack?: Some Key Points Related To StackDocument23 pagesWhat Is A Stack?: Some Key Points Related To StackKamran RaziNo ratings yet
- Stack: It Is Type of Linear Data Structure. Only Two Operations Are Allowed On StackDocument3 pagesStack: It Is Type of Linear Data Structure. Only Two Operations Are Allowed On StackGamer DavyNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 StackDocument73 pagesUnit 2 StackNone OtherNo ratings yet
- 5 StacksDocument9 pages5 Stacksofficials.chaitanyaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument7 pagesUntitledTanvi KakadNo ratings yet
- DS - Unit IDocument32 pagesDS - Unit IMuthu ManiyaNo ratings yet
- Stacks and ArrayDocument18 pagesStacks and ArrayAyushi KumariNo ratings yet
- Ktu Btech Module 2 Data Structures Semester 3Document12 pagesKtu Btech Module 2 Data Structures Semester 3Nazla Alwan P BNo ratings yet
- Stack Data Structure: Stack Introduction Implementation in PythonDocument7 pagesStack Data Structure: Stack Introduction Implementation in PythonKanchan jainNo ratings yet
- Data Structures: StackDocument19 pagesData Structures: StackShah GeeNo ratings yet
- Data Structures AssDocument11 pagesData Structures AssFiraol TesfayeNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4. Stack & QueueDocument26 pagesChapter-4. Stack & QueueQuazi Hasnat IrfanNo ratings yet
- Stack QueueDocument62 pagesStack QueuedmumminaNo ratings yet
- STACKS wk7Document29 pagesSTACKS wk7brightnanor19No ratings yet
- Stacks in JAVADocument30 pagesStacks in JAVAPulkit NarsariaNo ratings yet
- Data Structure: Stacks'.: PPO PresentationDocument18 pagesData Structure: Stacks'.: PPO PresentationPraveenVishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 StacksDocument23 pagesUnit 2 Stackstestingupon1No ratings yet
- UNIT4Document49 pagesUNIT4Balasatyaappaji99 KurellaNo ratings yet
- Module 7Document11 pagesModule 7pangan.kenneth117No ratings yet
- Data Structures Using CDocument78 pagesData Structures Using Cbiswadeepbasak0212No ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Stack DataStructure in C++Document40 pagesLecture 6 Stack DataStructure in C++Simple lyrics100% (1)
- Unit 3 NotesDocument67 pagesUnit 3 NotesRiya SuryavenshiNo ratings yet
- Exp 3 - Dsa Lab FileDocument10 pagesExp 3 - Dsa Lab Fileparamita.chowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 NotesDocument33 pagesUnit 3 Notesnkrithika65No ratings yet
- Unit 3Document135 pagesUnit 3Tansu GangopadhyayNo ratings yet
- Module - IIDocument54 pagesModule - IIangel0724No ratings yet
- StacksDocument22 pagesStacksad599066No ratings yet
- Unit Ii Linear Data Structures - Stacks, QueuesDocument201 pagesUnit Ii Linear Data Structures - Stacks, QueuesohmmuruganNo ratings yet
- UNIT III Data Structures OUDocument34 pagesUNIT III Data Structures OUjason.orchard.5341No ratings yet
- Stack ADT: What Is A Stack?Document10 pagesStack ADT: What Is A Stack?abhishekNo ratings yet
- Abstract Data Types (Linked List and Stack)Document30 pagesAbstract Data Types (Linked List and Stack)MOSES ALLENNo ratings yet
- Viva Final DS - LabDocument30 pagesViva Final DS - LabAsquare FoundationNo ratings yet
- CC4 ReviewerDocument20 pagesCC4 ReviewerCj RomeroNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Fundamentals of AlgorithmsDocument14 pagesUnit-1 Fundamentals of AlgorithmsNiloy SarkarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Stacks and Queue Chapter 4. Stacks and QueueDocument21 pagesChapter 5 Stacks and Queue Chapter 4. Stacks and QueueAbdissa Abera BachaNo ratings yet
- Stack@ C++ 12Document17 pagesStack@ C++ 12Vinod SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Stack OperationDocument13 pagesStack OperationHarvey AdorcoNo ratings yet
- Unit - 2 Linear Data Structures - Array & StackDocument19 pagesUnit - 2 Linear Data Structures - Array & StackDarshna SharmaNo ratings yet
- Stack and QueueDocument61 pagesStack and QueueshemseNo ratings yet
- Stacks: Basic Features of StackDocument32 pagesStacks: Basic Features of StackAneeb ArayilakathNo ratings yet
- Basic Operations in Stack:: Push OperationDocument3 pagesBasic Operations in Stack:: Push Operationذیشان چودھریNo ratings yet
- Data Structure and Algorithm: Ms. Zainab Imtiaz StackDocument5 pagesData Structure and Algorithm: Ms. Zainab Imtiaz StackUsama TariqNo ratings yet
- Data StructureDocument476 pagesData Structuredaman khuranaNo ratings yet
- Data Structures - Unit-3Document19 pagesData Structures - Unit-3Naresh BabuNo ratings yet
- ITC - Lab 10Document12 pagesITC - Lab 10aishaNo ratings yet
- Stacks and Queues Queues COS3711Document27 pagesStacks and Queues Queues COS3711JohannesNo ratings yet
- Sample - Bank Management SystemDocument9 pagesSample - Bank Management SystemRizwan UllahNo ratings yet
- A Micro Project On Dsu1111Document10 pagesA Micro Project On Dsu1111shaikhnumn22No ratings yet
- Unit-I: COMP302TH: Data Structure and File ProcessingDocument84 pagesUnit-I: COMP302TH: Data Structure and File ProcessingkkkkNo ratings yet
- Chapterfour StacksDocument16 pagesChapterfour Stacksamareadios60No ratings yet
- DSC Mod2Document27 pagesDSC Mod2Abrar AhmedNo ratings yet
- QueueDocument16 pagesQueueLol TelrNo ratings yet
- JAVA Imp For Mca 1st Year 1st Sem PDFDocument1 pageJAVA Imp For Mca 1st Year 1st Sem PDFLol TelrNo ratings yet
- Dsa 2 PDFDocument12 pagesDsa 2 PDFLol TelrNo ratings yet
- DSAmicronew3 PDFDocument22 pagesDSAmicronew3 PDFLol TelrNo ratings yet
- DataAnalyst Shanmukh Resume Updated PDFDocument1 pageDataAnalyst Shanmukh Resume Updated PDFLol TelrNo ratings yet
- 2) Binary Search Tree PDFDocument21 pages2) Binary Search Tree PDFLol TelrNo ratings yet
- 1) Linked ListDocument18 pages1) Linked ListLol TelrNo ratings yet
- 3) Data StructureDocument9 pages3) Data StructureLol TelrNo ratings yet
- 2) QueueDocument13 pages2) QueueLol TelrNo ratings yet
- Manual Tablespace ReorganizationDocument2 pagesManual Tablespace Reorganizationshaik.naimeNo ratings yet
- DBMS Final Report Music Database LibraryDocument11 pagesDBMS Final Report Music Database LibraryBilal100% (2)
- XPath Extension FunctionsDocument69 pagesXPath Extension FunctionsAlfaNo ratings yet
- Power BI Developer: Professional SummaryDocument6 pagesPower BI Developer: Professional Summarysudeepkumar345No ratings yet
- SPIDER Storage Engine Database Sharding by Storage EngineDocument55 pagesSPIDER Storage Engine Database Sharding by Storage EngineSantiago LertoraNo ratings yet
- Sales APIDocument16 pagesSales APIcuriousnavinNo ratings yet
- ASM LUN Creation On Multiple NodesDocument3 pagesASM LUN Creation On Multiple Nodesprince264No ratings yet
- Known Issues When Modeling in IBM Cognos TransformerDocument5 pagesKnown Issues When Modeling in IBM Cognos TransformerSwamy DanthuriNo ratings yet
- Enable TDE in Oracle GG Classic ModeDocument5 pagesEnable TDE in Oracle GG Classic ModeAvinash SinghNo ratings yet
- DS Lecture LinksDocument3 pagesDS Lecture LinksGHULAM MOHIUDDINNo ratings yet
- ASP Dot Net ProgramsDocument53 pagesASP Dot Net ProgramsMayankNo ratings yet
- SM2244LT Product BriefDocument1 pageSM2244LT Product BriefTo DickNo ratings yet
- SQL Server Data TypesDocument3 pagesSQL Server Data TypesOliver O DuCilleNo ratings yet
- HDD/SSD Hybrid Pci-Express Card: WWW - LogilinkDocument2 pagesHDD/SSD Hybrid Pci-Express Card: WWW - LogilinkGyörgy Tamás ViziNo ratings yet
- The Difference Between OBIEEDocument2 pagesThe Difference Between OBIEEsasibushangNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Database Management SystemDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Database Management SystemLemuel PorrasNo ratings yet
- FI SL ExtractionDocument6 pagesFI SL ExtractionChandra NagineniNo ratings yet
- BBA2106 - Week7 - Introduction To Pivot TableDocument14 pagesBBA2106 - Week7 - Introduction To Pivot TableSupanut KaewumpaiNo ratings yet
- FactoryTalk View SE - Unable To Access ODBC Data SourceDocument2 pagesFactoryTalk View SE - Unable To Access ODBC Data Sourcepankaj mankarNo ratings yet
- Sop DBA AjayDocument76 pagesSop DBA Ajayganesh100% (1)
- Chapter 4 - Secondary StorageDocument45 pagesChapter 4 - Secondary StorageNur Amira NadiaNo ratings yet
- How To Run Lockbox Case 2Document7 pagesHow To Run Lockbox Case 2konetiNo ratings yet
- SAP NetWeaver 7.0 - BI Systemcopy ABAPDocument46 pagesSAP NetWeaver 7.0 - BI Systemcopy ABAPrudhrasNo ratings yet
- Using Administration Tool UtilitiesDocument13 pagesUsing Administration Tool UtilitiesMohamed AbrarNo ratings yet
- Keys DbmsDocument34 pagesKeys Dbms467-056 ChandanaNo ratings yet
- Dbms - Assignment 1 SolDocument2 pagesDbms - Assignment 1 SolbijdraagtNo ratings yet
- BI Security OverviewDocument68 pagesBI Security OverviewApple VodkaaNo ratings yet
- Logcat Prev CSC LogDocument293 pagesLogcat Prev CSC LogDavid NenNo ratings yet
- Transcend-StoreJet25M3 ManualDocument2 pagesTranscend-StoreJet25M3 ManualanaaaNo ratings yet
- Nosql DatawarehouseDocument11 pagesNosql DatawarehouseGunjan chandwaniNo ratings yet