0% found this document useful (0 votes)
237 views37 pagesMachine Elements
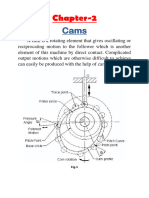
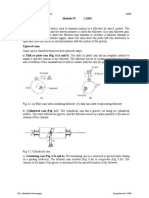
This document discusses cams and followers and their applications. It defines a cam as a rotating machine element that gives reciprocating or oscillating motion to another element called a follower. Cams are classified based on their shape, the motion of the follower, and the manner of constraint of the follower. Common types of cams include wedge cams, radial cams, and cylindrical cams. Followers are also classified based on their shape, motion, and path of motion. The document provides examples of different cam profiles and problems involving the design of cam profiles based on given follower specifications and motion requirements.
Uploaded by
VeilCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
237 views37 pagesMachine Elements
This document discusses cams and followers and their applications. It defines a cam as a rotating machine element that gives reciprocating or oscillating motion to another element called a follower. Cams are classified based on their shape, the motion of the follower, and the manner of constraint of the follower. Common types of cams include wedge cams, radial cams, and cylindrical cams. Followers are also classified based on their shape, motion, and path of motion. The document provides examples of different cam profiles and problems involving the design of cam profiles based on given follower specifications and motion requirements.
Uploaded by
VeilCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd