0% found this document useful (0 votes)
88 views37 pagesScience Training on Stars and Constellations
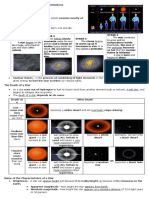
Here are 3 characteristics of stars:
1. Color - A star's color depends on its surface temperature. Hotter stars appear blue-white, while cooler stars appear red.
2. Size - Stars vary greatly in size, from small red dwarfs to supergiant stars hundreds of times the size of our Sun.
3. Composition - The main chemical elements found in stars are hydrogen and helium, though heavier elements are also present. Stellar composition affects properties like temperature and lifespan.
Uploaded by
Ma'am LeiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
88 views37 pagesScience Training on Stars and Constellations
Here are 3 characteristics of stars:
1. Color - A star's color depends on its surface temperature. Hotter stars appear blue-white, while cooler stars appear red.
2. Size - Stars vary greatly in size, from small red dwarfs to supergiant stars hundreds of times the size of our Sun.
3. Composition - The main chemical elements found in stars are hydrogen and helium, though heavier elements are also present. Stellar composition affects properties like temperature and lifespan.
Uploaded by
Ma'am LeiCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd