0% found this document useful (0 votes)
175 views16 pagesProject Management Plan Overview
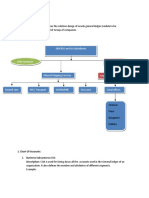
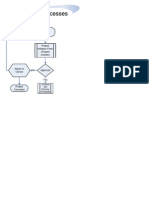
The document provides an overview of developing a project management plan through multiple sections. It defines a plan, discusses the key components of a plan, and explains that a project management plan brings together all other project plans. The summary outlines the major project planning documents that make up the project management plan, including scope, schedule, cost, risk, quality, and communication management plans. Finally, it shows a project plan spiral that depicts how individual plans are developed incrementally and integrated over time.
Uploaded by
Cassandri LabuschagneCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
175 views16 pagesProject Management Plan Overview
The document provides an overview of developing a project management plan through multiple sections. It defines a plan, discusses the key components of a plan, and explains that a project management plan brings together all other project plans. The summary outlines the major project planning documents that make up the project management plan, including scope, schedule, cost, risk, quality, and communication management plans. Finally, it shows a project plan spiral that depicts how individual plans are developed incrementally and integrated over time.
Uploaded by
Cassandri LabuschagneCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd