Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Atelectasis
Uploaded by
Aurelia0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views12 pagesAn presentation on atelectasis. Symptoms and signs, diagnosis..
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAn presentation on atelectasis. Symptoms and signs, diagnosis..
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views12 pagesAtelectasis
Uploaded by
AureliaAn presentation on atelectasis. Symptoms and signs, diagnosis..
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
ATELECTASIS
PRESENTATION BY – Jossileen C Jose
WHAT IS ATELECTASIS ?
Atelectasis is the collapse or closure of a lung resulting in reduced or absent
gas exchange. It is usually unilateral, affecting part or all of one lung.
It is a condition where the alveoli are deflated down to little or no volume, as
distinct from pulmonary consolidation, in which they are filled with liquid. It
is often called a collapsed lung, although that term may also refer to
pneumothorax.
It may be caused by normal exhalation or by various medical conditions.
The most common cause is post-surgical atelectasis, causing restricted
breathing after abdominal surgery.
Another cause is poor surfactant spreading during inspiration, causing the
surface tension to be at its highest which tends to collapse smaller alveoli.
DIAGNOSIS & FINDINGS
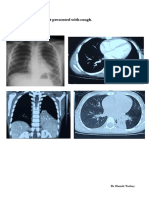
Atelectasis is generally visible on chest X-ray.
Chest CT or bronchoscopy may be necessary if the cause of atelectasis
is not clinically apparent.
Direct signs of atelectasis include displacement of interlobar fissures
and mobile structures within the thorax.
Patients may present with indirect signs and symptoms such as
elevation of the diaphragm, shifting of the trachea, heart and
mediastinum; displacement of the hilus and shifting granulomas.
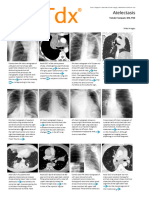
Atelectasis of a person's right lung
Atelectasis of the middle lobe on Atelectasis of the right lower Computed tomography (CT) scan
a sagittal CT reconstruction. lobe seen on chest X-ray. revealing atelectasis of the right lower
Key findings on X-ray are:
• Sharply defined opacity of vessels
• Volume loss resulting in displacement of diaphragm ,fissures, or
mediastinum.
Right upper lobe atelectasis findings:
1.triangular density
2.elevated right hilus
3.obliteration of the retrosternal clear space (arrow)
On the PET-CT a lungneoplasm is seen with subsequent
atelectasis of the right upper lobe due to obstruction of
the upper lobe bronchus.
A common finding in atelectasis of the right upper lobe
is 'tenting' of the diaphragm (blue arrow).
This patient had a centrally located lungcarcinoma with
metastases in both lungs (red arrows).
The findings are:
•Large density on the left with loss of cardiac silhouette.
•High position left diaphragm with tenting.
•Low position minor fissure
•Low position right hilum
These findings indicate a total atelectasis of the left upper lobe
and possibly also partial atelectasis on the right.
Since the silhouette of the right heart border is still visible, there is
probably partial atelectasis of the lower lobe and not of the middle
lobe.
Notice the bulging of the fissure on the lateral view.
This is comparable to the golden-S sign in right upper
lobe atelectasis and is suspective of a centrally
obstructing mass.
Luft sichel means a sickle of air (blue arrow).
ACUTE & CHRONIC ATELECTASIS
Atelectasis may be an acute or chronic condition.
In acute atelectasis, the lung has recently collapsed and is primarily notable
only for airlessness.
In chronic atelectasis, the affected area is often characterized by a complex
mixture of airlessness, infection, widening of the bronchi (bronchiectasis),
destruction, and scarring (fibrosis).
TYPES OF ATELECTASIS
Absorption (resorption) atelectasis
Stems from complete obstruction of an airway. Over time, air is
reabsorbed from the dependent alveoli,which collapse. Since lung volume
is diminished ,the mediastinum shifts toward the atelectatic lung.
Compression (relaxation) atelectasis
Results whenever significant volumes of fluid (transudate ,exudate or
blood),tumor, or air (pneumothorax) accumulate within the pleural
cavity . With compression atelectasis, the mediastinum shifts away from
the affected lung.
Cicatrization (contraction) atelectasis
Occurs when focal or generalized pulmonary or pleural fibrosis prevents full lung
expansion.
Notice the increased density of the lung
tissue and the volume loss.
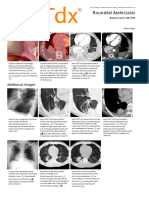
Rounded atelectasis
In rounded atelectasis (folded lung or Blesovsky syndrome), an outer portion of the lung slowly collapses as a
result of scarring and shrinkage of the membrane layers covering the lungs (pleura), which would show as
visceral pleural thickening and entrapment of lung tissue.
This produces a rounded appearance on X-ray that doctors may mistake for a tumor. Rounded atelectasis is
usually a complication of asbestos-induced disease of the pleura, but it may also result from other types of
chronic scarring and thickening of the pleura.
The typical findings of rounded atelectasis on CT are pleural thickening, pleural-based mass and comet tail sign.
On the lateral view there is a mass-like lesion that is pleural-based.
The first impresson is, that this is a pleural lesion.
The CT shows a lesion that originates in the lung.
There is also some pleural thickening (red arrow) and
vessels seem to swirl around the mass (blue arrows).
This is also described as the comet tail sign.
Plate-like atelectasis
Plate-like atelectasis is a common finding on chest x-rays and detected
almost every day. They are characterized by linear shadows of
increased density at the lung bases.They are usually horizontal,
measure 1-3 mm in thickness and are only a few cm long.
In most cases these findings have no clinical significance and are seen
in smokers and elderly. They are seen in patients, that are in a poor
condition and who breathe superficially, for instance after abdominal
surgery.
Plate-like atelectasis due to poor inspiration in a patient who had abdominal
surgery(figure).
Plate-like atelectasis is frequently seen in patients
in the ICU due to poor ventilation.
Platelike atelectasis is also frequently seen in
pulmonary embolism.
Plate-like atelectasis in a patient with pulmonary embolism (figure)
REFERENCES
The Radiology Assistant : Chest X-Ray - Lung disease
Robbins Basic Pathology - 10th Edition - Elsevier
THANKYOU!
You might also like
- Lobar AtelectasisDocument5 pagesLobar AtelectasisRachman ⎝⏠⏝⏠⎠ BuyungNo ratings yet
- Atelectasis Imaging FindingsDocument19 pagesAtelectasis Imaging FindingsRachmi MerrinaNo ratings yet
- Chest X Rays Made EasyDocument3 pagesChest X Rays Made EasyHaluk AlibazogluNo ratings yet
- Atelectasis-Dr JokoDocument20 pagesAtelectasis-Dr JokoMamanHermawanNo ratings yet
- Pathology Disease ProcessesDocument11 pagesPathology Disease ProcessesprtemnNo ratings yet
- AtelectasisDocument24 pagesAtelectasisTiara RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- The Radiology Assistant: Chest X-Ray: 4-Pattern ApproachDocument57 pagesThe Radiology Assistant: Chest X-Ray: 4-Pattern ApproachMarina Ivosevic MilosavljevicNo ratings yet
- This Is The Case of G.B., 65 Year Old Female Presented With Difficulty of Breathing. Sought Consult at The OPD and Requested With Chest X-RayDocument64 pagesThis Is The Case of G.B., 65 Year Old Female Presented With Difficulty of Breathing. Sought Consult at The OPD and Requested With Chest X-Rayadhik_deepakNo ratings yet
- Atelectasis SignsDocument26 pagesAtelectasis SignsArini NurlelaNo ratings yet
- AtelectasisDocument4 pagesAtelectasisYanyan PanesNo ratings yet
- Radiation Fibrosis CaseDocument159 pagesRadiation Fibrosis CaseSlm BngshNo ratings yet
- Plate-Like Atelectasis: PembimbingDocument5 pagesPlate-Like Atelectasis: Pembimbingandi140207No ratings yet
- X Ray InterprationDocument6 pagesX Ray InterprationMelvita KurniawanNo ratings yet
- AtelectasisDocument37 pagesAtelectasisSandara ParkNo ratings yet
- Auntminnie SignsDocument56 pagesAuntminnie SignsHey ReelNo ratings yet
- ThoraxDocument56 pagesThoraxpriskilas911No ratings yet
- Rounded Atelectasis - Print Friendly - STATdxDocument2 pagesRounded Atelectasis - Print Friendly - STATdxmihaelaNo ratings yet
- Radiology 111Document51 pagesRadiology 111Sherika A. BurgessNo ratings yet
- Chest Radio GraphsDocument13 pagesChest Radio Graphsdranees12No ratings yet
- Chest X Ray - 4Document64 pagesChest X Ray - 4melindamentariNo ratings yet
- 1) Describe The Life-Threatening Conditions in The Chest in This Patient?Document5 pages1) Describe The Life-Threatening Conditions in The Chest in This Patient?Don JuanNo ratings yet
- 4 Respiratory ExaminationsDocument53 pages4 Respiratory Examinationscawsey mohamedNo ratings yet
- ATOTW 150: Interpretation of chest radiograph abnormalities in ICU patientsDocument12 pagesATOTW 150: Interpretation of chest radiograph abnormalities in ICU patientsbandarascbNo ratings yet
- Flail Chest Diagnosis and Treatment in 40 CharactersDocument6 pagesFlail Chest Diagnosis and Treatment in 40 CharactersFrinkaWijayaNo ratings yet
- Chest X-Ray: Confirm DetailsDocument14 pagesChest X-Ray: Confirm DetailsNosheen HafeezNo ratings yet
- Lung Disease X-ray Diagnosis GuideDocument4 pagesLung Disease X-ray Diagnosis GuideMadeline WanhartNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Contusion: ClassificationDocument6 pagesPulmonary Contusion: ClassificationTad SchmittNo ratings yet
- Lung Collapse Types and Signs on Chest X-RayDocument15 pagesLung Collapse Types and Signs on Chest X-RayAmit Kumar RanoNo ratings yet
- Skill Lab CT-Scan Technique and InterpretationDocument137 pagesSkill Lab CT-Scan Technique and InterpretationRofi Irman100% (1)
- Bonus Learning Chest X-RaysDocument13 pagesBonus Learning Chest X-RaysdeehteeNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Step 2 CK NoteDocument41 pagesRespiratory Step 2 CK NoteXboyx MahdiNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Pulmonary Radiology 2Document41 pages2.2 Pulmonary Radiology 2Casey Rae YanoNo ratings yet
- Lung Collapse PDFDocument65 pagesLung Collapse PDFRibhav GuptaNo ratings yet
- CXR Interpretation Guide: ABCDE ApproachDocument1 pageCXR Interpretation Guide: ABCDE ApproachValentina SepúlvedaNo ratings yet
- C 1-Rad Lecture-Cxr AnormalitiesDocument59 pagesC 1-Rad Lecture-Cxr AnormalitiesgetemeselewNo ratings yet
- Atelectasis, (Lung Collapse) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related DiseasesFrom EverandAtelectasis, (Lung Collapse) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related DiseasesNo ratings yet
- Distinguishing Causes of CT Mosaic Lung Attenuation PatternDocument7 pagesDistinguishing Causes of CT Mosaic Lung Attenuation PatternSafia RehmanNo ratings yet
- Journal Reading RadiologiDocument49 pagesJournal Reading RadiologiPhilipusHendryHartonoNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument8 pagesThe Respiratory SystemJane Rose SuperadaNo ratings yet
- Thoracic Imaging Radiographic BasicsDocument130 pagesThoracic Imaging Radiographic BasicsIsak ShatikaNo ratings yet
- Journal of Thoracic ImagingDocument11 pagesJournal of Thoracic Imagingestues2No ratings yet
- Emphysema Is A LongDocument54 pagesEmphysema Is A LongryemoralesNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Radiologi AtelektasisDocument14 pagesJurnal Radiologi AtelektasisferisiswonoNo ratings yet
- DifdgDocument54 pagesDifdgMarina Ivosevic MilosavljevicNo ratings yet
- Atelectasis OverviewDocument12 pagesAtelectasis OverviewPrince Juzzel BanagNo ratings yet
- Signs and Types of AtelectasisDocument89 pagesSigns and Types of AtelectasiswahyuNo ratings yet
- Early Primary Repair of Tetralogy of Fallot: Richard A. JonasDocument9 pagesEarly Primary Repair of Tetralogy of Fallot: Richard A. JonasResiden KardiologiNo ratings yet
- AtelectasisDocument2 pagesAtelectasisiMaibelle BelleNo ratings yet
- Chestx RayinterpretationDocument81 pagesChestx RayinterpretationTIRUCHANURUNo ratings yet
- Atelectasis - Print Friendly - STATdxDocument5 pagesAtelectasis - Print Friendly - STATdxmihaelaNo ratings yet
- Back to Basics – ‘Must Know’ Classical Signs in Thoracic RadiologyDocument30 pagesBack to Basics – ‘Must Know’ Classical Signs in Thoracic Radiologyvalencia suwardiNo ratings yet
- Prenotes C23Document40 pagesPrenotes C23Erika Boots CabalunaNo ratings yet
- ATELECTASISDocument5 pagesATELECTASISAngellene GraceNo ratings yet
- Atelectasis Case StudyDocument14 pagesAtelectasis Case StudySanhati Ghosh BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Respiratory: Welcome!Document119 pagesRespiratory: Welcome!Majo ParagasNo ratings yet
- DX Imaging 1 MT and FinalDocument24 pagesDX Imaging 1 MT and FinalRaymondNo ratings yet
- Tetralogy of Fallot.......Document7 pagesTetralogy of Fallot.......Sam AlipioNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Infarction Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument7 pagesPulmonary Infarction Diagnosis and TreatmentHieu PhanNo ratings yet
- PneumothoraxDocument36 pagesPneumothoraxEira Lopez60% (5)
- A Simple Guide to Pulmonary Infarction, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Pulmonary Infarction, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet