100% found this document useful (1 vote)
144 views31 pagesUrinary System
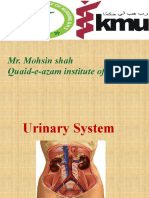
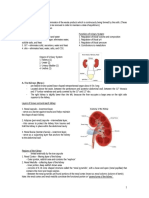
The urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. The kidneys filter waste from the blood to form urine. Urine travels from the kidneys down the ureters into the urinary bladder, where it is stored until urination. In males, the urethra carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body, while in females it is shorter and opens into the vagina. Sphincter muscles control the release of urine from the bladder through the urethra.
Uploaded by
Ayro Business CenterCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
144 views31 pagesUrinary System
The urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. The kidneys filter waste from the blood to form urine. Urine travels from the kidneys down the ureters into the urinary bladder, where it is stored until urination. In males, the urethra carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body, while in females it is shorter and opens into the vagina. Sphincter muscles control the release of urine from the bladder through the urethra.
Uploaded by
Ayro Business CenterCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd