Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Java 4
Uploaded by
Deep Vala0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views8 pagesOriginal Title
1614145003005_java_4
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views8 pagesJava 4
Uploaded by
Deep ValaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
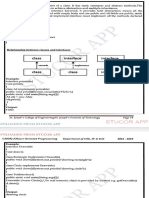
Interfaces
• An interface is a collection of abstract methods.
• A class implements an interface, thereby
inheriting the abstract methods of the interface.
• An interface is not a class.
• Writing an interface is similar to writing a class,
but they are two different concepts.
• A class describes the attributes and behaviors of
an object.
• An interface contains behaviors that a class
implements.
An interface is similar to a class
• An interface can contain any number of
methods.
• An interface is written in a file with a .java
extension, with the name of the interface
matching the name of the file.
• The bytecode of an interface appears in
a .class file.
• Interfaces appear in packages.
interface is different from a class in several ways,
• An interface does not contain any
constructors.
• All of the methods in an interface are abstract.
• An interface is not extended by a class; it is
implemented by a class.
• An interface can extend multiple interfaces.
Example………..
interface printable
{
void print();
}
class A6 implements printable
{
public void print()
{
System.out.println("Hello");
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
A6 obj = new A6();
obj.print();
}
}
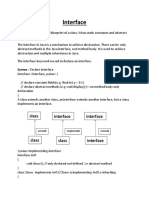
Multiple inheritance in Java by interface
Example………..
interface Printable
{
void print();
}
interface Showable
{
void show();
}
class A7 implements Printable,Showable
{
public void print()
{
System.out.println("Hello");
}
public void show()
{
System.out.println("Welcome");
}
}
Example………..
Class demo
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
A7 obj = new A7();
obj.print();
obj.show();
}
}
You might also like
- Interface and Abstract ClassDocument9 pagesInterface and Abstract ClassValarmathiNo ratings yet
- Interfaces and PackagesDocument15 pagesInterfaces and PackagesavavNo ratings yet
- Fepj - 3Document21 pagesFepj - 3Ankush ThakurNo ratings yet
- Lecture-2.3Document21 pagesLecture-2.3gdgdNo ratings yet
- L22 InterfaceDocument35 pagesL22 Interfaceadarsh rajNo ratings yet
- JAVA OOPS AbstratClass&InterfacesDocument20 pagesJAVA OOPS AbstratClass&Interfacesujjawalr9027No ratings yet
- Interface in JavaDocument12 pagesInterface in Javashivaji bossNo ratings yet
- Interface & PackageDocument23 pagesInterface & PackageDeathstroke gamingNo ratings yet
- Java Assignment 2Document6 pagesJava Assignment 2MD khaja moinuddinNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Data Structures and Abstract Data Types (Adts)Document30 pagesIntroduction To Data Structures and Abstract Data Types (Adts)DARKSAITAMA.973No ratings yet
- Abstract and InterfaceDocument28 pagesAbstract and InterfaceJirou ShibaNo ratings yet
- BCA AbstractionDocument17 pagesBCA AbstractionSarthak SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Java SemienarDocument6 pagesJava SemienarSuresh VaidyaNo ratings yet
- Interfaces & PackagesDocument38 pagesInterfaces & PackagesSonali EkatpureNo ratings yet
- 16 InterfacesDocument18 pages16 Interfacessrishreyan10bNo ratings yet
- Interface in JavaDocument9 pagesInterface in JavaDEEPAK SRINIVAS M CSENo ratings yet
- Java 2Document29 pagesJava 2Bhavya BabuNo ratings yet
- Interface in Java: Reasons of Using InterfaceDocument6 pagesInterface in Java: Reasons of Using InterfaceAman RaiNo ratings yet
- IAT2 - JAVA - Answer KeyDocument15 pagesIAT2 - JAVA - Answer Keyprsh22mcaNo ratings yet
- Types of Interfaces in JavaDocument5 pagesTypes of Interfaces in Javajagdish donNo ratings yet
- Java Programming - UNIT-III Part ADocument30 pagesJava Programming - UNIT-III Part A2311cs050086No ratings yet
- AbstractionDocument11 pagesAbstractionAkshay PatilNo ratings yet
- Java Summer Training PresentationDocument16 pagesJava Summer Training PresentationJitendra Singh RauthanNo ratings yet
- Java - InterfacesDocument4 pagesJava - InterfacesmesworksolutionNo ratings yet
- StaticclassDocument20 pagesStaticclassriyaNo ratings yet
- Java Notes 20CS43PDocument5 pagesJava Notes 20CS43PsayyanNo ratings yet
- Interface in Java: Unit - IIIDocument33 pagesInterface in Java: Unit - IIIBarani KumarNo ratings yet
- Java InterfacesDocument4 pagesJava InterfacesmjrkmailNo ratings yet
- Abstract Classes and InterfaceDocument15 pagesAbstract Classes and InterfaceSupinder SekhonNo ratings yet
- TY - Interface in JavaDocument7 pagesTY - Interface in JavaAkash KashidNo ratings yet
- Multiple InhDocument7 pagesMultiple Inhyatin bahlNo ratings yet
- Programming in Java: Abstract Class and InterfaceDocument23 pagesProgramming in Java: Abstract Class and Interfaceobed jamirNo ratings yet
- CS 241 Lec 2Document58 pagesCS 241 Lec 2Essam El-UddalyNo ratings yet
- Java Unit 3 and 4Document58 pagesJava Unit 3 and 4darknight978745No ratings yet
- 1.interfaces and Lambda Expressions in JavaDocument59 pages1.interfaces and Lambda Expressions in JavaVivek BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Java InterfacesDocument5 pagesJava InterfacesprathyushaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Java Re-VisitDocument125 pagesLecture 1 - Java Re-VisitYu Ming SohNo ratings yet
- Java Unit-IiiDocument28 pagesJava Unit-IiiKrishna Chaitanya YedubatiNo ratings yet
- Abstract Class in PythonDocument2 pagesAbstract Class in Pythonandrew stankovikNo ratings yet
- InterfacesDocument45 pagesInterfacesnaganejyoti69No ratings yet
- Abstract Class in JavaDocument20 pagesAbstract Class in JavaNeenu PrasannanNo ratings yet
- Week 9-10 Oop NoteDocument54 pagesWeek 9-10 Oop Noteramakantaswain1302No ratings yet
- SD Abstract Class & Interface PDFDocument25 pagesSD Abstract Class & Interface PDFRahjuNo ratings yet
- Java Is A Programming Language Originally Developed at Sun Microsystems (Which IsDocument4 pagesJava Is A Programming Language Originally Developed at Sun Microsystems (Which IsMj BermudezNo ratings yet
- by Default.: in The InterfaceDocument3 pagesby Default.: in The InterfaceKalirajanNo ratings yet
- JavaDocument24 pagesJavaProximoNo ratings yet
- Java Module 5Document39 pagesJava Module 5Aman VermaNo ratings yet
- Advance Computer Programming: by Hasnat AliDocument35 pagesAdvance Computer Programming: by Hasnat Alidavid jhonNo ratings yet
- Access SpecifierDocument25 pagesAccess Specifierjit SahooNo ratings yet
- Java Chap 2 - MergedDocument104 pagesJava Chap 2 - MergedAnuj PalNo ratings yet
- Java - First Project: Console and Dialog I/ODocument15 pagesJava - First Project: Console and Dialog I/OTri VoNo ratings yet
- Class Interface InterfaceDocument2 pagesClass Interface InterfaceBanani BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Interview Questions On JavaDocument10 pagesInterview Questions On Javaapi-3736604No ratings yet
- Java Notes6 PDFDocument14 pagesJava Notes6 PDFOmkar KhedekarNo ratings yet
- Interface in JavaDocument5 pagesInterface in Javayuvikatuteja4No ratings yet
- Interface & PackagesDocument12 pagesInterface & PackagesAditya ChavanNo ratings yet
- InterfaceDocument7 pagesInterfacehonaday945No ratings yet
- Inheritance & PolymorphismDocument11 pagesInheritance & PolymorphismLord PuffinNo ratings yet
- String and ScannerDocument27 pagesString and ScannerMansuba Tabasssum (192014014)No ratings yet
- Java Programming Tutorial With Screen Shots & Many Code ExampleFrom EverandJava Programming Tutorial With Screen Shots & Many Code ExampleNo ratings yet
- Java 2Document41 pagesJava 2Deep ValaNo ratings yet
- JavaDocument74 pagesJavaDeep ValaNo ratings yet
- Libpack & ClassDocument34 pagesLibpack & ClassDeep ValaNo ratings yet
- OSI Reference Model With 7 LayersDocument5 pagesOSI Reference Model With 7 LayersDeep ValaNo ratings yet
- Projectppt 180718104646Document89 pagesProjectppt 180718104646Deep ValaNo ratings yet
- Front Page of Food Ordering System ProjectDocument2 pagesFront Page of Food Ordering System ProjectDeep ValaNo ratings yet
- Project ReportDocument37 pagesProject ReportDeep ValaNo ratings yet
- Paper Presentation of Job PortalDocument72 pagesPaper Presentation of Job PortalDeep ValaNo ratings yet
- DFDERDBMSDocument10 pagesDFDERDBMSDeep ValaNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument3 pagesAbstractDeep ValaNo ratings yet
- Common GuidelinesDocument1 pageCommon GuidelinesDeep ValaNo ratings yet
- Java Exam Paper 619402Document1 pageJava Exam Paper 619402Deep ValaNo ratings yet