0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views19 pagesAnatomy and Functions of the Urinary System
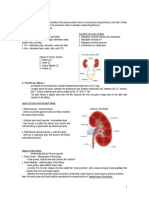
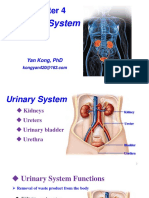
The urinary system includes the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. The kidneys filter waste from the blood and produce urine. Urine travels from the kidneys down the ureters into the bladder. The bladder stores urine until urination, when urine exits the body through the urethra. In males, the urethra passes through the prostate gland and penis, while in females it is shorter and opens anterior to the vagina.
Uploaded by
adnanahmed9107Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views19 pagesAnatomy and Functions of the Urinary System
The urinary system includes the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. The kidneys filter waste from the blood and produce urine. Urine travels from the kidneys down the ureters into the bladder. The bladder stores urine until urination, when urine exits the body through the urethra. In males, the urethra passes through the prostate gland and penis, while in females it is shorter and opens anterior to the vagina.
Uploaded by
adnanahmed9107Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd